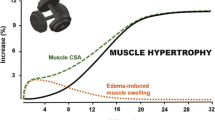
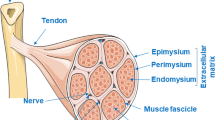
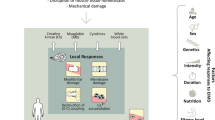
Abstract
MMP-14 (also known as MT1-MMP) is a membrane-bound collagenase and member of the Matrix Metalloprotease (MMP) family known to target a broad range of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. Remodelling of the ECM is of particular importance following skeletal muscle injury involving myofiber necrosis, when satellite cells are activated to facilitate myogenesis and regeneration. Myogenesis (broadly encompassed by the processes of satellite cell activation, proliferation, migration, differentiation and fusion) requires the myoblast to move either on or through a changing milieu of ECM components. The ECM composition, and especially the degree of fibrosis, influences ability of satellite cells to mediate a successful regenerative program. As a result, MMP activity is central to this regeneration; its activity increases following skeletal muscle injury, while inhibition of MMP reduces regeneration in this tissue. Besides its direct effect on matrix invasion, MMP-14 itself can affect this regeneration via activation of other MMPs (MMP-2, -9 and -13) as well as cytokines, chemokines and growth factors. Indeed recent research suggests that MMP-14 is necessary for the migration of human myoblasts into a collagen I matrix. Here we provide a current review on MMP-14 in the context of its role as a critical mediator of skeletal muscle regeneration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari AS, Chai J, Dunn AR (2011) Mechanical load induces a 100-fold increase in the rate of collagen proteolysis by MMP-1. J Am Chem Soc 133:1686–1689
Alameddine HS (2012) Matrix metalloproteinases in skeletal muscles: friends or foes? Neurobiol Dis 48:508–518
Anilkumar N, Uekita T, Couchman JR, Nagase H, Seiki M, Itoh Y (2005) Palmitoylation at Cys574 is essential for MT1-MMP to promote cell migration. FASEB J 19:1326–1328
Baoge L, Van Den Steen E, Rimbaut S, Philips N, Witvrouw E, Almqvist KF, Vanderstraeten G, Vanden Bossche LC (2012) Treatment of skeletal muscle injury: a review. ISRN Orthopedics 1–7
Barnes BR, Szelenyi ER, Warren GL, Urso ML (2009) Alterations in mRNA and protein levels of metalloproteinases-2, -9, and -14 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 responses to traumatic skeletal muscle injury. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:C1501–C1508
Bentzinger CF, Wang YX, Rudnicki MA (2012) Building muscle: molecular regulation of myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4:a008342
Bröhl D, Vasyutina E, Czajkowski MT, Griger J, Rassek C, Rahn HP, Purfürst B, Wende H, Birchmeier C (2012) Colonization of the satellite cell niche by skeletal muscle progenitor cells depends on Notch signals. Dev Cell 23:469–481
Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, Daubas P, Hadchouel J, Meilhac S, Montarras D, Rocancourt D, Relaix F (2003) The formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb. J Anat 202:59–68
Cao J, Rehemtulla A, Bahou W, Zucker S (1996) Membrane type matrix metalloproteinase 1 activates pro-gelatinase a without furin cleavage of the N-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 271:30174–30180
Carmeli E, Moas M, Reznick AZ, Coleman R (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases and skeletal muscle: a brief review. Muscle Nerve 29:191–197
Cavallo-Medved D, Ruby D, Blum G, Bogyo M, Caglic D, Sloane BF (2009) Live-cell imaging demonstrates extracellular matrix degradation in association with active cathepsin B in caveolae of endothelial cells during tube formation. Exp Cell Res 315:1234–1246
Charge SBP, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84:209–238
Charrin S, Latil M, Soave S, Polesskaya A, Chrétien F, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E (2013) Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81. Nat Commun 4:1674
