Abstract
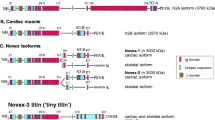
Many sarcomeric proteins in the myocardium alter their isoform pattern during perinatal development to adjust to the intensified pump function of the postnatal heart. These changes also involve the giant protein titin/connectin. Here we show by low-percentage polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis that developmentally regulated switching of cardiac titin/connectin size occurs in the hearts of mouse, rat, pig, and chicken. Mammalian hearts express, well before birth, large foetal (∼3.7 MDa) N2BA-titin/connectin isoform but no N2B-isoform (3.0 MDa). During perinatal heart development the 3.7-MDa N2BA-isoform is replaced by a mix of smaller isoforms. At birth a plethora of intermediate-size N2BA-isoforms appears together with the N2B-isoform. In postnatal heart development the larger-size N2BA-isoforms disappear and smaller-size N2BA-isoforms are upregulated, whereas the proportion of N2B-titin/connectin increases to species-specific adult levels. The time courses of isoform switching are faster in small than in large mammals. Titin/connectin isoform switching also takes place in developing chicken hearts, but the largest embryonic isoform found here was less than 3.4 MDa. At hatching, various smaller-size isoforms appeared and within a week the adult expression pattern was established representing a major 3.0-MDa isoform and a minor 3.15-MDa isoform. The ratio between the two adult isoforms differed between the left ventricle and the right atrium. The perinatal changes toward smaller cardiac titin/connectin isoforms in mammals and chicken greatly increase the myofibrillar passive tension of postnatal hearts. Plasticity of titin/connectin at approximately the time of birth thus affects myocardial mechanics but could also be an important factor in developmentally regulated assembly and signalling processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarkova I, Auerbach D, Ehler E, Perriard JC (2000) A novel marker for vertebrate embryonic heart, the EH-myomesin isoform. J Biol Chem 275:10256–10264
Anderson PA, Manring A, Glick KL, Crenshaw CC Jr (1982) Biophysics of the developing heart III. A comparison of the left ventricular dynamics of the foetal and neonatal lamb heart. Am J Obstet Gynecol 143:195–203
Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt CC, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S (2001) The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res 89:1065–1072
Borg TK, Gay RE, Johnson LD (1982) Changes in the distribution of fibronectin and collagen during development of neonatal rat heart. Coll Relat Res 2:211–218
Cappelli V, Bottinelli R, Poggesi C, Moggio R, Reggiani C (1989) Shortening velocity and myosin and myofibrillar ATPase activity related to myosin isoenzyme composition during postnatal development in rat myocardium. Circ Res 65:446–457
Carrier L, Boheler KR, Chassagne C, de la Bastie D, Wisnewsky C, Lakatta EG, Schwartz K (1992) Expression of sarcomeric actin isogenes in the rat heart with development and senescence. Circ Res 70:999–1005
Carver W, Terracio L, Borg TK (1993) Expression and accumulation of interstitial collagen in the neonatal rat heart. Anat Rec 236:511–520
Cazorla O, Freiburg A, Helmes M, Centner T, McNabb M, Wu Y, Trombitas K, Labeit S, Granzier H (2000) Differential expression of cardiac titin isoforms and modulation of cellular stiffness. Circ Res 86:59–67
Cazorla O, Wu Y, Irving TC, Granzier H (2001) Titin-based modulation of calcium sensitivity of active tension in mouse skinned cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 88:1028–1035
Engelmann GL (1993) Coordinate gene expression during neonatal rat heart development. A possible role for the myocyte in extracellular matrix biogenesis and capillary angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 27:1598–1605
Fisher DJ, Towbin J (1988) Maturation of the heart. Clin Perinatol 15:421–446
Freiburg A, Trombitas K, Hell W, Cazorla O, Fougerousse F, Centner T, Kolmerer B, Witt C, Beckmann JS, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S (2000) Series of exon-skipping events in the elastic spring region of titin as the structural basis for myofibrillar elastic diversity.Circ Res 86:1114–1121
