Abstract
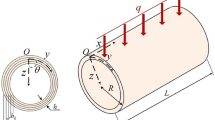
The present article deals with the design of optimal vibration control of smart fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composite shell structures using genetic algorithm (GA) based linear quadratic regulator (LQR) and layered shell coupled electro-mechanical finite element analysis. Open loop procedure has been used for optimal placement of actuators considering the control spillover of the higher modes to prevent closed loop instability. An improved real coded GA based LQR control scheme has been developed for designing an optimal controller in order to maximize the closed loop damping ratio while keeping actuators voltages within limit. Results show that increased closed loop-damping has been achieved with a large reduction of control effort considering control spillover.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, M.M., Richardson, A., Hanif, J.: Placement of sensors/actuators on civil structures using genetic algorithms. Earthquake Eng. Struct. Dynam. 30(8), 1167–1184 (2001). doi:10.1002/eqe.57
Ahamad, S., Irons, B.M., Zienkiewicz, O.C.: Analysis of thick and thin shell structure by curved elements. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 2, 419–451 (1970). doi:10.1002/nme.1620020310
Ang, K.K., Wang, S.Y., Quek, S.T.: Weighted energy linear quadratic regulator vibration control of piezoelectric composite plates. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 11, 98–106 (2002). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/11/1/311
Bailey, T., Hubbard, J.E.: Distributed piezoelectric polymer active vibration control of a cantilever beam. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 85, 605–611 (1985). doi:10.2514/3.20029
Balagurugan, V., Narayanan, S.: Active vibration control of smart shells using distributed piezoelectric sensors and actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 10, 173–180 (2001). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/10/2/301
Balagurugan, V., Narayanan, S.: A piezoelectric higher-order plate finite for the analysis of multi-layer smart composite laminates. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 2026–2039 (2007). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/16/6/005
Balagurugan, V., Narayanan, S.: A piezolaminated composite degenerated shell finite element for active control of structures with distributed piezosensors and actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 015031 (18 pp) (2008)
Bhattacharya, P., Suhail, H., Sinha, P.K.: Finite element analysis and distributed control of laminated composite shells using LQR/IMSC approach. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 6, 273–281 (2002). doi:10.1016/S1270-9638(02)01159-8
Bruch, J.C., Sloss, J.M., Sadek, I.S.: Optimal piezo-actuator locations/lengths and applied voltage for shape control of beams. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 9, 205–211 (2002)
Chee, C.Y.K., Tong, L., Steven, G.P.: A mixed model for composite beams with piezoelectric actuators and sensors. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 8, 417–432 (1999). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/8/3/313
Chen, S.H., Yao, G.F., Huang, C.: A new intelligent thin shell element. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 9, 10–18 (2000). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/9/1/302
Christensen, R.H., Santos, I.F.: Design of active controlled rotor-blade systems based on time-variant modal analysis. J. Sound Vibrat. 280, 863–882 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2003.12.046
Crawley, E.F., Luis, J.: Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 25(10), 1373–1385 (1987). doi:10.2514/3.9792
Deb, K., Gulati, S.: Design of truss-structures for minimum weight using genetic algorithms. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 37, 447–465 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0168-874X(00)00057-3
Guo, H.Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, L.L., Zhou, J.X.: Optimal placement of sensors for structural health monitoring using improved genetic algorithm. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 528–534 (2004). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/13/3/011
Han, J.H., Lee, L.: Optimal placement of piezoelectric sensors and actuators for vibration control of a composite plate using genetic algorithms. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 8, 257–267 (1999). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/8/2/012
Hiramoto, K., Doki, H., Obinata, G.: Optimal sensor/actuator placement for active vibration control using explicit solution of algebraic Riccati equation. J. Sound Vibrat. 229(5), 1057–1075 (2000). doi:10.1006/jsvi.1999.2530
Hwang, W.S., Park, H.C.: Finite element modeling of piezoelectric sensors and actuators. AIAA J. 31(5), 930–937 (1993). doi:10.2514/3.11707
Kang, Y.K., Park, H.C., Kim, J., Choi, S.B.: Interaction of active and passive vibration control of laminated composite beams with piezoceramics sensors/actuators. Mater. Des. 23, 277–286 (2002)
Kulkarni, S.A., Bajoria, K.M.: Finite element modeling of smart plates/shells using higher order shear deformation theory. Compos. Struct. 62, 41–50 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0263-8223(03)00082-5
