Abstract
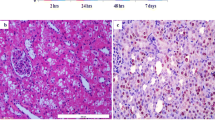
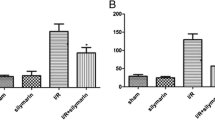
Oxidative stress is important in the pathogenesis of renal ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury; however whether imbalances in reactive oxygen production and disposal account for susceptibility to injury is unclear. The purpose of this study was to compare necrosis, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in IR-resistant Brown Norway rats vs. IR-susceptible Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats in an in vivo model of renal IR injury. As superoxide (O ·−2 ) interacts with nitric oxide (NO) to form peroxynitrite, inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and nitrotyrosine were also examined. Renal IR was induced in SD and BN rats by bilateral clamping of renal arteries for 45 min followed by reperfusion for 24 h (SD 24 and BN 24, respectively). BN rats were resistant to renal IR injury as evidenced by lower plasma creatinine and decreased acute tubular necrosis. TUNEL staining analysis demonstrated significantly decreased apoptosis in the BN rats vs. SD rats after IR. Following IR, O ·−2 levels were also significantly lower in renal tissue of BN rats vs. SD rats (P < 0.05) in conjunction with a preservation of the O ·−2 dismutating protein, CuZn superoxide dismutase (CuZn SOD) (P < 0.05). This was accompanied by an overall decrease in 4-hydroxynonenal adducts in the BN but not SD rats after IR. BN rats also displayed lower iNOS expression (P < 0.05) resulting in lower tissue NO levels and decreased nitrotyrosine formation (P < 0.01) following IR. Collectively these results show that the resistance of the BN rat to renal IR injury is associated with a favorable balance of oxidant production vs. oxidant removal.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edelstein CL, Ling H, Schrier RW (1997) The nature of renal cell injury. Kidney Int 51:1341–1351
Lameire N (2005) The pathophysiology of acute renal failure. Crit Care Clin 21:197–210
Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2005) Acute renal failure. Lancet 365:417–430
Chien CT, Lee PH, Chen CF et al (2001) De novo demonstration and co-localization of free-radical production and apoptosis formation in rat kidney subjected to ischemia/reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:973–982
McCord JM, Roy RS (1982) The pathophysiology of superoxide: roles in inflammation and ischemia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60:1346–1352
McCord JM, Roy RS, Schaffer SW (1985) Free radicals and myocardial ischemia. The role of xanthine oxidase. Adv Myocardiol 5:183–189
Unal D, Yeni E, Erel O et al (2002) Antioxidative effects of exogenous nitric oxide versus antioxidant vitamins on renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Urol Res 30:190–194
Wink DA, Hanbauer I, Krishna MC et al (1993) Nitric oxide protects against cellular damage and cytotoxicity from reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9813–9817
Wink DA, Miranda KM, Espey MG et al (2001) Mechanisms of the antioxidant effects of nitric oxide. Antioxid Redox Signal 3:203–213
Martinez-Mier G, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Bussell S et al (2000) Nitric oxide diminishes apoptosis and p53 gene expression after renal ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplantation 70:1431–1437
Chatterjee PK, Patel NS, Kvale EO et al (2002) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 61:862–871
Zahmatkesh M, Kadkhodaee M, Arab HA et al (2006) Effects of co-administration of an iNOS inhibitor with a broad-spectrum reactive species scavenger in rat renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Nephron Exp Nephrol 103:e119–e125
Beckman JS (2002) Protein tyrosine nitration and peroxynitrite. FASEB J 16:1144
Beckman JS, Chen J, Ischiropoulos H et al (1994) Oxidative chemistry of peroxynitrite. Methods Enzymol 233:229–240
Beckman JS, Ischiropoulos H, Zhu L et al (1992) Kinetics of superoxide dismutase- and iron-catalyzed nitration of phenolics by peroxynitrite. Arch Biochem Biophys 298:438–445
Goligorsky MS, Brodsky SV, Noiri E (2002) Nitric oxide in acute renal failure: NOS versus NOS. Kidney Int 61:855–861
Gow AJ, Ischiropoulos H (2001) Nitric oxide chemistry and cellular signaling. J Cell Physiol 187:277–282
Davies SJ, Reichardt-Pascal SY, Vaughan D et al (1995) Differential effect of ischaemia-reperfusion injury on anti-oxidant enzyme activity in the rat kidney. Exp Nephrol 3:348–354
Jassem W, Fuggle SV, Rela M et al (2002) The role of mitochondria in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Transplantation 73:493–499
Dobashi K, Ghosh B, Orak JK et al (2000) Kidney ischemia-reperfusion: modulation of antioxidant defenses. Mol Cell Biochem 205:1–11
Cruthirds DL, Novak L, Akhi KM et al (2003) Mitochondrial targets of oxidative stress during renal ischemia/reperfusion. Arch Biochem Biophys 412:27–33
Cruthirds DL, Saba H, MacMillan-Crow LA (2005) Overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase protects against ATP depletion-mediated cell death of proximal tubule cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 437:96–105
Yin M, Wheeler MD, Connor HD et al (2001) Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase gene attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2691–2700
Baker JE, Konorev EA, Gross GJ et al (2000) Resistance to myocardial ischemia in five rat strains: is there a genetic component of cardioprotection?. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H1395–1400
Basile DP, Donohoe D, Cao X et al (2004) Resistance to ischemic acute renal failure in the Brown Norway rat: a new model to study cytoprotection. Kidney Int 65:2201–2211
