Abstract
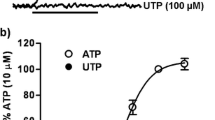
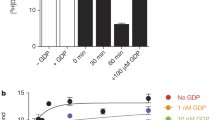
Purification of HA-tagged P2Y2 receptors from transfected human 1321N1 astrocytoma cells yielded a protein with a molecular size determined by SDS-PAGE to be in the range of 57–76 kDa, which is typical of membrane glycoproteins with heterogeneous complex glycosylation. The protein phosphatase inhibitor, okadaic acid, attenuated the recovery of receptor activity from the agonist-induced desensitized state, suggesting a role for P2Y2 receptor phosphorylation in desensitization. Isolation of HA-tagged P2Y2 nucleotide receptors from metabolically [32P]-labelled cells indicated a (3.8 ± 0.2)-fold increase in the [32P]-content of the receptor after 15 min of treatment with 100 μM UTP, as compared to immunoprecipitated receptors from untreated control cells. Receptor sequestration studies indicated that ∼40% of the surface receptors were internalized after a 15-min stimulation with 100 μM UTP. Point mutation of three potential GRK and PKC phosphorylation sites in the third intracellular loop and C-terminal tail of the P2Y2 receptor (namely, S243A, T344A, and S356A) extinguished agonist-induced receptor phosphorylation, caused a marked reduction in the efficacy of UTP to desensitize P2Y2 receptor signalling to intracellular calcium mobilization, and impaired agonist-induced receptor internalization. Activation of PKC isoforms with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate that caused heterologous receptor desensitization did not increase the level of P2Y2 receptor phosphorylation. Our results indicate a role for receptor phosphorylation by phorbol-insensitive protein kinases in agonist-induced desensitization of the P2Y2 nucleotide receptor. (Mol Cell Biochem xxx: 35–45, 2005)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAA-P2Y2, S243A, T344A, and S356A:
-
triple mutant of P2Y2
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- [Ca2+] i :
-
intracellular free calcium ion concentration
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- EC50 :
-
agonist concentration that produces 50% of a response
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- GRK:
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase
- HA:
-
hemagglutinin
- Hepes:
-
N-[2-Hydroxyethyl]piperazine-N′-[2-ethanesulfonic acid]
- IC50 :
-
agonist concentration that inhibits 50% of the response
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- PLC-β:
-
phospholipase C-β
- P2Y2-1321N1:
-
HA-tagged P2Y2 transfected 1321N1 cells
- PMA:
-
phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- S.E.M.:
-
standard error of the mean
- WT-P2Y2 :
-
wild type P2Y2
References
Hanley PJ, Musset B, Renigunta V, Limberg SH, Dalpke AH, Sus R, Heeg KM, Preisig-Muller R, Daut J: Extracellular ATP induces oscillations of intracellular Ca2+ and membrane potential and promotes transcription of IL-6 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 9479–9484, 2004
Kannan S: Neutrophil chemotaxis: potential role of chemokine receptors in extracellular nucleotide induced Mac-1 expression. Med Hypotheses 61: 577–579, 2003
Neary JT, Baker L, Jorgensen SL, Norenberg MD: Extracellular ATP induces stellation and increases glial fibrillary acidic protein content and DNA synthesis in primary astrocyte cultures. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87: 8–13, 1994
Chorna NE, Santiago-Perez LI, Erb L, Seye CI, Neary JT, Sun GY, Weisman GA, Gonzalez FA: P2Y receptors activate neuroprotective mechanisms in astrocytic cells. J Neurochem 91: 119–132, 2004
Stutts MJ, Chinet TC, Mason SJ, Fullton JM, Clarke LL, Boucher RC: Regulation of Cl− channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by extracellular ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1621–1625, 1992
Nour M, Quiambao AB, Peterson WM, Al-Ubaidi MR, Naash MI: P2Y(2) receptor agonist INS37217 enhances functional recovery after detachment caused by subretinal injection in normal and rds mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44: 4505–4514, 2003
Kellerman DJ: P2Y(2) receptor agonists: a new class of medication targeted at improved mucociliary clearance. Chest 121: 201S–205S, 2002
Garrad RC, Otero MA, Erb L, Theiss PM, Clarke LL, Gonzalez FA, Turner JT, Weisman GA: Structural basis of agonist-induced desensitization and sequestration of the P2Y2 nucleotide receptor. Consequences of truncation of the C terminus. J Biol Chem 273: 29437–29444, 1998
Otero M, Garrad RC, Velazquez B, Hernandez-Perez MG, Camden JM, Erb L, Clarke LL, Turner JT, Weisman GA, Gonzalez FA: Mechanisms of agonist-dependent and -independent desensitization of a recombinant P2Y2 nucleotide receptor. Mol Cell Biochem 205: 115–123, 2000
Bouvier M, Hausdorff WP, De Blasi A, O'Dowd BF, Kobilka BK, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ: Removal of phosphorylation sites from the β 2-adrenergic receptor delays onset of agonist-promoted desensitization. Nature 333: 370–373, 1988
Hausdorff WP, Bouvier M, O'Dowd BF, Irons GP, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ: Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the β 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem 264: 12657–12665, 1989
Premont RT, Inglese J, Lefkowitz RJ: Protein kinases that phosphorylate activated G protein-coupled receptors. Faseb J 9: 175–182, 1995
Gurevich VV, Pals-Rylaarsdam R, Benovic JL, Hosey MM, Onorato JJ: Agonist-receptor-arrestin, an alternative ternary complex with high agonist affinity. J Biol Chem 272: 28849–28852, 1997