Chen X, Li Y (2009) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in skeletal muscle migration differentiation, regeneration and fibrosis. Cell Adh Migr 3:337–341 Commentary & view
Collins CA, Olsen I, Zammit PS, Heslop L, Petrie A, Partridge TA, Morgan JE (2005) Stem cell function, self-renewal, and behavioral heterogeneity of cells from the adult muscle satellite cell niche. Cell 122:289–301
Colognato H, Winkelmann DA, Yurchenco PD (1999) Laminin polymerization induces a receptor-cytoskeleton network. J Cell Biol 145:619–631
Cornelison DDW, Filla MS, Stanley HM, Rapraeger AC, Olwin BB (2001) Syndecan-3 and Syndecan-4 specifically mark skeletal muscle satellite cells and are implicated in satellite cell maintenance and muscle regeneration. Dev Biol 239:79–94
Cornelison DDW, Wlicox-Adelman SA, Goetinick PF, Rauvala H, Rapraeger AC, Olwin BB (2004) Essential and separable roles for Syndecan-3 and Syndecan-4 in skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Genes Dev 18:2231–2236
Eisenach PA, de Sampaio PC, Murphy G, Roghi C (2012) Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) ubiquitination at Lys581 increases cellular invasion through type I collagen. J Biol Chem 287:11533–11545
Fernandez-Catalan C, Bode W, Huber R, Turk D, Calvete JJ, Lichte A, Tschesche H, Maskos K (1998) Crystal structure of the complex formed by the membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase with the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2, the soluble progelatinase A receptor. EMBO J 17:5238–5248
Fields GB (2010) Synthesis and biological applications of collagen-model triple-helical peptides. Org Biomol Chem 8:1237–1258
Fukushima K, Badlani N, Usas A, Riano F, Fu FH, Huard J (2001) The use of an antifibrosis agent to improve muscle recovery after laceration. Am J Sports Med 29:394–402
Galvez BG, Matıas-Roman S, Yanez-Mo M, Vicente-Manzanares M, Sanchez-Madrid F, Arroyo AG (2004) Caveolae are a novel pathway for membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase traffic in human endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 15:678–687
Gayraud-Morel B, Chrétien F, Plamant P, Gomès D, Zammit PS, Chabria M, Tajbakhsh S (2007) A role for the myogenic determination gene Myf5 in adult regenerative myogenesis. Dev Biol 312:13–28
Goetsch KP, Kallmeyer K, Niesler CU (2011) Decorin modulates collagen I-stimulated, but not fibronectin-stimulated, migration of C2C12 myoblasts. Matrix Biol 30:109–117
Goetsch KP, Myburgh KH, Niesler CU (2013) In vitro myoblast motility models: investigating migration dynamics for the study of skeletal muscle repair. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 34:333–347
Golubkov VS, Chekanov AV, Shiryaev SA, Aleshin AE, Ratnikov BI, Gawlik K, Radichev I, Motamedchaboki K, Smith JW, Strongin AY (2007) Proteolysis of the membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase prodomain: implications for a two-step proteolytic processing and activation. J Biol Chem 282:36283–36291
Gonzalo P, Guadamillas MC, Hernández-Riquer MV, Pollán A, Grande-García A, Bartolomé RA, Vasanji A, Ambrogio C, Chiarle R, Teixidó J et al (2010) MT1-MMP is required for myeloid cell fusion via regulation of Rac1 signaling. Dev Cell 18:77–89
Grefte S, Vullinghs S, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, Torensma R, Von den Hoff JW (2012) Matrigel, but not collagen I, maintains the differentiation capacity of muscle derived cells in vitro. Biomed Mater. doi:10.1088/1748-6041/7/5/055004
Grounds MD (2008) Complexity of extracellular matrix and skeletal muscle regeneration. In: Schiaffino S, Partridge T (eds) Skeletal muscle repair and regeneration. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 269–301
Grounds MD (2014) The need to more precisely define aspects of skeletal muscle regeneration. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 56:56–65
Hocking DC, Smith RK, McKeown-Longo PJ (1996) A novel role for the integrin-binding III-10 module in fibronectin matrix assembly. J Cell Biol 133:431–444
