Abstract
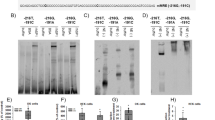
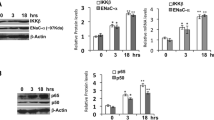
Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (SK) of the SK2 subtype are widely expressed in the central nervous system where they contribute to the control of neuronal excitability. Two SK2 isoforms, SK2-S and SK2-L, the latter representing an N-terminally extended protein of SK2-S, are expressed in similar patterns in the brain. However, our understanding of mechanisms by which the expression of SK2 is regulated is limited. We identified one functional glucocorticoid response element (GRE) at position −2248 bp and two functional nuclear factor-kappB (NF-kappaB) response elements at positions –1652 and –1586 bp in the SK2-S promoter. An increase in SK2-S promoter activity was observed in PC12 cells transiently transfected with a wild-type SK2-S promoter-luciferase reporter gene construct and treated with aldosterone or dexamethasone. The mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist spironolactone or the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) antagonist mifepristone fully inhibited aldosterone or dexamethasone activation of the SK2-S promoter, respectively. SK2-S promoter activity was also induced by the cell-permeable ceramide analog, N-acetylsphingosine (C2-ceramide). Antisense oligonucleotides directed to NF-kappaB p65 or p50 suppressed SK2-S transcription induced by C2-ceramide. Deletion studies showed that only the −1586 bp NF-kappaB binding site was necessary for maximum C2-ceramide response. Finally, we showed that activation of GRs but not of MRs repressed the NF-kappaB-mediated induction of SK2-S transcription. These findings suggest a possible transcriptional cross talk between GRs and NF-kappaB in the intronic promoter regulation of SK2-S channel gene transcription.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SK:
-
small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel
- GRE:
-
glucocorticoid response element
- AHP:
-
afterhyperpolarization
- GR:
-
glucocorticoid receptor
- MR:
-
mineralocorticoid receptor
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
References
De Kloet ER, Oitzl MS, Joels M (1999) Stress and cognition: are corticosteroids good or bad guys? Trends Neurosci 22: 422–426
Kim JJ, Diamond DM (2002) The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 453–462
Smith MA, Makino S, Kvetnansky R, Post RM (1995) Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus J Neurosci 15: 1768–1777
Joels M, Velzing E, Nair S, Verkuyl JM, Karst H (2003) Acute stress increases calcium current amplitude in rat hippocampus: temporal changes in physiology and gene expression Eur J Neurosci 18: 1315–1324
Nijholt I, Farchi N, Kye M, Sklan EH, Shoham S, Verbeure B, Owen D, Hochner B, Spiess J, Soreq H, Blank T (2004) Stress-induced alternative splicing of acetylcholinesterase results in enhanced fear memory and long-term potentiation Mol Psychiatry 9: 174–183
Blank T, Nijholt I, Spiess J (2004) Molecular determinants mediating effects of acute stress on hippocampus-dependent synaptic plasticity and learning Mol Neurobiol 29: 131–138
McEwen BS, De Kloet ER, Rostene W (1986) Adrenal steroid receptors and actions in the nervous system Physiol Rev 66: 1121–1188
De Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E, Oitzl MS, Joels M (1998) Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease Endocr Rev 19: 269–301
De Kloet ER, Oitzl MS, Joels M (1993) Functional implications of brain corticosteroid receptor diversity Cell Mol Neurobiol 13: 433–455
Van Steensel B, van Binnendijk EP, Hornsby CD, van der Voort HT, Krozowski ZS, De Kloet ER, van Driel R (1996) Partial colocalization of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in discrete compartments in nuclei of rat hippocampus neurons J Cell Sci 109: 787–792
Kye M, Nijholt I, Spiess J, Blank T (2003) Stress and corticosterone regulate SK2 gene expression in mouse hippocampus Soc Neurosci Abstr 29: 25217
