Abstract
Objectives
Cigarettes, alcoholic beverages, and street drugs contain substances potentially toxic to the developing embryo. We investigated whether maternal cigarette smoking, secondhand smoke exposure, and alcohol or street drug use contributed to neural tube defect (NTD) occurrence in offspring.
Methods
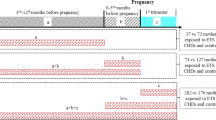
We conducted a population-based case-control study among Mexican American women who were residents of the 14 Texas counties bordering Mexico. Case women had an NTD-affected pregnancy and delivered during 1995–2000. Control women were those who delivered live born infants in the same study area, without an apparent congenital malformation, randomly selected by year and facility. We interviewed women in person, 1–3 months postpartum, to solicit relevant information.
Results
Nonsmoking mothers exposed to secondhand smoke during the first trimester had an NTD odds ratio (OR) of 2.6 (95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.6, 4.0) compared to those who neither smoked nor were exposed to secondhand smoke. Compared to the referent, the OR among women who smoked less than half a pack a day during the first trimester was 2.2 (95% CI = 1.0, 4.8) and 3.4 (95% CI = 1.2, 10.0) among those who smoked a half pack or more. Adjustment for maternal age, education, body mass index, and folate intake had a negligible effect on results. Alcohol and street drug use had no relation to NTD risk when adjusted for cigarette smoking.
Conclusions
This study suggests that cigarette smoke including secondhand exposure is not only hazardous to the mother but may also interfere with neural tube closure in the developing embryo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oakley, G. P., Bell, K. N., & Weber, M. B. (2004). Recommendations for accelerating global action to prevent folic acid-preventable birth defects and other folate-deficiency diseases: Meeting of experts on preventing folic acid-preventable neural tube defects. Birth Defects Research Part A Clinical and Molecular Teratology, 70, 835–837.
Ray, J. G., & Blom, H. J. (2003). Vitamin B12 insufficiency and the risk of fetal neural tube defects. QJM, 96, 289–295.
Suarez, L., Hendricks, K., Felkner, M., & Gunter, E. (2003). Maternal serum B12 levels and risk for neural tube defects in a Texas–Mexico border population. Annals of Epidemiology, 13, 81–88.
Moretti, M. E., Bar-Oz, B., Fried, S., & Koren, G. (2005). Maternal hyperthermia and the risk for neural tube defects in offspring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology, 16, 216–219.
Suarez, L., Felkner, M., & Hendricks, K. (2004). The effect of fever, febrile illnesses, and heat exposures on the risk of neural tube defects in a Texas–Mexico border population. Birth Defects Research Part A Clinical and Molecular Teratology, 70, 815–819.
Felkner, M., Hendricks, K., Suarez, L., & Waller, D. K. (2003). Diarrhea: A new risk factor for neural tube defects? Birth Defects Research Part A Clinical and Molecular Teratology, 67, 504–508.
Missmer, S. A., Suarez, L., Felkner, M., Wang, E., Merrill, A. H., Rothman, K. J., & Hendricks, K. A. (2006). Exposure to fumonisins and the occurrence of neural tube defects along the Texas–Mexico border. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114, 237–241.
Webster, W. S., & Messerle, K. (1980). Changes in the mouse neuroepithelium associated with cadmium-induced neural tube defects. Teratology, 21, 79–88.
Fernandez, E. L., Svenson, C., Dencker, L., & Gustafson, A. L. (2004). Disturbing endoderm signaling to anterior neural plate of vertebrates by the teratogen cadmium. Reproductive Toxicology, 18, 653–660.
Zhao, Z., & Reece, E. A. (2005). Nicotine-induced embryonic malformations mediated by apoptosis from increasing intracellular calcium and oxidative stress. Birth Defects Research Part B Clinical and Molecular Teratology, 74, 383–391.
Alexander, P. G., & Tuan R. S. (2003). Carbon monoxide-induced axial skeletal dysmorphogenesis in the chick embryo. Birth Defects Research Part A Clinical and Molecular Teratology, 67, 219–230.
Kelsey, J. L., Dwyer, T., Holford, T. R., & Bracken, M. B. (1978). Maternal smoking and congenital malformations: An epidemiological study. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 32, 102–107.
Ericson, A., Kallen, B., & Westerholm, P. (1979). Cigarette smoking as an etiologic factor in cleft lip and palate. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 135, 348–351.
Evans, D. R., Newcombe, R. G., & Campbell, H. (1979). Maternal smoking habits and congenital malformations: A population study. British Medical Journal, 2, 171–173.
Seidman, D. S., Ever-Hadani, P., & Gale, R. (1990). Effect of maternal smoking and age on congenital anomalies. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 76, 1046–1050.
Christianson, R. E. (1980). The relationship between maternal smoking and the incidence of congenital anomalies. American Journal of Epidemiology, 112, 684–695.
Hemminki, K., Mutanen, P., & Saloniemi, I. (1983). Smoking and the occurrence of congenital malformations and spontaneous abortions: Multivariate analysis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 145, 61–66.
Shiono, P. H., Klebanoff, M. A., & Berendes, H. W. (1986). Congenital malformations and maternal smoking during pregnancy. Teratology, 34, 65–71.