Fukuda N, Sasaki D, Ishiwata S, Kurihara S (2001) Length dependence of tension generation in rat skinned cardiac muscle: role of titin in the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart. Circulation 104:1639–1645
Fukuda N, Wu Y, Farman G, Irving TC, Granzier HL (2003) Titin isoform variance and length dependence of activation in skinned bovine cardiac muscle. J Physiol 553:147–154
Funatsu T, Kono E, Higuchi H, Kimura S, Ishiwata S, Yoshioka T, Maruyama K, Tsukita S (1993) Elastic filaments in situ in cardiac muscle: deep-etch replica analysis in combination with selective removal of actin and myosin filaments. J Cell Biol 120:711–724
Fürst DO, Osborn M, Nave R, Weber K (1988) The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the M line. J Cell Biol 106:1563–1572
Gautel M, Lehtonen E, Pietruschka F (1996) Assembly of the cardiac I-band region of titin/connectin: expression of the cardiac-specific regions and their relation to the elastic segments. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 17:449–461
Godt RE, Fogaca RT, Silva IK, Nosek TM (1993) Contraction of developing avian heart muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 105:213–218
Grant DA, Walker AM (1996) Pleural and pericardial pressures limit foetal right ventricular output. Circulation 94:555–561
Grant DA, Fauhere JC, Eede KJ, Tyberg JV, Walker AM (2001) Left ventricular stroke volume in the foetal sheep is limited by extracardiac constraint and arterial pressure. J Physiol 535:231–239
Grant DA, Kondo CS, Maloney JE, Walker AM, Tyberg JV (1992) Pulmonary and pericardial limitations to diastolic filling of the left ventricle in lamb. Circulation 86:1615–1621
Granzier HL, Irving TC (1995) Passive tension in cardiac muscle: contribution of collagen, titin, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. Biophys J 68:1027–1044
Granzier HL, Labeit S (2004) The giant protein titin: a major player in myocardial mechanics, signaling, and disease. Circ Res 94:284–295
Greaser ML, Berri M, Warren CM, Mozdziak PE (2002) Species variations in cDNA sequence and exon splicing patterns in the extensible I-band region of cardiac titin: relation to passive tension. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23:473–482
Hattori A, Ishii T, Tatsumi R, Takahashi K (1995) Changes in the molecular types of connectin and nebulin during development of chicken skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1244:179–184
Hoh JF, McGrath PA, Hale PT (1978) Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of rat cardiac myosin: effects of hypophysectomy and thyroxine replacement. J Mol Cell Cardiol 10:1053–1076
Horowits R, Kempner ES, Bisher ME, Podolsky RJ (1986) A physiological role for titin and nebulin in skeletal muscle. Nature 323:160–164
Itoh Y, Suzuki T, Kimura S, Ohashi K, Higuchi H, Sawada H, Shimizu T, Shibata M, Maruyama K (1988) Extensible and less-extensible domains of connectin filaments in stretched vertebrate skeletal muscle sarcomeres as detected by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy using monoclonal antibodies. J Biochem 104:504–508
Kellermayer MS, Smith SB, Granzier HL, Bustamante C (1997) Folding-unfolding transitions in single titin molecules characterized with laser tweezers. Science 276:1112–1116
Kirkpatrick SE, Covell JW, Friedman WF (1973) A new technique for the continuous assessment of foetal and neonatal heart performance. Am J Obstet Gynecol 116:963–972
Kulke M, Fujita-Becker S, Rostkova E, Neagoe C, Labeit D, Manstein DJ, Gautel M, Linke WA (2001) Interaction between PEVK-titin and actin filaments: origin of a viscous force component in cardiac myofibrils. Circ Res 89:874–881
Labeit S, Kolmerer B (1995) Titins, giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science 270:293–296
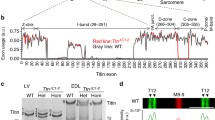
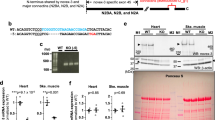
Lahmers S, Wu Y, Call DR, Labeit S, Granzier H (2004) Developmental control of titin isoform expression and passive stiffness in foetal and neonatal myocardium. Circ Res 94:505–513
Li H, Linke WA, Oberhauser AF, Carrion-Vazquez M, Kerkvliet JG, Lu H, Marszalek PE, Fernandez JM (2002) Reverse engineering of the giant muscle protein titin. Nature 418:998–1002
Lim SS, Woodroofe MN, Lemanski LF (1983) An analysis of contractile proteins in developing chick heart by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and electron microscopy. J Embryol Exp Morphol 77:1–14