Stocker M, Pedarzani P (2000) Differential distribution of three Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel subunits, SK1, SK2, and SK3, in the adult rat central nervous system Mol Cell Neurosci 15: 476–493
Sailer CA, Hu H, Kaufmann WA, Trieb M, Schwarzer C, Storm JF, Knaus HG (2002) Regional differences in distribution and functional expression of small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in rat brain J Neurosci 22: 9698–9707
Villalobos C, Shakkottai VG, Chandy KG, Michelhaugh SK, Andrade R (2004) SKCa channels mediate the medium but not the slow calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in cortical neurons J Neurosci 24: 3537–3542
Bond CT, Herson PS, Strassmaier T, Hammond R, Stackman R, Maylie J, Adelman JP (2004) Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel knock-out mice reveal the identity of calcium-dependent afterhyperpolarization currents J Neurosci 24: 5301–5306
Gu N, Vervaeke K, Hu H, Storm JF (2005) Kv7/KCNQ/M and HCN/h, but not KCa2/SK channels, contribute to the somatic medium after-hyperpolarization (mAHP) and excitability control in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells J Physiol 566: 689–715
Stocker M, Krause M, Pedarzani P (1999) An apamin-sensitive Ca2+-activated K+ current in hippocampal pyramidal neurons Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 4662–4667
Stackman RW, Hammond RS, Linardatos E, Gerlach A, Maylie J, Adelman JP, Tzounopoulos T (2002) Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels modulate synaptic plasticity and memory encoding J Neurosci 22: 10163–10171
Strassmaier T, Bond CT, Sailer CA, Knaus HG, Maylie J, Adelman JP (2005) A Novel Isoform of SK2 Assembles with Other SK Subunits in Mouse Brain J Biol Chem 280: 21231–21236
Baldwin AS Jr (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa-B proteins: new discoveries and insights Annu Rev Immunol 14: 649–683
Blank T, Nijholt I, Kye MJ, Radulovic J, Spiess J (2003) Small-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel SK3 generates age-related memory and LTP deficits Nat Neurosci 6: 911–912
Lin YZ, Yao SY, Veach RA, Torgerson TR, Hawiger J (1995) Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-κB by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence J Biol Chem 270: 14255–14258
Darios F, Corti O, Lucking CB, Hampe C, Muriel MP, Abbas N, Gu WJ, Hirsch EC, Rooney T, Ruberg M, Brice A (2003) Parkin prevents mitochondrial swelling and cytochrome c release in mitochondria-dependent cell death Hum Mol Genet 12: 517–526
France-Lanord V, Brugg B, Michel PP, Agid Y, Ruberg M (1997) Mitochondrial free radical signal in ceramide-dependent apoptosis: a putative mechanism for neuronal death in Parkinson’s disease J Neurochem 69; 1612–1621
De Kloet ER (1995) Steroids, stability and stress. Front Neuroendocrinol 16: 416–425
De Kloet ER, Rots NY, Cools AR (1996) Brain-corticosteroid hormone dialogue: slow and persistent Cell Mol Neurobiol 16: 345–356
Bierhaus A, Wolf J, Andrassy M, Rohleder N, Humpert PM, Petrov D, Ferstl R, von Eynatten M, Wendt T, Rudofsky G, Joswig M, Morcos M, Schwaninger M, McEwen B, Kirschbaum C, Nawroth PP (2003) A mechanism converting psychosocial stress into mononuclear cell activation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 1920–1925
Mattson MP, Culmsee C, Yu ZF, Camandola S (2000) Roles of nuclear factor κB in neuronal survival, plasticity. J Neurochem 74: 443–465
Carroll JE, Howard EF, Hess DC, Wakade CG, Chen Q, Cheng C (1998) Nuclear factor-kappa B activation during cerebral reperfusion: effect of attenuation with N-acetylcysteine treatment. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 56: 186–191
Clemens JA, Stephenson DT, Smalstig EB, Dixon EP, Little SP (1997) Global ischemia activates nuclear factor-kappa B in forebrain neurons of rats. Stroke 28: 1073–1080
Culmsee C, Siewe J, Junker V, Retiounskaia M, Schwarz S, Camandola S, El-Metainy S, Behnke H, Mattson MP, Krieglstein J (2003) Reciprocal inhibition of p53 and nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional activities determines cell survival or death in neurons. J Neurosci 23: 8586–8595
Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Neumann H, Wekerle H, Baeuerle PA (1994) Constitutive NF-kappaB activity in neurons. Mol Cell Biol 14: 3981–3992
Bakalkin GY, Yakovleva T, Terenius L (1993) NF-kappaB-like factors in the murine brain. Developmentally-regulated and tissue-specific expression. Mol Brain Res 20: 137–146
Guerrini L, Blasi F, Denis-Donini S (1995) Synaptic activation of NF-kappaB by glutamate in cerebellar granule neurons in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 9077–9081
Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Baeuerle PA (1995) Stimulation of ionotropic glutamate receptors activates transcription factor NF-kappa B in primary neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 9618–9622
Meberg PJ, Kinney WR, Valcourt EG, Routtenberg A (1996) Gene expression of the transcription factor NF-kappaB in hippocampus: regulation by synaptic activity. Mol Brain Res 38: 179–190
Unlap T, Jope RS (1995) Inhibition of NF-kappaB DNA binding activity by glucocorticoids in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 198: 41–44
Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M (1995) Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: Inhibition of NF- kappaB activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science 270: 286–290
Scheinman RI, Cogswell PC, Lofquist AK, Baldwin AS, Jr (1995) Role of transcriptional activation of I kappaB in mediation of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids. Science 270: 283–286
Van de Stolpe A, Caldenhoven E, Raaijmakers JA, van der Saag PT, Koenderman L (1993) Glucocorticoid-mediated repression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in human monocytic and bronchial epithelial cell lines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 8: 340–347
Wissink S, van Heerde EC, van der Burg B, van der Saag PT (1998) A dual mechanism mediates repression of NF-kappaB activity by glucocorticoids. Mol Endocrinol 12: 355–363
Liden J, Delaunay F, Rafter I, Gustafsson J, Okret S (1997) A new function for the C-terminal zinc finger of the glucocorticoid receptor repression of RelA transactivation. J Biol Chem 272: 21467–21472
Wissink S, van Heerde EC, Schmitz ML, Kalkhoven E, van der Burg B, Baeuerle PA, van der Saag PT (1997) Distinct domains of the RelA NF-kappaB subunit are required for negative cross-talk and direct interaction with the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem 272: 22278–22284
Meijer OC, Williamson A, Dallman MF, Pearce D (2000) Transcriptional repression of the 5-HT1A receptor promoter by corticosterone via mineralocorticoid receptors depends on the cellular context. J Neuroendocrinol 12: 245–254
Wissink S, Meijer O, Pearce D, van Der Burg B, van Der Saag PT (2000) Regulation of the rat serotonin-1A receptor gene by corticosteroids. J Biol Chem 275: 1321–1326
Rong Y, Baudry M (1996) Seizure activity results in a rapid induction of nuclear factor-kappa B in adult but not juvenile rat limbic structures. J Neurochem 67: 662–668
Matsuoka Y, Kitamura Y, Okazaki M, Terai K, Taniguchi T (1999) Kainic acid-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res 124: 215–222
Goodman Y, Mattson MP (1996) Ceramide protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative insults, and amyloid ß-peptide toxicity. J Neurochem 66: 869–872
Lee AL, Dumas TC, Tarapore PE, Webster BR, Ho DY, Kaufer D, Sapolsky RM (2003) Potassium channel gene therapy can prevent neuron death resulting from necrotic and apoptotic insults. J Neurochem 86: 1079–1088
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Max-Planck Society and␣NIH grant 2U54NSO39406-06. The authors are thankful to Saravanna Murthy for his critical comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kye, MJ., Spiess, J. & Blank, T. Transcriptional regulation of intronic calcium-activated potassium channel SK2 promoters by nuclear factor-kappa B and glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Biochem 300, 9–17 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9320-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9320-6