Abstract
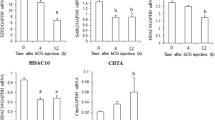
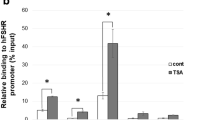
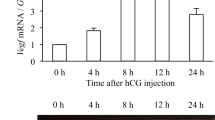
This study examined the molecular mechanism by which BMP-4 inhibits progesterone production and the expression of genes involved in steroidogenesis. Granulosa cells were cultured in medium with or without BMP-4 for 0–96 h. BMP-4 inhibited progesterone secretion in granulosa cells and suppressed the expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) at the mRNA and protein levels, whereas BMP-4 did not affect the proliferation of granulosa cells. In addition, we found that BMP-4 affected the expression of SR-B1 mRNA but not LDL-R in granulosa cells. To examine the protein–DNA interaction at specific sites within the StAR gene promoter, we used the quantitative real-time PCR and the ChIP technique. We demonstrated that BMP-4 suppresses the acetylation of histone H3 associated with the StAR promoter region at 48 and 72 h of culture in bovine granulosa cells. Our results showed for the first time that BMP-4 inhibited the acetylation of histone H3 associated with the StAR promoter region in bovine granulosa cells. Taken together, we propose that the inhibition of the acetylation of histone H3 associated with the StAR promoter region by BMP-4 may be one of the inhibitory molecular mechanisms of progesterone synthesis in granulosa cells. Our data suggested that theca cell-derived BMP-4 is important as a regulator of steroid hormone synthesis in granulosa cells during follicular development in the mammalian ovary.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimasaki S, Moore RK, Ostuka F, Erickson GF (2004) The bone morphogenetic protein system in mammalian reproduction. Endocr Rev 25:72–101
Kayamori T, Kosaka N, Miyamoto A, Shimizu T (2009) The differential pathways of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-4 and -7 in the suppression of the bovine granulosa cell apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 323:161–168
Pierre A, Pisselet C, Dupont J, Mandon-Pepin B, Monniaux D, Monget P, Fabre S (2004) Molecular basis of bone morphogenetic protein-4 inhibitory action on progesterone secretion by ovine granulosa cells. J Mol Endocrinol 33:805–817
Glister C, Kemp CF, Knight PG (2004) Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) ligands and receptors in bovine ovarian follicle cells: actions of BMP-4, -6 and -7 on granulosa cells and differential modulation of Smad-1 phosphorylation by follistatin. Reproduction 127:239–254
Glister C, Richards SL, Knight PG (2005) Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP)-4, -6, and -7 potently suppress basal and luteinizing hormone-induced androgen production by bovine theca interna cells in primary culture: could ovarian hyperandrogenic dysfunction be caused by a defect in thecal BMP signaling? Endocrinology 146:1881–1892
Shimizu T, Yokoo M, Miyake Y, Sasada H, Sato E (2004) Differential expression of bone morphogenetic protein 4–6 (BMP-4, -5, and -6) and growth differentiation factor-9 (GDF-9) during ovarian development in neonatal pigs. Domest Anim Endocrinol 27:397–405
Nilsson EE, Skinner MK (2003) Bone morphogenetic protein-4 acts as an ovarian follicle survival factor and promotes primordial follicle development. Biol Reprod 69:1265–1272
Onagbesan OM, Bruggeman V, Van As P, Tona K, Williams J, Decuypere E (2003) BMPs and BMPRs in chicken ovary and effects of BMP-4 and -7 on granulosa cell proliferation and progesterone production in vitro. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E973–E983
Lee WS, Ostuka F, Moore RK, Shimasaki S (2001) Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-7 on folliculogenesis and ovulation in the rat. Biol Reprod 65:994–999
Dooley CA, Attia GR, Rainey WE, Moore DR, Carr BR (2000) Bone morphogenetic protein inhibits ovarian androgen production. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3331–3337
Inagaki K, Ostuka F, Miyoshi T, Yamashita M, Takahashi M, Goto J, Suzuki J, Makino H (2009) p38-Mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulated steroidogenesis in granulosa cell-oocyte cocultures: role of bone morphogenetic protein 2 and 4. Endocrinology 150:1921–1930
Erickson GF, Shimasaki S (2003) The spatiotemporal expression pattern of the bone morphogenetic protein family in rat ovary cell types during the estrous cycle. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 1:9
Miyazono K, ten Dijke P, Heldin CH (2000) TGF-beta signaling by Smad proteins. Adv Immunol 75:115–157
Miyazawa K, Shinozaki M, Hara T, Furuya T, Miyazono K (2002) Two major Smad pathways in TGF-beta superfamily signaling. Genes Cells 7:1191–1204
Shimasaki S, Zachow RJ, Li D, Kim H, Iemura S, Ueno N, Sampath K, Chang RJ, Erickson GF (1999) A functional bone morphogenetic protein system in the ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7282–7287
Jayawardana BC, Shimizu T, Nishimoto H, Kaneko E, Tetsuka M, Miyamoto A (2006) Hormonal regulation of expressions of growth differentiation factor-9 (GDF-9) receptor type I and II genes in bovine ovarian follicle. Reproduction 131:545–553
Shimizu T, Jayawardana BC, Nishimoto H, Kaneko E, Tetsuka M, Miyamoto A (2006) Involvement of bone morphogenetic protein/receptor system during follicle development in bovine ovary: hormonal regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP-7) and its receptors (ActRII and ALK-2) expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 249:78–83
Wilson T, Wu XY, Juengel JL, Ross IK, Lumsden JM, Lord EA, Dodds KG, Walling GA, McEwan JC, O’Connell AR, McNatty KP, Montgomery GW (2001) Highly prolific Booroola sheep have a mutation in the intracellular kinase domain of bone morphogenetic protein IB receptor (ALK-6) that is expressed in both oocytes and granulosa cells. Biol Reprod 64:1225–1235
Souza CJ, Campbell BK, McNcilly AS, Baird DT (2002) Effect of bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) on oestradiol and inhibin A production by sheep granulosa cells, and localization of BMP receptors in the ovary by immunohistochemistry. Reproduction 123:363–369