Holmbeck K, Bianco P, Caterina J, Yamada S, Kromer M, Kuznetsov SA, Mankani M, Robey PG, Poole AR, Pidoux I et al (1999) MT1-MMP-deficient mice develop dwarfism, osteopenia, arthritis, and connective tissue disease due to inadequate collagen turnover. Cell 99:81–92
Hoshino D, Koshikawa N, Suzuki T, Quaranta V, Weaver AM, Seiki M, Ichikawa K (2012) Establishment and validation of computational model for MT1-MMP dependent ECM degradation and intervention strategies. PLoS Comput Biol 8:e1002479
Huijbregts J, White JD, Grounds MD (2001) The absence of MyoD in regenerating skeletal muscle affects the expression pattern of basement membrane, interstitial matrix and integrin molecules that is consistent with delayed myotube formation. Acta Histochem 103:379–396
Islam M, Gor J, Perkins SJ, Ishikawa Y, Bächinger HP, Hohenester E (2013) The concave face of decorin mediates reversible dimerization and collagen binding. J Biol Chem 288:35526–35533
Kajita M, Itoh Y, Chiba T, Mori H, Okada A, Kinoh H, Seiki M (2001) Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves Cd44 and promotes cell migration. J Cell Biol 153:893–904
Karalaki M, Fili S, Philippou A, Koutsilieris M (2009) Muscle regeneration: cellular and molecular events. In Vivo 23:779–796
Kjaer M (2004) Role of extracellular matrix in adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to mechanical loading. Physiol Rev 84:649–698
Lehti K, Valtanen H, Wickström S, Lohi J, Keski-Oja J (2000) Regulation of membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase activity by its cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem 275:15006–15013
Li Y, Foster W, Deasy BM, Chan Y, Prisk V, Tang Y, Cummins J, Huard J (2004) Transforming growth factor-β1 Induces the Differentiation of Myogenic Cells into Fibrotic Cells in injured skeletal muscle. a key event in muscle fibrogenesis. Am J Phathol 164:1007–1019
Lluri G, Jaworski DM (2005) Regulation of TIMP-2, MT1-MMP, and MMP-2 expression during C2C12 differentiation. Muscle Nerve 32:492–499
Lund DK, Mouly V, Cornelison DDW (2014) MMP-14 is necessary but not sufficient for invasion of three-dimensional collagen by human muscle satellite cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 307:C140–C149
Mann C, Perdiguero E, Kharraz Y, Aguilar S, Pessina P, Serrano A, Muñoz-Cánoves P (2011) Aberrant repair and fibrosis development in skeletal muscle. Skelet Muscle 1:21–40
Mao Y, Schwarzbauer JE (2005) Fibronectin fibrillogenesis, a cell-mediated matrix assembly process. Matrix Biol 24:389–399
Maskos K (2005) Crystal structures of MMPs in complex with physiological and pharmacological inhibitors. Biochimie 87:249–263
Mercuri E, Muntoni F (2013) Muscular dystrophies. Lancet 381:845–860
Mimura T, Han KY, Onguch IT, Chang JH, Kim T, Kojima T, Zhou Z, Azar DT (2009) MT1-MMP-mediated cleavage of decorin in corneal angiogenesis. J Vasc Res 46:541–550
Miyazaki D, Nakamura A, Fukushima K, Yoshida K, Takeda S, Ideka S-I (2011) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 ablation in dystrophin-deficient mdx muscles reduces angiogenesis resulting in impaired growth of regenerated muscle fibers. Hum Mol Genet 20:1787–1799
Murphy G, Nagase H (2011) Localizing matrix metalloproteinase activities in the pericellular environment. FEBS J 278:2–15
Mylona E, Jones KA, Mills ST, Pavlath GK (2006) CD44 regulates myoblast migration and differentiation. J Cell Physiol 209:314–321
Nagase H, Visse R, Murphy G (2006) Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc Res 69:562–573
Ndinguri MW, Bhowmick M, Tokmina-Toszyk D, Robichaud TK, Fields GB (2012) Peptide-based selective inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase-mediated activities. Molecules 17:14230–14248
Ohtake Y, Tojo H, Seiki M (2006) Multifunctional roles of MT1-MMP in myofiber formation and morphostatic maintenance of skeletal muscle. J Cell Sci 119:3822–3832
Ohuchi E, Imai K, Fujii Y, Sato H, Seiki M, Okada Y (1997) Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase digests interstitial collagens and other extracellular matrix macromolecules. J Biol Chem 272:2446–2451