Shi Y, Hutchins W, Ogawa H et al (2005) Increased resistance to myocardial ischemia in the Brown Norway vs. Dahl S rat: role of nitric oxide synthase and Hsp90. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38:625–635
Blydt-Hansen TD, Katori M, Lassman C et al (2003) Gene transfer-induced local heme oxygenase-1 overexpression protects rat kidney transplants from ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:745–754
Pieper GM, Nilakantan V, Zhou X et al (2005) Treatment with {alpha}-phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone, a free radical-trapping agent, abrogates inflammatory cytokine gene expression during alloimmune activation in rat cardiac allografts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:774–779
Khadour FH, Panas D, Ferdinandy P (2002) Enhanced NO and superoxide generation in dysfunctional hearts from endotoxemic rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H1108–H1115
Nilakantan V, Zhou X, Hilton G et al (2005) Hierarchical change in antioxidant enzyme gene expression and activity in acute cardiac rejection: role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Mol Cell Biochem 270:39–47
Nilakantan V, Halligan NL, Nguyen TK et al (2005) Post-translational modification of manganese superoxide dismutase in acutely rejecting cardiac transplants: role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Heart Lung Transplant 24:1591–1599
Wang Q, Tompkins KD, Simonyi A et al (2006) Apocynin protects against global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and injury in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res 1090:182–189
Dodd OJ, Pearse DB (2000) Effect of the NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin on ischemia-reperfusion lung injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279:H303–H312
Rhoden E, Teloken C, Lucas M et al (2000) Protective effect of allopurinol in the renal ischemia-reperfusion in uninephrectomized rats. Gen Pharmacol 35:189–193
Taylor NE, Glocka P, Liang M et al (2006) NADPH oxidase in the renal medulla causes oxidative stress and contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats. Hypertension 47:692–698
Afonso V, Santos G, Collin P et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha down-regulates human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase 1 promoter via JNK/AP-1 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 41:709–721
Eschwege P, Paradis V, Conti M et al (1999) In situ detection of lipid peroxidation by-products as markers of renal ischemia injuries in rat kidneys. J Urol 162:553–557
Walker LM, York JL, Imam SZ et al (2001) Oxidative stress and reactive nitrogen species generation during renal ischemia. Toxicol Sci 63:143–148
Erdogan H, Fadillioglu E, Yagmurca M et al (2006) Protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation after renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: protective effects of erdosteine and N-acetylcysteine. Urol Res 34:41–46
Noiri E, Nakao A, Uchida K et al (2001) Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F948–F957
Yu L, Gengaro PE, Niederberger M et al (1994) Nitric oxide: a mediator in rat tubular hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1691–1695
Noiri E, Peresleni T, Miller F et al (1996) In vivo targeting of inducible NO synthase with oligodeoxynucleotides protects rat kidney against ischemia. J Clin Invest 97:2377–2383
Peresleni T, Noiri E, Bahou WF et al (1996) Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to inducible NO synthase rescue epithelial cells from oxidative stress injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 270:F971–F977
Ling H, Edelstein C, Gengaro P et al (1999) Attenuation of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in inducible nitric oxide synthase knockout mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 277:F383–F390
Ling H, Gengaro PE, Edelstein CL (1998) Effect of hypoxia on proximal tubules isolated from nitric oxide synthase knockout mice. Kidney Int 53:1642–1646
Chander V, Chopra K (2006) Possible role of nitric oxide in the protective effect of resveratrol in 5/6th nephrectomized rats. J Surg Res 133:129–135
Chander V, Chopra K (2006) Renal protective effect of molsidomine and L-arginine in ischemia-reperfusion induced injury in rats. J Surg Res 128:132–139
Mark LA, Robinson AV, Schulak JA (2005) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Surg Res 129:236–241
Yamakura F, Matsumoto T, Fujimura T et al (2001) Modification of a single tryptophan residue in human Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase by peroxynitrite in the presence of bicarbonate. Biochim Biophys Acta 1548:38–46
Yamakura F, Matsumoto T, Ikeda K et al (2005) Nitrated and oxidized products of a single tryptophan residue in human Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase treated with either peroxynitrite-carbon dioxide or myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-nitrite. J Biochem (Tokyo) 138:57–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by a Medical College of Wisconsin-Research Affairs Committee Grant to V. Nilakantan, and by divisional funds to V. Nilakantan and B.D. Shames.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nilakantan, V., Hilton, G., Maenpaa, C. et al. Favorable balance of anti-oxidant/pro-oxidant systems and ablated oxidative stress in Brown Norway rats in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem 304, 1–11 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9480-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9480-z