Fabre S, Pierre A, Pisselet C, Mulsant P, Lecerf F, Pohl J, Monget P, Monniaux D (2003) The booroola mutation in sheep is associated with an alteration of the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-IB functionality. Reproduction 177:435–444
Juengel JL, Reader KL, Bibby AH, Lun S, Ross I, Haydon L, McNatty KP (2006) The role of bone morphogenetic proteins 2, 4, 6 and 7 during ovarian follicular development in sheep: contrast to rat. Reproduction 131:501–513
Otsuka F, Moore RK, Shimasaki S (2001) Biological function and cellular mechanism of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in the ovary. J Biol Chem 276:32889–32895
Stocco DM, Clark BJ (1996) Regulation of the acute production of steroids in steroidogenic cells. Endocr Rev 17:221–244
Miller WL (2007) StAR search-what we know about how the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein mediates mitochondrial cholesterol import. Mol Endocrinol 21:589–601
Niswender GD (2002) Molecular control of luteal secretion of progesterone. Reproduction 123:333–339
Fortune JE (1986) Bovine theca and granulosa cells interact to promote androgen production. Biol Reprod 35:292–299
Stocco DM (2001) StAR protein and the regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol 63:193–213
Shimizu T, Sudo N, Yamashita H, Murayama C, Miyazaki H, Miyamoto A (2009) Histone H3 acetylation of StAR and decrease in DAX-1 is involved in the luteinization of bovine granulosa cells during in vitro culture. Mol Cell Biochem 328:41–47
Miyamoto A, Okuda K, Schweigert FJ, Schams D (1992) Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor, transforming growth factor-beta and nerve growth factor on the secretory function of the bovine corpus luteum in vitro. J Endocrinol 135:103–114
Acosta TJ, Miyamoto A, Ozawa T, Wijayagunawardane MP, Sato K (1998) Local release of steroid hormones, prostaglandin E2, and endothelin-1 from bovine mature follicles in vitro: effects of luteinizing hormone, endothelin-1, and cytokines. Biol Reprod 59:437–443
Grummer RR, Carroll DJ (1988) A review of lipoprotein cholesterol metabolism: importance to ovarian function. J Anim Sci 66:3160–3173
Pate JL, Condon WA (1982) Effects of serum and lipoproteins on steroidogenesis in cultured bovine luteal cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 28:551–562
Carroll DJ, Grummer RR, Mao FC (1992) Progesterone production by cultured luteal cells in the presence of bovine low- and high-density lipoproteins purified by heparin affinity chromatography. J Anim Sci 70:2516–2526
Stocco DM, Kilgore MK (1988) Induction of mitochondrial proteins in MA-10 Leydig tumor cells with human choriogonadotropin. Biochem J 249:95–103
Stocco DM, Ascoli M (1993) The use of genetic manipulation of MA-10 Leydig tumor cells to demonstrate the role of mitochondrial proteins in the acute regulation of steroidogenesis. Endocrinology 133:2827–2832
Clark BJ, Wells J, King SR, Stocco DM (1994) The purification, cloning and expression of a novel LH-induced mitochondrial protein in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells: characterization of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR). J Biol Chem 269:28314–28322
Acton S, Rigotti A, Landschultz KT, Xu S, Hobbs HH, Krieger M (1996) Identification of scavenger receptor SR-B1 as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science 271:518–520
Rigotti A, Trigatti B, Babitt J, Penman M, Xu S, Krieger M (1997) Scavenger receptor B1: a cell surface receptor for high density lipoprotein. Curr Opin Lipidol 8:181–188
Christenson LK, Johnson PF, McAllister JM, Strauss JF III (1999) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins regulate expression of the human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene. J Biol Chem 274:26591–26598
Sugawara T, Kiriakidou M, McAllister JM, Kallen CB, Strauss JF III (1997) Multiple steroidogenic factor 1 binding elements in the human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene 5′-flanking region are required for maximal promoter activity and cyclic AMP responsiveness. Biochemistry 36:7249–7255
Reinhart AJ, Williams SC, Clark BJ, Stocco DM (1999) SF-1 (steroidogenic factor-1) and C/EBP beta (CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta) cooperate to regulate the murine StAR (steroidogenic acute regulatory) promoter. Mol Endocrinol 13:729–741
Clark BJ, Soo SC, Caron KM, Ikeda Y, Parker KL, Stocco DM (1995) Hormonal and developmental regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. Mol Endocrinol 9:1346–1355
Silverman E, Eimerl S, Orly J (1999) CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta and GATA-4 binding regions within the promoter of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene are required for transcription in rat ovarian cells. J Biol Chem 274:17987–17996
Grunstein M (1997) Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389:349–352
Legube G, Trouche D (2003) Regulating histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases. EMBO Rep 4:944–947
Christenson LK, Stouffer RL, Strauss JF III (2001) Quantitative analysis of the hormone-induced hyperacetylation of histone H3 associated with the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene promoter. J Biol Chem 276:27392–27399
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. K. Okuda of Okayama University, Japan, for donating the progesterone antibodies. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), Japan. The authors declare that no conflicts of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this study exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, H., Murayama, C., Takasugi, R. et al. BMP-4 suppresses progesterone production by inhibiting histone H3 acetylation of StAR in bovine granulosa cells in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem 348, 183–190 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0653-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0653-9