Olguin HC, Santander C, Brandan E (2003) Inhibition of myoblast migration via decorin expression is critical for normal skeletal muscle differentiation. Dev Biol 259:209–224
Ong S-E, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A, Mann M (2002) Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 1:376–386
Orgel JPRO, Eid A, Antipova O, Bella J, Scott JE (2009) Decorin core protein (Decoron) shape complements collagen fibril surface structure and mediates its binding. PLoS One 4:e7028
Overall CM (2002) Molecular determinants of metalloproteinase substrate specificity. Mol Biotechnol 22:51–86
Pankov R, Yamada KM (2002) Fibronectin at a glance. J Cell Sci 115:3861–3863
Philippou A, Maridaki M, Koutsilieris M (2008) The role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1) in muscle regeneration. In Vivo 22:735–750
Piccard H, Van den Steen PE, Opdenakker G (2007) Hemopexin domains as multifunctional liganding modules in matrix metalloproteinases and other proteins. J Leukoc Biol 81:870–892
Relaix F, Zammit PS (2012) Satellite cells are essential for skeletal muscle regeneration: the cell on the edge returns centre stage. Development 139:2845–2856
Remacle AG, Chekanov AV, Golubkov VS, Savinov AY, Rozanov DV, Strongin AY (2006) O-Glycosylation regulates autolysis of cellular membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). J Biol Chem 281:16897–16905
Rodríguez D, Morrison CJ, Overall CM (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: what do they not do? New substrates and biological roles identified by murine models and proteomics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:39–54
Rozanov DV, Deryugina EI, Ratnikov BI, Monosov EZ, Marchenko GN, Quigley JP, Strongin AY (2001) Mutation analysis of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP): the role of the cytoplasmic tail Cys574, the active site Glu240, and furin cleabage motifs in oligomerization, processing and self-proteolysis of MT1-MMP expressed in breast carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 276:25705–25714
Rullman E, Rundqvist H, Wagsater D, Fischer H, Eriksson P, Sundberg CJ, Jansson E, Gustafsson T (2007) A single bout of exercise activates matrix metalloproteinase in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 102:2346–2351
Rullman E, Norrbom J, Strömberg A, Wågsäter D, Rundqvist H, Haas T, Gustafsson T (2009) Endurance exercise activates matrix metalloproteinases in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 106:804–812
Sabourin LA, Girgis-Gabardo A, Seale P, Asakura A, Rudnicki MA (1999) Reduced differentiation potential of primary MyoD 2/2 myogenic cells derived from adult skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 144:631–643
Sakamoto T, Seiki M (2009) Cytoplasmic tail of MT1-MMP regulates macrophage motility independently from its protease activity. Genes Cells 14:617–626
Sanes JR (2003) The basement membrane/basal lamina of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 278:12601–12604
Schuler F, Sorokin LM (1995) Expression of laminin isoforms in mouse myogenic cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci 108:3795–3805
Serrano AL, Muñoz-Cánoves P (2010) Regulation and dysregulation of fibrosis in skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res 316:3050–3058
Shi F, Sottile J (2011) MT1-MMP regulates the turnover and endocytosis of extracellular matrix fibronectin. J Cell Sci 124:4039–4050
Siegal AL, Atchison K, Fisher KE, Davis GE, Cornelison DDW (2009) 3D timelapse analysis of muscle satellite cell motility. Stem Cells 27:2527–2538
Somerville RPT, Oblander SA, Apte SS (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases: old dogs with new tricks. Genome Biol 4:216
Springman EB, Angleton EL, Birkedal-Hansen H, van Wart HE (1990) Multiple modes of activation of latent human fibroblast collagenase: evidence for the role of a Cys73 active-site zinc complex in latency and a “cysteine switch” mechanism for activation (collagenase/matrix metalloproteinase/chemical modification). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:364–368
