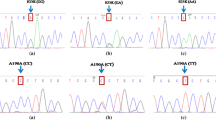
Abstract
Objective: Based on onset-age stratified analysis may be useful to determine the association of NeuroD1-Ala45Thr variation with susceptibility to genetic heterogeneous type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), we investigated the Ala45Thr variation in unrelated early-onset and late-onset T2DM with or without diabetic pedigree and unrelated non-diabetic control subjects in Chinese.
Methods: 175 early-onset and 194 late-onset type 2 diabetic patients were further divided into two subgroups according to with or without diabetic pedigree respectively. This NeuroD1-Ala45Thr variation were screened by PCR-direct sequencing in above 369 type 2 diabetic patients and 87 unrelated non-diabetic control subjects. We then compared the distribution of the Ala45Thr variation among the groups, searching for the predictive trends.
Results: Frequencies of the variant (AA + GA genotype) in early-onset T2DM are obviously elevated, especially among diabetic pedigree subjects when compared to non-diabetic controls (p= 0.003) and late-onset T2DM subjects (p = 0.014). However, no significant differences were observed between late-onset T2DM with or without diabetic pedigree and non-diabetic control subjects.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that 1) the NeuroD1-Ala45Thr variation may itself have an important role in susceptibility to or be in disequilibrium with early-onset T2DM in Chinese; 2) the Ala45Thr may affect the onset pattern of T2DM, i.e., early-onset but not late-onset T2DM in Chinese; and 3) onset-age stratified analysis may be useful to determine the association of NeuroD1-Ala45Thr variation with susceptibility to genetic heterogeneous T2DM in Chinese.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hani EH, Stoffers DA, Chevre JC, Durand E, Stanojevic V, Dina C, Habener JF, Froguel P: Defective mutations in the insulin promoter factor-1 (IPF-1) gene in late-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 104(9): R41–48, 1999
Macfarlane WM, Frayling TM, Ellard S, Evans JC, Allen LI, Bulman MP, Ayres S, Shepherd M, Clark P, Millward A, Demaine A, Wilkin T, Docherty K, Hattersley AT: Missense mutations in the insulin promoter factor-1 gene predispose to type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 104(9): R33–39, 1999
Iwasaki N, Oda N, Ogata M, Hara M, Hinokio Y, Oda Y, Yamagata K, Kanematsu S, Ohgawara H, Omori Y, Bell GI: Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha/MODY3 gene in Japanese subjects with early- and late-onset NIDDM. Diabetes 46(9): 1504–1508, 1997
Hani EH, Suaud L, Boutin P, Chevre JC, Durand E, Philippi A, Demenais F, Vionnet N, Furuta H, Velho G, Bell GI, Laine B, Froguel P: A missense mutation in hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha, resulting in a reduced transactivation activity, in human late-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 101(3): 521–526, 1998
Malecki MT, Jhala US, Antonellis A, Fields L, Doria A, Orban T, Saad M, Warram JH, Montminy M, Krolewski AS: Mutations in NEUROD1 are associated with the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nature Genetics 23: 323–328, 1999
Awata T, Inoue K, Inoue I, Abe T, Takino H, KanazawaY, Katayama S: Lack of association of the Ala45Thr variant in the NeuroD/BETA2 with type 1 diabetes in Japanese. Diab Res Clin Pract 49: 61–63, 2000
Dupont S, Vionnet N, Chevre JC, Gallina S, Dina C, Seino Y, Yamada Y, Froguel P: No evidence of linkage or diabetes-associated mutations in the transcription factors BETA2/NEUROD1 and PAX4 in Type II diabetes in France. Diabetologia 42: 480–484, 1999
Hansen L, Jensen JN, Urioste S, Petersen HV, Pociot F, Eiberg H, Kristiansen OP, Hansen T, Serup P, Nerup J, Pedersen O: NeuroD/BETA2 gene variability and diabetes: no associations to late-onset type 2 diabetes but an A45 allele may represent a susceptibility marker for type 1 diabetes among Danes. Danish Study Group of Diabetes in Childhood, and the Danish IDDM Epidemiology and Genetics Group. Diabetes 49(5): 876–878, 2000
Kanatsuka A, Tokuyama Y, Nozaki O, Matsui K, Egashira T: β-cell dysfunction in late –onset diabetic subjects carrying homozygous mutation in transcription factors NeuroD1 and PAX4. Metabolism 51: 1161–1165, 2002
Malecki MT, Cyganek K, Klupa T, Sieradzki J: The Ala45Thr polymorphism of BETA2/NeuroD1 gene and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Polish population. Acta Diabeto l40(2): 109–111, 2003
Jackson AE, Cassell P, North B, Vijayaraghavan S, Gelding S, Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Hitman G: Polymorphic variations in the neurogenic differentiation-1, neurogenin-3, and hapatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha genes contribute to glucose intolerance in a south Indian population. Diabetes 53: 2122–2125, 2004
Naya FJ, Stellrecht CM, Tsai MJ: Tissue-specific regulation of the insulin gene by a novel basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. Genes Dev 9(8): 1009 –19, 1995
Naya FJ, Huang HP, Qiu Y, Mutoh H, DeMayo FJ, Leiter AB, Tsai MJ: Diabetes, defective pancreatic morphogenesis, and abnormal enteroendocrine differentiation in BETA2/neuroD-deficient mice. Genes Dev 11(18): 2323 –2334, 1997
Zimmet PZ: Kelly West Lecture 1991. Challenges in diabetes epidemiology -from West to the rest. Diabetes Care 15(2): 232–252, 1992
The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus: Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabete s Mellitus(Position Statement). Diabetes Care26(Suppl 1): S5–S24, 2003
Fukui M, Nakano K, Obayashi H, Kitagawa Y, Nakamura N, Mori H, Kajiyama S, Wada S, Fujii M, Yoshimori K, Kanaitsuka T, Shigeta H, Kondo M: High prevalence of mitochondrial diabetes mellitus in Japanese patients with major risk factors. Metabolism 46(7): 793–795, 1997
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T: A laboratory manual. In Molecular Cloning. 2nd ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989, pp. E3–E4
Furuta H, Horikawa Y, Iwasaki N, Hara M, Sussel L, Le Beau MM, Davis EM, Ogata M, Iwamoto Y, German MS, Bell GI: Beta-cell transcription factors and diabetes: mutations in the coding region of the BETA2/NeuroD1 (NEUROD1) and Nkx2.2 (NKX2B) genes are not associated with maturity-onset diabetes of the young in Japanese. Diabetes 47(8): 1356–1358, 1998
Kavvoura FK, Ioannidis JP: Ala45Thr polymorphism of the NEUROD1 gene and diabetes susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Hum Genet. 2005 Feb 116(3): 192–199, Epub 2004 Dec 11
Leonardi O, Mints G, Hussain MA: Beta-cell apoptosis in the pathogenesis of human type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrino l149(2): 99–102, 2003
Yamada S, Motohashi Y, Yanakawa T, Maruyama T, Kasuga A, Hirose H, Matsubara K, Saruta T: NeuroD/BETA2 gene GA polymorphism may affect onset pattern of type 1 diabetes in Japanese. Diab Care 24: 1438–1441, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Jia, W., Zheng, T. et al. Ala45Thr variation in neuroD1 gene is associated with early-onset type 2 diabetes with or without diabetic pedigree in Chinese. Mol Cell Biochem 290, 199–204 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9217-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9217-4