Kusculuoglu, Z.K., Royston, T.J.: Finite element formulation for composite plates with piezoelectric layers for optimal vibration control applications. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 14, 1139–1153 (2005). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/14/6/007
Lee, C.K.: Theory of laminated piezoelectric plates for the design of distributed sensors/actuators Part 1: governing equations and reciprocal relationships. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87(3), 1144–1158 (1990). doi:10.1121/1.398788
Lee, S., Goo, N.S., Park, H.C., Yoon, K.J., Cho, C.: A nine- node assumed strain shell element for analysis of a coupled electro-mechanical system. Smart Mater. Struct. 12, 355–362 (2003). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/12/3/306
Lewis, F.L.: Optimal control. Wiley, New York (1986)
Li, Q.S., Liu, D.K., Tang, J., Zhang, N., Tam, C.M.: Combinatorial optimal design of number and positions of actuators in actively controlled structures using genetic algorithm. J. Sound Vibrat. 270, 611–624 (2004). doi:10.1016/S0022-460X(03)00130-5
Liu, W., Hou, Z.K., Demetriou, M.A.: A computational scheme for the optimal sensor/actuator placement of flexible structures using spatial H-2 measures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 20(4), 881–895 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.08.030
Marinković, D., Köppe, H., Gabbert, U.: Degenerate shell element for geometrically nonlinear analysis of thin-walled piezoelectric active structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 015030 (10 pp) (2008)
Narayanan, S., Balamurugan, V.: Finite element modeling of piezolaminated smart structures for active vibration control with distributed sensors and actuators. J. Sound Vibrat. 262, 529–562 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0022-460X(03)00110-X
Nguyen, Q., Tong, L.: Voltage and evolutionary piezoelectric actuator design optimisation for static shape control of smart plate structures. Mater. Des. 28, 387–399 (2007)
Ram, K.S.S., Kiran, S.K.: Static behavior of laminated composite spherical shell cap with piezoelectric actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 015010 (9 pp) (2008)
Ray, M.C., Bhattacharyya, R., Samanta, B.: Static analysis of intelligent structure by the finite element method. Comput. Struc. 52(4), 617–631 (1994). doi:10.1016/0045-7949(94)90344-1
Reddy, J.N.: Exact solution of moderately thick laminated shells. J. Eng. Mech. 110(5), 794–809 (1984)
Robandi, I., Nishimori, K., Nishimura, R., Ishihara, N.: Optimal feedback control design using genetic algorithm in multimachine power system. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 23, 263–271 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0142-0615(00)00062-4
Roy, T., Chakraborty, D.: GA-LQR based optimal vibration control of smart FRP composite structures with bonded PZT patches. J. Reinforced Plastics Composites (2008). doi:10.1177/0731684408089506
Sadri, A.M., Wright, J.R., Wynne, R.: Modeling and optimal placement of piezoelectric actuators in isotropic plates using genetic algorithm. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 8, 490–498 (1999). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/8/4/306
Saravanos, D.A., Christoforou, A.P.: Impact response of adaptive piezoelectric laminated plates. AIAA J. 40(10), 2087–2095 (2002)
Swann, C., Chattopadhyay, A.: Optimization of piezoelectric sensor location for delamination detection in composite laminates. Eng. Optim. 38(5), 511–528 (2006). doi:10.1080/03052150600557841
Tzou, H.S., Tsang, C.I.: Distributed piezoelectric sensor/actuator design for dynamic measurement/control of distributed parameter systems: a finite element approach. J. Sound Vibrat. 138(1), 17–24 (1990). doi:10.1016/0022-460X(90)90701-Z
Tzou, H.S., Ye, R.: Analysis of piezoelectric structures with laminated piezoelectric triangle shell elements. AIAA J. 34, 110–115 (1996). doi:10.2514/3.12907
Wan, J.G., Tao, B.Q.: Design and study on a 1-3 anisotropy piezocomposite sensor. Mater. Des. 21, 533–536 (2000)
Wang, Q., Wang, C.: A controllability index for optimal design of piezoelectric actuators in vibration control of beam structures. J. Sound Vibrat. 242(3), 507–518 (2001). doi:10.1006/jsvi.2000.3357
Wang, S.Y., Tai, K., Quek, S.T.: Topology optimization of piezoelectric sensors/actuators for torsional vibration control of composite plates. J. Smart Mater. Struct. 15(2), 253–269 (2006)
Yang, Y., Jin, Z., Soh, C.K.: Integrated optimal design of vibration control system for smart beams using genetic algorithm. J. Sound Vibrat. 282, 1293–1307 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2004.03.048
Zhang, N., Kirpitchenko, I.: Modelling dynamics of a continuous structure with a piezoelectric sensor/actuator for passive structural control. J. Sound Vibrat. 249(2), 251–261 (2002). doi:10.1006/jsvi.2001.3792
Zheng, S., Wang, X., Chen, W.: The formulation of refined hybrid enhanced assumed strain solid shell element and its application to model smart structures containing distributed piezoelectric sensors/actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 13(43-N), 50 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, T., Chakraborty, D. Genetic algorithm based optimal design for vibration control of composite shell structures using piezoelectric sensors and actuators. Int J Mech Mater Des 5, 45–60 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-008-9085-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-008-9085-z