Linke WA, Fernandez JM (2002) Cardiac titin: Molecular basis of elasticity and cellular contribution to elastic and viscous stiffness components in myocardium. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23:483–497
Linke WA, Leake MC (2004) Multiple sources of passive stress relaxation in muscle fibers. Phys Med Biol 49:3613–3627
Linke WA, Ivemeyer M, Labeit S, Hinssen H, Rüegg JC, Gautel M (1997) Actin–titin interaction in cardiac myofibrils: Probing a physiological role. Biophys J 73:905–919
Linke WA, Ivemeyer M, Mundel P, Stockmeier MR, Kolmerer B (1998) Nature of PEVK-titin elasticity in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8052–8057
Linke WA, Ivemeyer M, Olivieri N, Kolmerer B, Rüegg JC, Labeit S (1996) Towards a molecular understanding of the elasticity of titin. J Mol Biol 261:62–71
Linke WA, Popov VI, Pollack GH (1994) Passive and active tension in single cardiac myofibrils. Biophys J 67:782–792
Linke WA, Rudy DE, Centner T, Gautel M, Witt C, Labeit S, Gregorio CC (1999) I-band titin in cardiac muscle is a three-element molecular spring and is critical for maintaining thin filament structure. J Cell Biol 146:631–644
Lompré AM, Nadal-Ginard B, Mahdavi V (1984) Expression of the cardiac ventricular α- and ß-myosin heavy chain genes is developmentally and hormonally regulated. J Biol Chem 260:6437–6446
Lyons GE, Schiaffino S, Sassoon D, Barton P, Buckingham M (1990) Developmental regulation of myosin gene expression in mouse cardiac muscle. J Cell Biol 111:2427–2436
Makarenko I, Opitz CA, Leake MC, Neagoe C, Kulke M, Gwathmey JK, del Monte F, Hajjar RJ, Linke WA (2004) Passive stiffness changes caused by upregulation of compliant titin isoforms in human dilated cardiomyopathy hearts. Circ Res 95:708–716
Maruyama K, Matsubara S, Natori R, Nonomura Y, Kimura S, Ohashi K, Murakami F, Handa S, Eguchi G (1977a) Connectin, an elastic protein of muscle: characterization and function. J Biochem (Tokyo) 82:317–337
Maruyama K, Murakami F, Ohashi K (1977b) Connectin, an elastic protein of muscle. Comparative Biochemistry. J Biochem (Tokyo) 82:339–345
Maruyama K, Natori R, Nonomura Y (1976) New elastic protein from muscle. Nature 262:58–60
Metzger DM, Michele DE, Rust EM, Borton AR, Westfall MV (2003) Sarcomere thin filament regulatory isoforms: Evidence of a dominant effect of slow skeletal troponin I on cardiac contraction. J Biol Chem 278:13118–13123
Miller MK, Granzier H, Ehler E, Gregorio CC (2004) The sensitive giant: the role of titin-based stretch sensing complexes in the heart. Trends Cell Biol 14:119–126
Minajeva A, Kulke M, Fernandez JM, Linke WA (2001) Unfolding of titin domains explains the viscoelastic behavior of skeletal myofibrils. Biophys J 80:1442–1451
Morimoto S, Goto T (2000) Role of troponin I isoform switching in determining the pH sensitivity of Ca2+ regulation in developing rabbit cardiac muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:912–917
Murphy AM (1996) Contractile protein phenotypic variation during development. Cardiovasc Res 31:E25–33
Nagueh SF, Shah G, Wu Y, Torre-Amione G, King NM, Lahmers S, Witt CC, Becker K, Labeit S, Granzier HL (2004) Altered titin expression, myocardial stiffness, and left ventricular function in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 110:155–162
Neagoe C, Kulke M, del Monte F, Gwathmey JK, de Tombe PP, Hajjar R, Linke WA (2002) Titin isoform switch in ischemic human heart disease. Circulation 106:1333–1341
Neagoe C, Opitz CA, Makarenko I, Linke WA (2003) Gigantic variety: expression patterns of titin isoforms in striated muscles and consequences for myofibrillar passive stiffness. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 24: 175–189
Opitz CA, Kulke M, Leake MC, Neagoe C, Hinssen H, Hajjar RJ, Linke WA (2003) Damped elastic recoil of the titin spring in myofibrils of human myocardium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12688–12693
Opitz CA, Leake MC, Makarenko I, Benes V, Linke WA. (2004) Developmentally regulated switching of titin size alters myofibrillar stiffness in the perinatal heart. Circ Res 94:967–975
Reiser PJ, Westfall MV, Schiaffino S, Solaro RJ (1994) Tension production and thin-filament protein isoforms in developing rat myocardium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 267:H1589–H1596
