Abstract
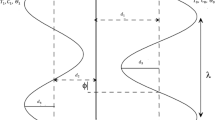
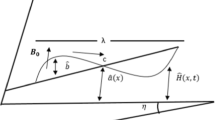
The significance of double-diffusivity convection and an inclined magnetic field on peristaltic propulsion of fourth-grade nanofluids through an inclined asymmetric channel is the focus of this study. A mathematical model of a fourth-grade nanofluid is presented, by considering a tilted magnetic field and double-diffusivity convection. The highly nonlinear partial differential equations (PDE's) are simplified with the lubrication methodology. Numerical technique is used to solve the coupled and highly nonlinear PDE's. To examine the impact of varying physical characteristics like Brownian motion, thermophoresis, Hartmann number, nanoparticle Grashof number, slip parameters and trapping on flow quantities, numerical and graphical results are provided. It is acquired that when Brownian motion is increased, the pressure gradient drops; however, when the thermophoresis parameter is increased, the pressure gradient boosts. It is also notable that the profile of velocity resembles a parabolic form and maximum velocity retain at channel’s center.


























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- G rF :
-
Nanoparticle Grashof number
- G rc :
-
Solutal Grashof number
- G rt :
-
Thermal Grashof number
- (ρc)f :
-
Fluid heat capacity
- (ρc)p :
-
Heat capacity of nanoparticle
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- M :
-
Hartmann number
- N b :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- N t :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- N CT :
-
Soret parameter
- D s :
-
Solutal diffusively
- Ω:
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction
- T :
-
Temperature
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- C :
-
Solutal concentration
- Ln :
-
Nanofluid Lewis number
- N TC :
-
Dufour parameter
- Le :
-
Lewis number
- D B :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- D CT :
-
Soret diffusively
- D TC :
-
Dufour diffusively
- D T :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- \({\beta }_\text{T}\) :
-
Volumetric thermal expansion
- \({\rho }_\text{f}\) :
-
Fluid density
- \(\delta\) :
-
Wave number
- \(\Psi\) :
-
Stream function
- \(\xi\) :
-
Inclination angle of MHD
- \(\eta\) :
-
Inclination angle of channel
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \({\beta }_\text{C}\) :
-
Volumetric solutal expansion
- \({\rho }_{\text{f}_{0}}\) :
-
Fluid density at T0
- \({\rho }_\text{p}\) :
-
Nanoparticle mass density
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Dimensionless solutal concentration
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Wavelength
- \(\mu\) :
-
Viscosity of fluid
- \(\Theta\) :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction
- \(a,b\) :
-
Wave amplitudes
- \(c\) :
-
Propagation of velocity
- \(d\) :
-
Channel width
- \(g\) :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(p\) :
-
Pressure
- \(t\) :
-
Time
- \(u\) :
-
Axial velocity
- \(v\) :
-
Transverse velocity
References
Hariharan P, Seshadri V, Banerjee RK. Peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian fluid in a diverging tube with different wave forms. Math Comput Modell. 2008;48:998–1017.
Latham TW. Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump, M.Sc. Thesis, MIT, Cambridge 1966.
Shapiro AH, Jaffrin MY, Weinberg SL. Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. Cambridge Uni Press. 1969;37:799–825.
Mishra M, Rao AR. Peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in an asymmetric channel. Z Angew Math Phys (ZAMP). 2003;54:532–50.
Tripathi D, Pandey SK, Das S. Peristaltic transport of a generalized Burgers’ fluid: application to the movement of chyme in small intestine. Acta Astronaut. 2011;69:30–8.
Ijaz N, Riaz A, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R, Sait SM. Buoyancy driven flow with gas-liquid coatings of peristaltic bubbly flow in elastic walls. Coatings. 2020;101:115.
Usha S, Rao AR. Effects of curvature and inertia on the peristaltic transport in a two-fluid system. Int J Eng Sci. 2000;38:1355–75.
Reddy MVS, Mishra M, Sreenadh S, Rao AR. Influence of lateral walls on peristaltic flow in a rectangular duct. J Fluids Eng. 2005;127:824–7.
