Abstract
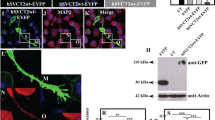
Inactivation of Rho GTPases inhibited the neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells. The role of Cdc42 in neurite outgrowth was then studied by selective inhibition of Cdc42 signals. Overexpression of ACK42, Cdc42 binding domain of ACK-1, inhibited NGF-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. ACK42 also inhibited the neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells induced by constitutively activated mutant of Cdc42, but not Rac. These results suggest that Cdc42 plays an important role in mediating NGF-induced neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells. Inhibition of neurite outgrowth was also demonstrated using a cell permeable chimeric protein, penetratin-ACK42. A dominant negative mutant of Rac, RacN17 inhibited Cdc42-induced neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells suggesting that Rac acts downstream of Cdc42. Further studies, using primary-cultures of rat cerebellar granule neurons, showed that Cdc42 is also involved in the neurite outgrowth of cerebellar granule neurons. Both penetratin-ACK42 and Clostridium difficile toxin B, which inactivates all members of Rho GTPases strongly inhibited the neurite outgrowth of cerebellar granule neurons. These results show that Cdc42 plays a similar and essential role in the development of neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells and cerebellar granule neurons. These results provide evidence that Cdc42 produces signals that are essential for the neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells and cerebellar granule neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACK42:
-
Cdc42 binding fragment of ACK-1
- GAP:
-
GTPase activating protein
- RHG:
-
Rho GAP domain of p190-A
- NGF:
-
nerve growth factor
- NOG:
-
neurite outgrowth
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- GST:
-
glutathione S-transferase
- PLL:
-
poly-L-lysine
- IPTG:
-
isopropyl-beta-thiogalactopyranoside
References
Hall A: Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279: 509–514, 1998
Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK, Juliano RL: Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev 50: 197–263, 1998
Tigyi G, Fischer DJ, Sebok A, Yang C, Dyer DL, Miledi R: Lysophosphatidic acid-induced neurite retraction in PC12 cells: control by phosphoinositide-Ca2+ signaling and Rho. J Neurochem 66: 537–548, 1996
Gebbink MF, Kranenburg O, Poland M, van Horck FP, Houssa B, Moolenaar WH: Identification of a novel, putative Rho-specific GDP/GTP exchange factor and a RhoA-binding protein: control of neuronal morphology. J Cell Biol 137: 1603–1613, 1997
Kozma R, Sarner S, Ahmed S, Lim L: Rho family GTPases and neuronal growth cone remodelling: Relationship between increased complexity induced by Cdc42Hs, Rac1, and acetylcholine and collapse induced by RhoA and lysophosphatidic acid. Mol Cell Biol 17: 1201–1211, 1997
Nishiki T, Narumiya S, Morii N, Yamamoto M, Fujiwara M, Kamata Y, Sakaguchi G, Kozaki S: ADP-ribosylation of the rho/rac proteins induces growth inhibition, neurite outgrowth and acetylcholine esterase in cultured PC-12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 167: 265–272, 1990
Just I, Selzer J, Wilm M, von Eichel-Streiber C, Mann M, Aktories K: Glucosylation of Rho proteins by Clostridium difficile toxin B. Nature 375: 500–503, 1995
Bradke F, Dotti CG: The role of local actin instability in axon formation. Science 283:1931–1934, 1999
Luo L, Liao YJ, Jan LY, Jan YN: Distinct morphogenetic functions of similar small GTPases: drosophila Drac1 is involved in axonal outgrowth and myoblast fusion. Genes Dev 8: 1787–1802, 1994
Luo L, Hensch TK, Ackerman L, Barbel S, Jan LY, Jan YN: Differential effects of the Rac GTPase on Purkinje cell axons and dendritic trunks and spines. Nature 379: 837–840, 1996
Kuhn TB, Meberg PJ, Brown MD, Bernstein BW, Minamide LS, Jensen JR, Okada K, Soda EA, Bamburg JR: Regulating actin dynamics in neuronal growth cones by ADF/cofilin and rho family GTPases. J Neurobiol 44: 126–144, 2000
Daniels RH, Hall PS, Bokoch GM: Membrane targeting of p21-activated kinase1 (PAK1) induces neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells. EMBO J 17: 754–764, 1998
Aoki K, Nakamura T, Matsuda M: Spatio-temporal regulation of Rac1 and Cdc42 activity during nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 279: 713–719, 2004
Aoki K, Nakamura T, Fujikawa K, Matsuda M: Local PIP3 Accumulation 13. Recruits Vav2 and Vav3 to Activate Rac1/Cdc42 and initiate neurite outgrowth in nerve growth factor-stimulated PC12 cells. Mol Biol Cell 16: 2207–2217, 2005