Stark DA, Karvas RM, Siegel AL, Cornelison DDW (2011) Eph/ephrin interactions modulate muscle satellite cell motility and patterning. Development 138:5279–5289
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behaviour. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:463–516
Sugiyama N, Gucciardo E, Tatti O, Varjosalo M, Hyytiäinen M, Gstaiger M, Lehti K (2013) EphA2 cleavage by MT1-MMP triggers single cancer cell invasion via homotypic cell repulsion. J Cell Biol 201:467–484
Takino T, Miyamori H, Kawaguchi N, Uekita T, Seiki M, Sato H (2003) Tetraspanin CD63 promotes targeting and lysosomal proteolysis of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304:160–166
Takino T, Tsuge H, Ozawa T, Sato H (2010) MT1-MMP promotes cell growth and ERK activation through c-Src and paxillin in three-dimensional collagen matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396:1042–1047
Tam EM, Moore TR, Butler GS, Overall CM (2004) Characterization of the distinct collagen binding, helicase and cleavage mechanisms of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 14 (gelatinase A and MT1-MMP). J Biol Chem 279:43336–43344
Tochowicz A, Goettig P, Evans R, Visse R, Shitomi Y, Palmisano R, Ito N, Richter K, Maskos K, Franke D et al (2011) The dimer interface of the membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase hemopexin domain. Crystal structure and biological functions. J Biol Chem 286:7587–7600
Toumi H, Best TM (2003) The inflammatory response: friend or enemy for muscle injury? Br J Sports Med 37:284–286
Udayakumar TS, Chen ML, Bair EL, von Bredow DC, Cress AE, Nagle RB, Bowden GT (2003) Membrane type-1-matrix metalloproteinase expressed by prostate carcinoma cells cleaves human laminin-5 β3 chain and induces cell migration. Cancer Res 63:2292–2299
Uekita T, Itoh Y, Yana I, Ohno H, Seiki M (2001) Cytoplasmic tail-dependent internalization of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is important for its invasion-promoting activity. J Cell Biol 155:1345–1356
Vachon PH, Loechel F, Xu H, Wewer UM, Engvall E (1996) Merosin and laminin in myogenesis; specific requirement for merosin in myotube stability and survival. J Cell Biol 134:1483–1497
Visse R, Nagase H (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 92:827–839
Watanabe A, Hosino D, Koshikawa N, Seiki M, Suzuki T, Ichikawa K (2013) Critical role of transient activity of MT1-MMP for ECM degradation in invadopodia. Plos One Comput Biol 9:e1003086
Will H, Atkinson SJ, Butler GS, Smith B, Murphy G (1996) The soluble catalytic domain of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves the propeptide of progelatinase A and initiates autoproteolytic activation. Regulation by TIMP-2 and TIMP-3. J Biol Chem 271:17119–17123
Wu YI, Munshi HG, Sen R, Snipas SJ, Salvesen GS, Fridman R, Stack MS (2003) Glycosylation broadens the substrate profile of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. J Biol Chem 279:8278–8289
Zarrabi K, Dufour A, Li J, Kuscu C, Pulkoski-Gross A, Zhi J, Hu Y, Sampson NS, Zucker S, Cao J (2011) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP-14)-mediated cancer cell migration. J Biol Chem 286:33167–33177
Zhou Z, Apte SS, Soininen R, Cao R, Baaklini GY, Rauser RW, Wang J, Cao Y, Tryggvason K (2000) Impaired endochondral ossification and angiogenesis in mice deficient in membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4052–4057
Zitka O, Kukacka J, Krizkova S, Huska D, Adam V, Masarik M, Prusa R, Kizek R (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Med Chem 17:3751–3768
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snyman, C., Niesler, C.U. MMP-14 in skeletal muscle repair. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 36, 215–225 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-015-9414-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-015-9414-4