Nadeem S, Riaz A, Ellahi R. Peristaltic flow of a Jeffrey fluid in a rectangular duct having complaint walls. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q. 2013;19:399–409.
Abd El-Naby AH, El-Misiery AEM. Effects of an endoscope and generalized Newtonian fluid on peristaltic motion. Appl Math Comput. 2002;128:19–35.
Elmaboud YA. Influence of induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow in an annulus. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat. 2012;17:685–98.
Ramesh K, Devakar M. Effects of heat and mass transfer on the peristaltic transport of MHD couple stress fluid through porous medium in a vertical asymmetric channel. J Fluids. 2015;2015:1–19.
Tripathi D, Bég OA. A study of unsteady physiological magneto-fluid flow and heat transfer through a finite length channel by peristaltic pumping. Proc I Mech E Part H J Eng Med. 2012;226:631–44.
Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Tripathi D, Ellahi R. Thermally developed peristaltic propulsion of magnetic solid particles in Biorheological fluids. Indian J Phys. 2018;92:423–30.
Reddy RH, Kavitha A, Sreenadh S, Saravana R. Effects of induced magnetic field on peristaltic transport of a Carreau fluid in an inclined channel filled with porous material. Int J Mech Mater Eng. 2011;6:240–9.
Kothandapani M, Pushparaj V, Prakash J. Effect of magnetic field on peristaltic flow of a fourth grade fluid in a tapered asymmetric channel. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci. 2018;30:86–95.
Riaz A, Zeeshan A, Ahmad S, Razaq A, Zubair M. Effects of external magnetic field on Non-newtonian two phase fluid in an annulus with peristaltic pumping. J Magn. 2019;24:1–8.
Abd-Alla AM, Abo-Dahab SM. Magnetic field and rotation effects on peristaltic transport of a Jeffrey fluid in an asymmetric channel. J Magn Magn Mater. 2015;374:680–9.
Munawar S, Saleem N. Second law analysis of ciliary pumping transport in an inclined channel coated with Carreau fluid under a magnetic field. Coatings. 2020;10:240.
Haider S, Ijaz N, Zeeshan A, Li YZ. Magneto-hydrodynamics of a solid-liquid two-phase fluid in rotating channel due to peristaltic wavy movement. Int J Numer Method H. 2019;30:2501–16.
Choi SUS. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluid with nanoparticles developments and Applications of non-Newtonian Flow, ASME Fed, 231;66: 99–105.
Bovand M, Rashidi S, Ahmadi G, Esfahani JA. Effects of trap and reflect particle boundary conditions on particle transport and convective heat transfer for duct flow—A two-way coupling of Eulerian-Lagrangian model. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;108:368–77.
Shehzad N, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R, Rashidi S. Modelling study on internal energy loss due to entropy generation for non-Darcy Poiseuille flow of silver-water nanofluid: an application of purification. Entropy. 2018;20:851.
Darbari B, Saman Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Sensitivity analysis of entropy generation in nanofluid flow inside a channel by response surface methodology. Entropy. 2016;18:52.
Bovand M, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Optimum interaction between magnetohydrodynamics and nanofluid for thermal and drag management. J Thermophys Heat Trans. 2017;31:218–29.
Darbari B, Rashidi S, Keshmiri A. Nanofluid heat transfer and entropy generation inside a triangular duct equipped with delta winglet vortex generators. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:1045–55.
Ajarostaghi SSM, Shirzad M, Rashidi S, Li LKB. Heat transfer performance of a nanofluid-filled tube with wall corrugations and center-cleared twisted-tape inserts. Energy Sources A Recov Util Environ Eff. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1841860.
Azadi M, Hosseinirad E, Hormozi F, Rashidi S. Second law analysis for nanofluid flow in mini-channel heat sink with finned surface: a study on fin geometries. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:1883–95.
Freidoonimehr N, Rashidi MM, Momenpour MH, Rashidi S. Analytical approximation of heat and mass transfer in MHD non-Newtonian nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with convective surface boundary conditions. Int J Biomath. 2017;10:1750008.
Akar S, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA, Karimi N. Targeting a channel coating by using magnetic field and magnetic nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137:381–8.