Satoh T, Nakamura S, Kaziro Y: Induction of neurite formation in PC12 cells by microinjection of proto-oncogenic Ha-ras protein preincubated with guanosine-5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). Mol Cell Biol 7: 4553–4556, 1987
Tang Y, Yu J, Field J: Signals from the Ras, Rac, and Rho GTPases converge on the Pak protein kinase in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1881–1891, 1999
Yao R, Cooper GM: Regulation of the Ras signaling pathway by GTPase-activating protein in PC12 cells. Oncogene 11: 1607–1614, 1995
Ashcroft M, Stephens RM, Hallberg B, Downward J, Kaplan DR: The selective and inducible activation of endogenous PI 3-kinase in PC12 cells results in efficient NGF-mediated survival but defective neurite outgrowth. Oncogene 18: 4586–4597, 1999
Qiu RG, Chen J, McCormick F, Symons M: A role for Rho in Ras transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11781–11785, 1995
Nobes CD, Hall A: Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81: 53–62, 1995
Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL, Diekmann D, Hall A: The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 70: 401–410, 1992
Chen XQ, Tan I, Leung T, Lim L: The myotonic dystrophy kinase-related Cdc42-binding kinase is involved in the regulation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 274: 19901–19905, 1999
Maruta H: Regulators of ras/Rho family GTPases: GAPs, GDSs and GDIs. In: H. Maruta, K. Kohama (eds). G proteins, cytoskeleton and cancer. R.G. Landes Bioscience, Austin, 1998, pp 151–170
Nur-E-Kamal A, Kamal JM, Qureshi MM, Maruta H: The CDC42-specific inhibitor derived from ACK-1 blocks v-Ha-Ras-induced transformation. Oncogene 18: 7787–7793, 1999
Wang DZ, Nur-E-Kamal A, Tikoo A, Montague W, Maruta H: The GTPase and Rho GAP domains of p190, a tumor suppressor protein that binds the M(r) 120,000 Ras GAP, independently function as anti-Ras tumor suppressors. Cancer Res 57: 2478–2484, 1997
Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Tan L, Lim L: A non-receptor tyrosine kinase that inhibits the GTPase activity of p21cdc42. Nature 363: 364–367, 1993
Nur-E-Kamal A, Sizeland A, D'Abaco G, Maruta H: Asparagine 26, glutamic acid 31, valine 45, and tyrosine 64 of Ras proteins are required for their oncogenicity. J Biol Chem 267: 1415–1418, 1992
Katoh-Semba R, Kitajima S, Yamazaki Y, Sano M: Neuritic growth from a new subline of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells: cyclic AMP mimics the action of nerve growth factor. J Neurosci Res 17: 36–44, 1987
Meiners S, Mercado ML, Nur-E-Kamal MS, Geller HM: Tenascin-C contains domains that independently regulate neurite outgrowth and neurite guidance. J Neurosci 19: 8443–8453, 1999
Nur-E-Kamal A, Varga M, Maruta H: The GTPase-activating NF1 fragment of 91 amino acids reverses v-Ha-Ras-induced malignant phenotype. J Biol Chem 268: 22331–22337, 1993
Settleman J, Albright CF, Foster LC, Weinberg RA: Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature 359: 153–154, 1992
Tatsis N, Lannigan DA, Macara IG: The function of the p190 Rho GTPase-activating protein is controlled by its N-terminal GTP binding domain. J Biol Chem 273: 34631–34638, 1998
Aktories K: Rho proteins: targets for bacterial toxins. Trends Microbiol 5: 282–288, 1997
Gallo G, Letourneau PC: Axon guidance: GTPases help axons reach their targets. Curr Biol 8: R80–R82, 1998
Kuo WL, Chung KC, Rosner MR: Differentiation of central nervous system neuronal cells by fibroblast-derived growth factor requires at least two signaling pathways: roles for Ras and Src. Mol Cell Biol 17: 4633–4643, 1997
Qiu RG, Abo A, McCormick F, Symons M: Cdc42 regulates anchorage-independent growth and is necessary for Ras transformation. Mol Cell Biol 17: 3449–3458, 1997
Yang W, Cerione RA: Cloning and characterization of a novel Cdc42-associated tyrosine kinase, ACK-2, from bovine brain. J Biol Chem 272: 24819–24824, 1997
Mott HR, Owen D, Nietlispach D, Lowe PN, Manser E, Lim L, Laue ED: Structure of the small G protein Cdc42 bound to the GTPase-binding domain of ACK. Nature 399: 384–388, 1999
Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Suetsugu S, Takenawa T: IRSp53 is an essential intermediate between Rac and WAVE in the regulation of membrane ruffling. Nature 408: 732–735, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, I., Calle, Y., Iwashita, S. et al. Role of Cdc42 in neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells and cerebellar granule neurons. Mol Cell Biochem 281, 17–25 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-0165-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-0165-9