Abstract
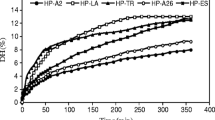
The purpose of this study was to separate and purify antioxidant peptides from the scorpion (Buthus martensii Karsch) protein hydrolysates (SPHs). Scorpion protein (SP) was first hydrolyzed by trypsin, papain, and alcalase, respectively. Results from hydrolysis tests revealed that peptides hydrolyzed with papain showed the highest degree of hydrolysis (DH), yield and antioxidant activity. The effect of papain hydrolysis on scorpion protein was optimized using the response surface methodology. The highest DH (31.31%) and yield (52.02%) of SPHs were obtained under the following conditions: hydrolysis time, 4.0 h; hydrolysis temperature, 50 °C; and enzyme/substrate ratio, 2.43%. Ultrafiltration, gel filtration and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography was used and two novel antioxidant peptides were obtained. The sequences of the peptides determined by MALDI–TOF–MS/MS were LPTETLH (MW: 810.43 Da, P4-1) and IEEDLER (MW: 903.44 Da, P4-2), respectively. The results revealed SPHs as a potential valuable bioresource for production of antioxidant peptides in the food system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal H, Joshi R, Gupta M (2017) Isolation and characterisation of enzymatic hydrolysed peptides with antioxidant activities from green tender sorghum. LWT 84:608–616
Agrawal H, Joshi R, Gupta M (2019) Purification, identification and characterization of two novel antioxidant peptides from finger millet (Eleusine coracana) protein hydrolysate. Food Res Int 120:697–707
Bing L, Aisa HA, Yili A (2018) Isolation and identification of two potential antioxidant peptides from sheep abomasum protein hydrolysates. Eur Food Res Technol 9:1–11
Chao-Zhi Z, Wan-Gang Z, Guang-Hong Z, Xing-Lian X, Zhuang-Li K, Yan Y (2013) Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides from jinhua ham. J Agric Food Chem 61(6):1265–1271
Chen Y, Xie MY, Nie SP, Li C, Wang YX (2008) Purification, composition analysis and antioxidant activity of a polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma atrum. Food Chem 107(1):231–241
Church FC, Swaisgood HE, Porter DH, Catignani GL (1983) Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J Dairy Sci 66(6):1219–1227
Díaz-García A, Morier-Díaz L, Frión-Herrera Y, Rodríguez-Sánchez H, Caballero-Lorenzo Y, Mendoza-Llanes D, Riquenes-Garlobo Y, Fraga-Castro JA (2013) In vitro anticancer effect of venom from Cuban scorpion Rhopalurus junceus against a panel of human cancer cell lines. J Venom Res 4:5–12
Escudero E, Mora L, Fraser PD, Aristoy MC, Toldrá F (2013) Identification of novel antioxidant peptides generated in Spanish dry-cured ham. Food Chem 138(2–3):1282–1288
Fan H, Wang J, Liao W, Jiang X, Wu J (2019) Identification and characterization of gastrointestinal-resistant angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from egg white proteins. J Agric Food Chem 67(25):7147–7156
Goudet C, Chi CW, Tytgat J (2002) An overview of toxins and genes from the venom of the Asian scorpion Buthus martensi Karsch. Toxicon 40(9):1239–1258
Guo X, Ma C, Du Q, Wei R, Wang L, Zhou M, Chen T, Shaw C (2013) Two peptides, TsAP-1 and TsAP-2, from the venom of the Brazilian yellow scorpion, Tityus serrulatus: evaluation of their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Biochimie 95(9):1784–1794
Guo Z, Liu H, Chen X, Xia J, Li P (2006) Hydroxyl radicals scavenging activity of N-substituted chitosan and quaternized chitosan. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16(24):6348–6350
Ha M, Bekhit Ael D, Carne A, Hopkins DL (2013) Characterisation of kiwifruit and asparagus enzyme extracts, and their; activities toward meat proteins. Food Chem 136(2):989–998
Harnedy PA, O'Keeffe MB, FitzGerald RJ (2017) Fractionation and identification of antioxidant peptides from an enzymatically hydrolysed Palmaria palmata protein isolate. Food Res Int 100:416–422
He Y, Zhao R, Di Z, Li Z, Xu X, Wei H, Wu Y, Zhao H, Li W, Cao Z (2013) Molecular diversity of Chaerilidae venom peptides reveals the dynamic evolution of scorpion venom components from Buthidae to non-Buthidae. J Proteom 89(16):1–14