Ferguson SS, Barak LS, Zhang J, Caron MG: G-protein-coupled receptor regulation: role of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 74: 1095–1110, 1996
Sterne-Marr R, Benovic JL: Regulation of G protein-coupled receptors by receptor kinases and arrestins. Vitam Horm 51: 193–234, 1995
Koenig JA, Edwardson JM: Endocytosis and recycling of G protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 18: 276–287, 1997
Zuker CS, Ranganathan R: The path to specificity. Science 283: 650–651, 1999
Erb L, Lustig KD, Sullivan DM, Turner JT, Weisman GA: Functional expression and photoaffinity labeling of a cloned P2U purinergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 10449–10453, 1993
Boarder MR, Weisman GA, Turner JT, Wilkinson GF: G protein-coupled P2 purinoceptors: from molecular biology to functional responses. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16: 133–139, 1995
Santiago-Perez LI, Flores RV, Santos-Berrios C, Chorna NE, Krugh B, Garrad RC, Erb L, Weisman GA, Gonzalez FA: P2Y(2) nucleotide receptor signaling in human monocytic cells: activation, desensitization and coupling to mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Cell Physiol 187: 196–208, 2001
Parr CE, Sullivan DM, Paradiso AM, Lazarowski ER, Burch LH, Olsen JC, Erb L, Weisman GA, Boucher RC, Turner JT: Cloning and expression of a human P2U nucleotide receptor, a target for cystic fibrosis pharmacotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 3275–3279, 1994
Nguyen T, Erb L, Weisman GA, Marchese A, Heng HH, Garrad RC, George SR, Turner JT, O'Dowd BF: Cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of the human uridine nucleotide receptor gene. J Biol Chem 270: 30845–30848, 1995
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY: A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260: 3440–3450, 1985
Freedman NJ, Liggett SB, Drachman DE, Pei G, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ: Phosphorylation and desensitization of the human β 1-adrenergic receptor. Involvement of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 270: 17953–17961, 1995
Holloway AC, Qian H, Pipolo L, Ziogas J, Miura S, Karnik S, Southwell BR, Lew MJ, Thomas WG: Side-chain substitutions within angiotensin II reveal different requirements for signaling, internalization, and phosphorylation of type 1A angiotensin receptors. Mol Pharmacol 61: 768–777, 2002
Seibold A, January BG, Friedman J, Hipkin RW, Clark RB: Desensitization of β2-adrenergic receptors with mutations of the proposed G protein-coupled receptor kinase phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem 273: 7637–7642, 1998
Mellor H, Parker PJ: The extended protein kinase C superfamily. Biochem J 332(Pt 2): 281–292, 1998
Weisman GA, Gonzalez FA, Erb L, Garrad RC, Turner JT: The cloning and expression of G protein-coupled P2Y nucleotide receptors. In: J.S. Fedan (ed). The P2 Nucleotide Receptors. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, 1998, pp 63–79
Turner JT, Weisman GA, Fedan JS: The P2 Nucleotide Receptors, 1998
Lefkowitz RJ: G protein-coupled receptors. III. New roles for receptor kinases and β-arrestins in receptor signaling and desensitization. J Biol Chem 273: 18677–18680, 1998
von Zastrow M, Kobilka BK: Ligand-regulated internalization and recycling of human β 2-adrenergic receptors between the plasma membrane and endosomes containing transferrin receptors. J Biol Chem 267: 3530–3538, 1992
Lattion AL, Diviani D, Cotecchia S: Truncation of the receptor carboxyl terminus impairs agonist-dependent phosphorylation and desensitization of the α 1B-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem 269: 22887–22893, 1994
Huang Z, Chen Y, Nissenson RA: The cytoplasmic tail of the G-protein-coupled receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related protein contains positive and negative signals for endocytosis. J Biol Chem 270: 151–156, 1995
Thomas WG, Thekkumkara TJ, Motel TJ, Baker KM: Stable expression of a truncated AT1A receptor in CHO-K1 cells. The carboxyl-terminal region directs agonist-induced internalization but not receptor signaling or desensitization. J Biol Chem 270: 207–213, 1995
Chabry J, Botto JM, Nouel D, Beaudet A, Vincent JP, Mazella J: Thr-422 and Tyr-424 residues in the carboxyl terminus are critical for the internalization of the rat neurotensin receptor. J Biol Chem 270: 2439–2442, 1995
Litosch I: Novel mechanisms for feedback regulation of phospholipase C-β activity. IUBMB Life 54: 253–260, 2002
Sato M, Moroi K, Nishiyama M, Zhou J, Usui H, Kasuya Y, Fukuda M, Kohara Y, Komuro I, Kimura S: Characterization of a novel C. elegans RGS protein with a C2 domain: evidence for direct association between C2 domain and Galphaq subunit. Life Sci 73: 917–932, 2003
Cunningham ML, Waldo GL, Hollinger S, Hepler JR, Harden TK: Protein kinase C phosphorylates RGS2 and modulates its capacity for negative regulation of Galpha 11 signaling. J Biol Chem 276: 5438–5444, 2001
Krasel C, Dammeier S, Winstel R, Brockmann J, Mischak H, Lohse MJ: Phosphorylation of GRK2 by protein kinase C abolishes its inhibition by calmodulin. J Biol Chem 276: 1911–1915, 2001
Lorenz K, Lohse MJ, Quitterer U: Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to GRK-2. Nature 426: 574–579, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flores, R.V., Hernández-Pérez, M.G., Aquino, E. et al. Agonist-induced phosphorylation and desensitization of the P2Y2 nucleotide receptor. Mol Cell Biochem 280, 35–45 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-8050-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-8050-5