Malloy, M. H., Kleinman, J. C., Bakewell, J. M., Schramm, W. F., & Land, G. H. (1989). Maternal smoking during pregnancy: No association with congenital malformations in Missouri 1980–83. American Journal of Public Health, 79, 1243–1246.
Wasserman, C. R., Shaw, G. M., O’Malley, C. D., Tolarova, M. M., & Lammer, E. J. (1996). Parental cigarette smoking and risk for congenital anomalies of the heart. neural tube, or limb. Teratology, 53, 261–267.
McDonald, A. D., Armstrong, B. G., & Sloan, M. (1992). Cigarette, alcohol, and coffee consumption and congenital defects. American Journal of Public Health, 82, 91–93.
Shaw, G. M., Velie, E. M., & Morland, K. B. (1996). Parental recreational drug use and risk for neural tube defects. American Journal of Epidemiology, 144, 1155–1160.
Kallen, K. (1998). Maternal smoking, body mass index, and neural tube defects. American Journal of Epidemiology, 147, 1103–1111.
Van den Eeden, S. K., Karagas, M. R., Daling, J. R., & Vaughn, T. L. (1990). A case-control study of maternal smoking and congenital malformations. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology, 4, 147–155.
Li, Z., Ren, A., Zhang, L., Guo, Z., & Li, Z. (2006). A population-based case-control study of risk factors for neural tube defects in four high-prevalence areas of Shanxi province, China. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology, 20, 43–53.
Mills, J. L., & Graubard, B. I. (1987). Is moderate drinking during pregnancy associated with an increased risk for malformations? Pediatrics, 80, 309–314.
Kronick, J. B. (1976). Teratogenic effects of ethyl alcohol administered to pregnant mice. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 124, 676–680.
Padmanabhan, R., Wasfi, I. A., & Craigmyle, M. B. L. (1994). Effect of pre-treatment with aspirin on alcohol-induced neural tube defects in the TO mouse fetuses. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 36, 175–186.
Chen, S. Y., Charness, M. E., Wilkemeyer, M. F., & Sulik, K. K. (2005). Peptide-mediated protection from ethanol-induced neural tube defects. Developmental Neuroscience, 27, 13–19.
Graham, J. M., & Ferm, V. H. (1985). Heat- and alcohol-induced neural tube defects: Interactions with folate in a golden hamster model. Pediatric Research, 19, 247–251.
Hendricks, K. A., Simpson, J. S., & Larsen, R. D. (1999). Neural tube defects along the Texas–Mexico border, 1993–1995. American Journal of Epidemiology, 149, 1119–1127.
Suarez, L., Hendricks, K. A., Cooper, S. P., Sweeney, A. M., Hardy, R. J., & Larsen, R. D. (2000). Neural tube defects among Mexican Americans living on the US–Mexico border: Effects of folic acid and dietary folate. American Journal of Epidemiology, 152, 1017–1023.
McPherson, R. S., Kohl, H. W., Garcia, G., Nichaman, M. Z., & Hanis, C. L. (1995). Food frequency questionnaire validation among Mexican Americans: Starr County, Texas. Annals of Epidemiology, 5, 378–385.
Patrick, D. L., Cheadle, A., Thompson, D. C., Diehr, P., Koepsell, T., & Kinne, S. (1994). The validity of self-reported smoking: A review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Public Health, 84, 1086–1093.
Ganji, V., & Kafai, M. R. (2003). Demographic, health, lifestyle, and blood vitamin determinants of serum total homocysteine concentrations in the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 77, 826–833.
Chrysohoou, C., Panagiotakos, D. B., Pitsavos, C., Zeimbekis, A., Papademetriou, L., Masoura, C., & Stefanadis, C. (2004). The associations between smoking, physical activity, dietary habits and plasma homocysteine levels in cardiovascular disease-free people: The ‘ATTICA’ study. Vascular Medicine, 9, 117–123.
Trobs, M., Renner, T., Scherer, G., Heller, W. D., Geiss, H. C., Wolfram, G., Haas, G. M., & Schwandt, P. (2002). Nutrition, antioxidants, and risk factor profile of nonsmokers, passive smokers and smokers of the Prevention Education Program (PEP) in Nuremberg, Germany. Preventive Medicine 34, 600–607.
Davis, J. A., Brown, A. T., Chen, H., Wang, Y., Poirier, L. A., Eidt, J. F., Cruz, C. P., & Moursi, M. M. (2004). Cigarette smoke increases intimal hyperplasia and homocysteine in a rat carotid endarterectomy. The Journal of Surgical Research, 121, 69–75.
Snow, C. F. (1999). Laboratory diagnosis of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency: A guide for the primary care physician. Archives of Internal Medicine, 159, 1289–1298.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Tejpratap Tiwari, EIS Officer, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, for his thoughtful contributions to the study during his tenure at the Texas Department of State Health Services. Funding was provided by the CDC Birth Defects Branch cooperative agreement U85/CCU608761-05 and the Texas Birth Defects Research Center/CDC cooperative agreement U50/CCU613232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suarez, L., Felkner, M., Brender, J.D. et al. Maternal Exposures to Cigarette Smoke, Alcohol, and Street Drugs and Neural Tube Defect Occurrence in Offspring. Matern Child Health J 12, 394–401 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-007-0251-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-007-0251-y