Rief M, Gautel M, Oesterhelt F, Fernandez JM, Gaub HE (1997) Reversible unfolding of individual titin immunoglobulin domains by AFM. Science 276:1109–1112
Sabry MA, Dhoot GK (1989) Identification of and changes in the expression of troponin T isoforms in developing avian and mammalian heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 21:85–91
Saggin L, Ausoni S, Gorza L, Sartore S, Schiaffino S (1988) Troponin T switching in the developing rat heart. J Biol Chem 263:18488–18492
Saggin L, Gorza L, Ausoni S, Schiaffino S (1989) Troponin I switching in the developing heart. J Biol Chem 264:16299–16302
Siedner S, Kruger M, Schroeter M, Metzler D, Roell W, Fleischmann BK, Hescheler J, Pfitzer G, Stehle R (2003) Developmental changes in contractility and sarcomeric proteins from the early embryonic to the adult stage in the mouse heart. J Physiol 548:493–505
Tatsumi R, Hattori A (1995) Detection of giant myofibrillar proteins connectin and nebulin by electrophoresis in 2% polyacrylamide slab gels strengthened with agarose. Anal Biochem 224: 28–31
Trinick J, Knight P, Whiting A (1984) Purification and properties of native titin. J Mol Biol 180:331–356
Trombitas K, Freiburg A, Centner T, Labeit S, Granzier H (1999) Molecular dissection of N2B cardiac titin’s extensibility. Biophys J 77: 3189–3196
Trombitas K, Jin JP, Granzier H (1995) The mechanically active domain of titin in cardiac muscle. Circ Res 77:856–861
Trombitas K, Wu Y, Labeit D, Labeit S, Granzier H (2001) Cardiac titin isoforms are coexpressed in the half-sarcomere and extend independently. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H1793–H1799
Trombitas K, Wu Y, McNabb M, Greaser M, Kellermayer MS, Labeit S, Granzier H (2003) Molecular basis of passive stress relaxation in human soleus fibers: assessment of the role of immunoglobulin-like domain unfolding. Biophys J 85:3142–3153
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J (2003) Titin: properties and family relationships. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:679–689
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J, Sleep JA, Simmons RM (1997) Elasticity and unfolding of single molecules of the giant muscle protein titin. Nature 387:308–312
Wang K, McClure J, Tu A (1979) Titin: major myofibrillar component of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:3698–3702
Wang K, Ramirez-Mitchell R, Palter D (1984) Titin is an extraordinary long, flexible, and slender myofibrillar protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3685–3689
Warren CM, Jordan MC, Roos KP, Krzesinski PR, Greaser ML (2003) Titin isoform expression in normal and hypertensive myocardium. Cardiovasc Res 59:86–94
Warren CM, Krzesinski PR, Campbell KS, Moss RL, Greaser ML (2004) Titin isoform changes in rat myocardium during development. Mech Dev 121:1301–1312
Whalen RG, Sell SM (1980) Myosin from foetal hearts contains the skeletal muscle embryonic light chain. Nature 286:731–733
Wu Y, Bell SP, Trombitas K, Witt CC, Labeit S, LeWinter MM, Granzier H (2002) Changes in titin isoform expression in pacing-induced cardiac failure give rise to increased passive muscle stiffness. Circulation 106:1384–1389
Wu Y, Cazorla O, Labeit D, Labeit S, Granzier H. (2000) Changes in titin and collagen underlie diastolic stiffness diversity of cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32:2151–2162
Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M (2002) Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assembly. J Cell Biol 154: 123–136
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Uta Opitz for continuous encouragement and the former members of the Linke lab in Heidelberg for their excellent work, which the present study is built upon. We gratefully acknowledge financial support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (grants Li 690/2-3, Li 690/6-2, SFB 629).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Muscle Elastic Proteins:
Koscak Maruyama Memorial Meeting, Chiba, Japan, November 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Opitz, C.A., Linke, W.A. Plasticity of cardiac titin/connectin in heart development. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26, 333–342 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9040-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9040-7