Abstract
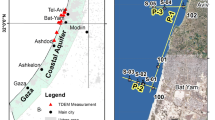
The effects of the ocean coast on magnetotelluric (MT) data have been studied and results are described in this article. MT soundings from various sites along coastal plains of Kachchh were acquired where volcanic rocks overlie Mesozoic sediments having potential resource prospects. The region of our study lies in the proximity of Gulf of Kachchh and Arabian Sea. This article describes the effects the presence of a conductive body on the acquired MT data. With the help of synthetic MT modelling and induction arrows we demonstrate the influence of shallow conductive body on the MT data. The modelling results when compared to the field observations show that much of the high frequencies are unaffected by the coast, however low frequencies of the data do seem to be distorted by onshore–offshore resistivity contrasts. The least affect on high frequencies can be attributed to very shallow water depth as well as to the fact that the onshore–offshore resistivity contrasts are not large enough to influence the high frequency data badly. The results presented here report for the first time the effect of the coast on the analysis on MT data from Kachchh. Due to several academic as well as industrial onshore–offshore MT experiments presently being carried out to explore its hydrocarbon potential, our results have an important bearing on designing and acquisition of future MT surveys in this region.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahr K (1991) Geological noise in magnetotelluric data: a classification of distortion types. Phys Earth Planet Sci Inter 60:24–38
Beamish D, Clark TDG, Clarke E, Thomson AWP (2002) Geomagnetically induced currents in the UK: geomagnetic variations and surface electric fields. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 64:1779–1792
Bilham R, Bendick R, Wallace K (2003) Flexture of the Indian plate and intraplate earthquakes. Earth Planet Sci 112:315–329
Biswas SK (1982) Rift basins in western margin of India and their hydrocarbon prospects with special reference to Kutch basin. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 66(10):1497–1513
Biswas SK (1987) Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of the western marginal basins of India. Tectonophysics 135(4):307–327
Bodin P, Horton S (2004) Source parameters and tectonic implications of aftershocks of the Mw 7.6 Bhuj earthquake of 26 January 2001. Bull Geol Soc Am 94:818–827
Dosso HW, Meng ZW (1992) The coast effect response in geomagnetic field measurements. Phys Earth Planet Sci Inter 70:39–56
Groom RW, Bailey RC (1989) Decomposition of magnetotelluric impedance tensors in the presence of local three-dimensional galvanic distortion. J Geophys Res 94(B2):1913–1925
Gupta HK, Harinarayana T, Kousalya M, Mishra DC, Mohan I, Puranachandra Rao N, Raju PS, Rastogi BK, Reddy PR, Sarkar D (2001) Bhuj Earthquake of 26th January, 2001. J Geol Soc India 57:275–278
Mandal P (2006) Sedimentary and crustal structure beneath Kachchh and Saurashtra regions, Gujrat, India. Phys Earth Planet Inter 155:286–299
Mandal P, Johnston A (2006) Estimation of source parameters for the aftershocks of 2001 Mw 7.7 Bhuj earthquake, India. Pure Appl Geophys 163:1537–1560
Menvielle M, Rossignol JC, Tarits P (1982) The coast effect in terms of deviated electric currents: A numerical study. Phys Earth Planet Sci Inter 28:118–128
Mishra DC, Chandrasekhar DV, Singh B (2005). Tectonics and crustal structures related to Bhuj earthquake of January 26, 2001: based on gravity and magnetic surveys constrained from seismic and seismological studies. Tectonophysics 396:195–207
Parkinson W (1959) Directions of rapid geomagnetic fluctuations. Geophys J Royal Astron Soc 2:1–13
Pandey DK (2003) Analyses of seismic and magnetotelluric data from Kutch, India. PhD thesis, University of Cambridge
Padilha A, Vitorello I, Brito P (2002) Magnetotelluric soundings across the Taubate basin, southeast Brazil. Earth Planets Space 54:617–627
Raval U, Weaver J, Dawson T (1981) The ocean-coast effect reexamined. Geophys J Royal Astron Soc 67:115–123
Santos FAM, Nolasco M, Almeida EP, Pous J, Mendes-Victor LA (2001) Coast effects on magnetic and magnetotelluric transfer functions and their correction: application to MT soundings carried out in SW Iberia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 186:283–295
Wannamaker PE, Stodt JA, Rijo L (1987) A stable finite element solution for two-dimensional magnetotelluric modelling. Geophys J Royal Astron Soc 88:277–296
Acknowledgements
The authors thank ONGC India for providing the data as a part of LITHOS consortium at University of Cambridge. DP is grateful to Cambridge Commonwealth Trust, Schlumberger Cambridge Research and Darwin College, Cambridge for financial support towards his research. Comments by anonymous reviewers helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, D., Sinha, M., MacGregor, L. et al. Ocean coast effect on magnetotelluric data: a case study from Kachchh, India. Mar Geophys Res 29, 185–193 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-008-9057-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-008-9057-6