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Lin XS, Wen Q, Huang ZL, Cai YZ, Halling PJ, Yang Z (2015) Impacts of ionic liquids on enzymatic synthesis of glucose laurate and optimization with superior productivity by response surface methodology. Process Biochem 50(11):1852–1858
Liu J, Huang Y, Tian Y, Nie S, Xie J (2013) Purification and identification of novel antioxidative peptide released; from Black-bone silky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus Brisson). Eur Food Res Technol 237(2):253–263
Marcuse R (1960) Antioxidative effect of amino-acids. Nature 186(4728):886–887
Nielsen PM, Petersen D, Dambmann C (2010) Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. J Food Sci 66(5):642–646
Oun Ki C, Go Eun H, Gi-Sung H, Kuk-Hwan S, Hyoun Wook K, Seok-Geun J, Mi-Hwa O, Beom-Young P, Jun-Sang H (2013) Novel antioxidant peptide derived from the ultrafiltrate of ovomucin hydrolysate. J Agric Food Chem 61(30):7294–7300
Pan X, Zhao YQ, Hu FY, Wang B (2016) Preparation and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skate (Raja porosa) cartilage. J Funct Foods 25:220–230
Rajapakse N, Mendis E, Jung WK, Je JY, Kim SK (2005) Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res Int 38(2):175–182
Ranathunga S, Rajapakse N, Kim SK (2006) Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptide derived from muscle of conger eel (Conger myriaster). Eur Food Res Technol 222(3–4):310–315
Salami M, Yousefi R, Ehsani MR, Razavi SH, Chobert JM, Haertlé T, Saboury AA, Atri MS, Niasari-Naslaji A, Ahmad F (2009) Enzymatic digestion and antioxidant activity of the native and molten globule states of camel α-lactalbumin: possible significance for use in infant formula. Int Dairy J 19(9):518–523
Shi L, Zhang T, Congying DU, Yuan R, Wang C, Feng LI (2015) Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of scorpio. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med 4:31
Shubho DG, Anindita D, Archita S, Biplab G, Gayatri T, Joseph Rajan V, Antony G, Aparna G (2007) Indian black scorpion (Heterometrus bengalensis Koch) venom induced antiproliferative and apoptogenic activity against human leukemic cell lines U937 and K562. Leuk Res 31(6):817–825
Song JJ, Wang Q, Du M, Ji XM, Mao XY (2017) Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from mare whey protein hydrolysates. J Dairy Sci 100(9):6885–6894
Tanyildizi MS, Elibol OM (2005) Optimization of α-amylase production by Bacillus sp. using response surface methodology. Process Biochem 40(7):2291–2296
Tovar-Pérez EG, Guerrero-Becerra L, Lugo-Cervantes E (2017) Antioxidant activity of hydrolysates and peptide fractions of glutelin from cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) seed. Cyta J Food 15(1):489–496
Yang R, Li X, Lin S, Zhang Z, Chen F (2017) Identification of novel peptides from 3 to 10 kDa pine nut (Pinus koraiensis) meal protein, with an exploration of the relationship between their antioxidant activities and secondary structure. Food Chem 219:311–320
Yangying S, Daodong P, Yuxing G, Junjiang L (2012) Purification of chicken breast protein hydrolysate and analysis of its antioxidant activity. Food Chem Toxicol 50(10):3397–3404
Yao R, Hui W, Lai F, Yang M, Li X, Tang Y (2014) Isolation and identification of a novel anticoagulant peptide from enzymatic hydrolysates of scorpion (Buthus martensii Karsch) protein. Food Res Int 64:931–938
Zhang Q, Tong X, Li Y (2019) Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean (Glycine max L.) hydrolysate and their cytoprotective effects in human intestinal Caco-2. CELLS. 67 (20), 5772–5781.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2017ZX09301045), and we thank Central Asian Drug Research and Development Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Informed Consent
The article does not contain any studies in patients by any of the authors.
Research Involving Human and Animals Participants
This article does not contain any studies involved with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wali, A., Wubulikasimu, A., yanhua, G. et al. Separation and Purification of Antioxidant Peptides from Enzymatically Prepared Scorpion (Buthus martensii Karsch) Protein Hydrolysates. Int J Pept Res Ther 26, 1803–1818 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-09976-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-09976-3