Abstract
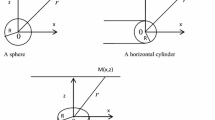
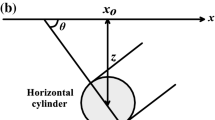
This paper introduces a practical approach to interpret magnetic anomalies related to simple geometric-shaped models such as thin dike and horizontal cylinder. This approach is mainly based on both the deconvolution technique and on the simplex algorithm for linear programming to best-estimate the model parameters, for example the depth to the top or to the center of a buried structure, the effective magnetization angle and the amplitude coefficient from magnetic anomaly profile. This approach has been tested first on synthetic data sets corrupted by different white Gaussian random noise levels to demonstrate the capability and the reliability of the method. The results acquired show that the estimated parameter values derived by this approach are close to the assumed true values of parameters. The validity of this approach is also demonstrated using real field magnetic anomalies from the United States and Brazil. A comparable and acceptable agreement is shown between the results derived by this approach and those from the real field data information.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman EM (1994) A rapid approach to depth determination from magnetic anomalies due to simple geometrical bodies. J Univ Kuwait (Sci) 21:109–115
Abdelrahman EM, Sharafeldin SM (1996) An iterative least-squares approach to depth determination from residual magnetic anomalies due to thin dikes. Appl Geophys 34:213–220
Atchuta Rao D, Ram Babu HV, Sankar Narayan PV (1980) Relationship of magnetic anomalies due to subsurface features and interpretation of solving contacts. Geophysics 45:32–36
Bhattacharyya BK (1965) Two-dimensional harmonic analysis as a tool for magnetic interpretation. Geophysics 30:829–857
Bradley SP, Hax AC, Magnanti TL (1977) Applied mathematical programming. Addison-Wesley publishing company, New York
Collins G W (2003) Fundamental numerical methods and data analysis. Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland
Gay SP (1963) Standard curves for the interpretation of magnetic anomalies over long tabular bodies. Geophysics 28:161–200
Gay SP (1965) Standard curves for the interpretation of magnetic anomalies over long horizontal cylinders. Geophysics 30:818–828
Gokturkler G, Balkaya C (2012) Inversion of self-potential anomalies caused by simple geometry bodies using global optimization algorithms. J Geophys Eng 9:498–507
Grant RS, West GF (1965) Interpretation theory in applied geophysics. McGraw-Hill Book Co, New York
Hartiman RR, Tesky DJ, Friedberg JL (1971) A system for rapid digital aeromagnetic interpretation. Geophysics 36:891–918
Hillier F, Lieberman GJ (1986) Introduction to operations research. Holden-Day Inc., Geelong
Jain SE (1976) An automatic method of direct interpretation of magnetic models. Geophysics 41:531
Ku CC, Sharp JA (1983) Werner deconvolution for automated magnetic interpretation and its refinement using Marquardt’s inverse modelling. Geophysics 48:754–774
McGrath H (1970) The dipping dike case: a computer curve-matching method of magnetic interpretation. Geophysics 35(5):831
McGrath PH, Hood PJ (1973) An automatic least-squares multimodel method for magnetic interpretation. Geophysics 38(2):349–358
Mehanee S (2014a) An efficient regularized inversion approach for self-potential data interpretation of ore exploration using a mix of logarithmic and non-logarithmic model parameters. Ore Geol Rev 57:87– 115
Mehanee S (2014b) Accurate and efficient regularized inversion approach for the interpretation of isolated gravity anomalies. Pure Appl Geophys (in press)
Mohan NL, Sundararajan N, Seshagiri Rao SV (1982) Interpretation of some two-dimensional magnetic bodies using Hilbert transforms. Geophysics 46:376–387
Nabighian MN, Hansen RO (2001) Unification of Euler and Werner deconvolution in three dimensions via the generalized Hilbert transform. Geophysics 66:1805–1810
Phillips DT, Ravindra A, Solber JJ (1976) Operations research. Wiley, New York
Prakasa Rao TKS, Subrahmanyan M, Srikrishna Murthy A (1986) Nomograms for direct interpretation of magnetic anomalies due to long horizontal cylinders. Geophysics 51:2150–2159
Salem A, Ravat D (2003) A combined analytic signal and Euler method (AN-EUL) for automatic interpretation of magnetic data. Geophysics 68(6):1952–1961
Salem A, Ravat D, Martin FM, Ushijima K (2004) Linearized least-squares method for interpretation of potential-field data from sources of simple geometry. Geophysics 69(3):783–788
Salem A (2005) Interpretation of magnetic data using analytic signal derivatives. Geophys Prospect 53:75–82
Salem A, Smith R (2005) Depth and structural index from normalized local wavenumber of 2D magnetic anomalies. Geophys Prospect 53:83–89
Silva JBC (1989) Transformation of nonlinear problems into linear ones applied to the magnetic field of a two-dimensional prism. Geophysics 54:114–121
Tlas M, Asfahani J (2011a) Fair function minimization for interpretation of magnetic anomalies due to thin dikes, spheres and faults. J Appl Geophys 75:237–243
Tlas M, Asfahani J (2011b) A new-best-estimate methodology for determining magnetic parameters related to field anomalies produced by buried thin dikes and horizontal cylinder-like structures. Pure Appl Geophys 168:861–870
Werner S (1953) Interpretation of magnetic anomalies at sheet-like bodies. Sveriges Geologiska Undersok Ser C Arsbok 43, No. 6
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. I. Othman Director General of the Syrian Atomic Energy Commission for his continuous encouragement and guidance to achieve this research. Special thanks to the anonymous reviewers and to the Prof. Colin Farquharson for the reviewing of this paper and for their constructive suggestions and critical remarks, which considerably enhance the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tlas, M., Asfahani, J. The Simplex Algorithm for Best-Estimate of Magnetic Parameters Related to Simple Geometric-Shaped Structures. Math Geosci 47, 301–316 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-014-9549-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-014-9549-7