Abstract
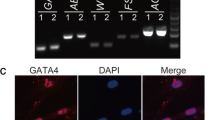
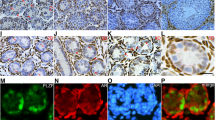
The roles of TGF-β and the interaction between TGF-β and EGFR signaling are critical in Sertoli cell, though the knowledge about them is limited. RT-PCR was used to characterize the status of TGF-β signaling in clinical testicular specimens with complete Sertoli cell-only syndrome (SCOS). The mouse Sertoli cell TM4 was used to investigate the interaction between TGF-β and EGFR signaling by using mitogenic assay, luciferase assay, and western blot, while TM3 (mouse leydig cell), 3T3 (mouse embryo fibroblasts), and B82 (mouse lung fibroblasts) were selected as control. The RT-PCR assay indicated that the expression levels of TβRII and Smad2 in SCOS testes were upregulated compared to that in the normal controls. In the in vitro experiment, the TGF-β1 downregulated cellular proliferation of TM3 and B82 cell (P < 0.05), but it did not changed the proliferation of TM4 and 3T3 cells (P > 0.05). On contrast, TGF-β1 only increased the TGF response elements p3TP-lux activity significantly (P < 0.05) in Sertoli cell TM4. Also, the Western blot assay shows an obvious increase of Smad2 in TM4, 3T3, and TM3 cells after TGF-β1 treatment while the EGFR expression level was significantly increased in TM4 cells only. In conclusion, the TGF-β pathway and the cross-link between TGF-β and EGFR signaling may play an important role on the dysfunction of Sertoli cells which induce germ stem cells’ disappearance in SCOS.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCOS:
-
Sertoli cell-only syndrome
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- TβRI:
-
Transforming growth factor β receptor I
- TβRII:
-
Transforming growth factor β receptor II
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- LH:
-
Luteotrophic hormone
- FSH:
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- NOA:
-
Non-obstructive azoospermia
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
References
Chipuk JE, Cornelius SC, Pultz NJ, Jorgensen JS, Bonham MJ, Kim SJ (2002) The androgen receptor represses transforming growth factor-beta signaling through interaction with Smad3. J Biol Chem 277:1240–1248. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108855200
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signaling. Exp Cell Res 284:31–53. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(02)00098-8
Cordenonsi M, Montagner M, Adorno M, Zacchigna L, Martello G, Mamidi A et al (2007) Integration of TGF-beta and Ras/MAPK signaling through p53 phosphorylation. Science 315:840–843. doi:10.1126/science.1135961
Xin ZC, Liu WJ, Tian L, Yuan YM, Xin H, Fu J et al (2003) Studies on the testis regression related gene profile in aged male. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 35:364–368
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Hung MC (2006) EGFR signaling pathway in breast cancers: from traditional signal transduction to direct nuclear translocalization. Breast Cancer Res Treat 95:211–218. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-9011-0
Jiang X, Sorking A (2002) Coordinated traffic of Grb2 and Ras during epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis visualized in living cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:1522–1535. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-11-0552
Maupas-Schwalm F, Robinet C, Auge N, Thiers JC, Garcia V, Cambus JP et al (2005) Activation of the {beta}-catenin/T-cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer factor-1 pathway by plasminogen activators in ECV304 carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 65:526–532
Lee C, Sutkowski DM, Sensibar JA, Zelner D, Kim I, Amsel I (1995) Regulation of proliferation and production of prostate-specific antigen in androgen-sensitive prostatic cancer cells, LNCaP, by dihydrotestosterone. Endocrinology 136:796–780. doi:10.1210/en.136.2.796
Kim IY, Kim JH, Zelner DJ, Ahn HJ, Sensibar JA, Lee C (1996) Transforming growth factor-beta1 is a mediator of androgen-regulated growth arrest in an androgen-responsive prostatic cancer cell line, LNCaP. Endocrinology 137:991–999. doi:10.1210/en.137.3.991
Kim IY, Zelner DJ, Sensibar JA, Ahn HJ, Park L, Kim JH et al (1996) Modulation of sensitivity to transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) and the level of type II TGF-beta receptor in LNCaP cells by dihydrotestosterone. Exp Cell Res 222:103–110. doi:10.1006/excr.1996.0013
Wrana JL, Attisano L, Carcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M et al (1992) TGF-β signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell 71:1003–1014. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90395-S
Vernet N, Dennefeld C, Guillou F, Chambon P, Ghyselinck NB, Mark M (2006) Prepubertal testis development relies on retinoic acid but not rexinoid receptors in Sertoli cells. EMBO J 25:5816–5825. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601447
Weller O, Yogev L, Yavetz H, Paz G, Kleiman S, Hauser R (2005) Differentiating between primary and secondary Sertoli-cell-only syndrome by histologic and hormonal parameters. Fertil Steril 83:1856–1858. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2004.11.074
Lin YH, Chuang L, Lin YM, Lin YH, Teng YN, Kuo PL (2005) Isochromosome of Yp in a man with Sertoli-cell-only syndrome. Fertil Steril 83:764–766. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2004.08.026
Sato Y, Yoshida K, Shinka T, Nozawa S, Nakahori Y, Iwamoto T (2006) Altered expression pattern of heat shock transcription factor, Y chromosome (HSFY) may be related to altered differentiation of spermatogenic cells in testes with deteriorated spermatogenesis. Fertil Steril 86:612–618. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.01.053
Anniballo R, Ubaldi F, Cobellis L, Sorrentino M, Rienzi L, Greco E et al (2000) Criteria predicting the absence of spermatozoa in the Sertoli cell-only syndrome can be used to improve success rates of sperm retrieval. Hum Reprod 15:2269–2277. doi:10.1093/humrep/15.11.2269
Johannessen LE, Pedersen NM, Pedersen KW, Madshus IH, Stang E (2006) Activation of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) receptor induces formation of EGF receptor- and Grb2-containing Clathrin-coated pits. Mol Cell Biol 26:389–401. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.2.389-401.2006
Blinov ML, Faeder JR, Goldstein B, Hlavacek WS (2006) A network model of early events in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling that accounts for combinatorial complexity. Biosystems 83:136–151. doi:10.1016/j.biosystems.2005.06.014
Lei X, Bandyopadhyay A, Le T, Sun L (2002) Autocrine TGFβ supports growth and survival of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Oncogene 21:7514–7523. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205966
Zhang H, Zou K, Tesseur I, Wyss-Coray T (2005) Small molecule TGF-beta mimetics as potential neuroprotective factors. Curr Alzheimer Res 2:183–186. doi:10.2174/1567205053585756
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CNSF 211 Project #No. 219. and CNSF No.30772285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, T., Xin, Z., Jin, Z. et al. Effect of TGF-β/Smad signaling on sertoli cell and possible mechanism related to complete sertoli cell-only syndrome. Mol Cell Biochem 319, 1–7 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9869-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9869-3