Kothandapani M, Prakash J. Effects of thermal radiation parameter and magnetic field on the peristaltic motion of Williamson nanofluids in a tapered asymmetric channel. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;8:234–45.
Sucharitha G, Lakshminarayana P, Sandeep N. Joule heating and wall flexibility effects on the peristaltic flow of magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;131:52–62.
Hayat T, Ahmed B, Abbasi FM, Alsaedi A. Numerical investigation for peristaltic flow of Carreau-Yasuda magneto-nanofluid with modified darcy and radiation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137:1359–67.
Akbar NS. Metallic nanoparticles analysis for the peristaltic flow in an asymmetric channel With MHD. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol. 2014;13:357–61.
Ramesh K, Prakash J. Thermal analysis for heat transfer enhancement in electroosmosis-modulated peristaltic transport of Sutterby nanofluids in a microfluidic vessel. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138:1311–26.
Beghein C, Haghighat F, Allard F. Numerical study of double-diffusive natural convection in a square cavity. Int J Heat Mass Tran. 1992;35:833–46.
Bég OA, Tripathi D. Mathematica simulation of peristaltic pumping with double-diffusive convection in nanofluids: a bio-nanoengineering model. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part N J Nanoeng Nanosyst. 2012;225:99–114.
Sharma A, Tripathi D, Sharma RK, Tiwari AK. Analysis of double diffusive convection in electroosmosis regulated peristaltic transport of nanofluids. Physica A. 2019;535:122148.
Asha SK, Sunitha G. Thermal radiation and hall effects on peristaltic blood flow with double diffusion in the presence of nanoparticles. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2020;17:100560.
Akram S, Razia A, Afzal F. Effects of velocity second slip model and induced magnetic field on peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian fluid in the presence of double-diffusivity convection in nanofluids. Arch Appl Mech. 2020;90:1583–603.
Alolaiyan H, Riaz A, Razaq A, Saleem N, Zeeshan A, Bhatti MM. Effects of double diffusion convection on Third grade nanofluid through a curved compliant peristaltic channel. Coatings. 2020;10:154.
Chu WKH, Fang J. Peristaltic transport in a slip flow. Eur Phys J B. 2000;16:543–7.
Akbar NS, Nadeem S, Hayat T, Hendi A. Peristaltic flow of a nanofluid with slip effects. Meccanica. 2012;47:1283–94.
Abbasi FM, Hayat T, Alsaadi F. Hydromagnetic peristaltic transport of water-based nanofluids with slip effects through an asymmetric channel. Int J Mod Phys B. 2015;29:1550151.
Mandviwalla X, Archer R. The influence of slip boundary conditions on peristaltic pumping in a rectangular channel. J Fluids Eng. 2008;130:124501.
Akram S, Mekheimer KhS, Elmaboud YA. Particulate suspension slip flow induced by peristaltic waves in a rectangular duct: effect of lateral walls. Alex Eng J. 2018;57:407–14.
Nadeem S, Akbar NS, Hayat T, Obaidat S. Peristaltic flow of a Williamson fluid in an inclined asymmetric channel with partial slip and heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:1855–62.
Ellahi R, Hussain F, Ishtiaq F, Hussain A. Peristaltic transport of Jeffrey fluid in a rectangular duct through a porous medium under the effect of partial slip: an application to upgrade industrial sieves/filters. Pramana. 2019;93:34.
Riaz A, Khan SUD, Zeeshan A, Khan SU, Hassan M, Muhammad T. Thermal analysis of peristaltic flow of nanosized particles within a curved channel with second-order partial slip and porous medium. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143:1997–2009.
Prakash J, Siva EP, Tripathi D, Beg OA. Thermal slip and radiative heat transfer effects on electroosmotic magneto nanoliquid peristaltic propulsion through a microchannel. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2019;48:2882–908.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through research groups program under grant number RGP.2/39/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, S., Athar, M., Saeed, K. et al. Slip impact on double-diffusion convection of magneto-fourth-grade nanofluids with peristaltic propulsion through inclined asymmetric channel. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 8933–8946 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-11150-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-11150-1