Abstract
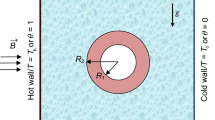
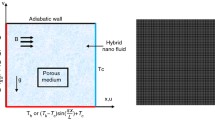
This paper aims to understand the characteristics of heat transfer and flow by natural convection of Al2O3–Cu/water-based hybrid nanofluid-filled square domain containing various configurations of a corrugated conducting solid under a horizontal magnetic field. The basic equations in their non-dimensional form are numerically solved using the finite volume discretization technique. The Corcione correlations are utilized to estimate the overall heat conductivity and overall viscosity of the hybrid nanoliquid when the nanoparticle’s Brownian motion is taken into account. The dependency of different governing factors of the investigation, namely volume fraction of the combined nanoparticles, Rayleigh and Hartmann numbers, undulation number, undulation amplitude and the fluid/solid heat conductivity ratio, on thermohydrodynamic characteristics are delineated. Results stated that the maximum heat transmission rate was obtained for weak values of Hartmann, undulation number, undulation amplitude and high values of Rayleigh and nanoparticles volumic fraction. In addition, the fluid/solid heat conductivity ratio parameter was found to boost the heat transfer at weak Rayleigh while reducing it at high Rayleigh.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Undulation amplitude
- B0 :
-
Magnetic field (N Am−2)
- C p :
-
Specific heat (J kg−1 K−1)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m s−2)
- H:
-
Width of the cavity (m)
- k*:
-
Ratio of fluid/solid heat conductivity
- k :
-
Heat conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- k b :
-
Constant of Boltzmann, 1.380648 × 10−23 (J K−1)
- L :
-
Size of the cylinder block
- N:
-
Number of undulations
- r i :
-
Main radius of the inner cylinder (m)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- T fr :
-
Freezing temperature of the water (273.15 K)
- u, v :
-
Dimensional velocities (m s−1)
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless velocities
- x, y :
-
Dimensional coordinates (m)
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinates
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- \(\upsilon\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2 s−1)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- \(\beta\) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (1 K−1)
- \(\phi\) :
-
Volumic concentration
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\psi\) :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- η :
-
Angular position (°)
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity (1 Ω−1 m−1)
- h:
-
Hot
- c:
-
Cold
- hnf:
-
Hybrid nanoliquid
- s:
-
Solid
- f:
-
Fluid
- hp:
-
Combined solid nanoparticles
- p:
-
Solid nanoparticles
References
Sajid MU, Ali HM. Recent advances in application of nanofluids in heat transfer devices: a critical review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2019;103:556–92.
Wahab A, Hassan A, Qasim MA, Ali HM, Babar H, Sajid MU. Solar energy systems—potential of nanofluids. J Mol Liq. 2019;111049.
Raja Sekhar Y, Sharma KV, Thundil Karupparaj R, Chiranjeevi C. Heat transfer enhancement with Al2O3 nanofluids and twisted tapes in a pipe for solar thermal applications. Proc Eng. 2013;64:1474–84.
Ali HM, Babar H, Shah TR, Sajid MU, Qasim MA, Javed S. Preparation techniques of TiO2 nanofluids and challenges: a review. Appl Sci. 2018;8(4):587.
Salata O. Applications of nanoparticles in biology and medicine. J Nanobiotechnol. 2004;1–6.
Soudagar MEM, Kalam MA, Sajid MU, Afzal A, Banapurmath NR, Akram N, et al. Thermal analyses of minichannels and use of mathematical and numerical models. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl. 2020;77(5):497–537.
Saidur R, Leong KY, Mohammad HA. A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2011;15:1646–68.
Sajid MU, Ali HM, Sufyan A, Rashid D, Zahid SU, Rehman WU. Experimental investigation of TiO2–water nanofluid flow and heat transfer inside wavy mini-channel heat sinks. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137(4):1279–94.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a sinusoidally heated enclosure utilizing hybrid nanofluid. Comput Therm Sci Int J. 2017;9.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. Natural convection enhancement in an eccentric horizontal cylindrical annulus using hybrid nanofluids. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl. 2017;71:1159–73.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. Free convection enhancement in an annulus between horizontal confocal elliptical cylinders using hybrid nanofluids. Numer Heat Transfer, Part A. 2016;70(10):1141–56.
Babar H, Sajid MU, Ali HM. Viscosity of hybrid nanofluids: a critical review. Therm Sci. 2019;23(3 Part B):1713–54.
Sajid MU, Ali HM. Thermal conductivity of hybrid nanofluids: a critical review. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:211–34.
Tayebi T, Öztop HF. Entropy production during natural convection of hybrid nanofluid in an annular passage between horizontal confocal elliptic cylinders. Int J Mech Sci. 2020;171:105378.
Labib MN, Nine MJ, Afrianto H, Chung H, Jeong H. Numerical investigation on effect of base fluids and hybrid nanofluid in forced convective heat transfer. Int J Therm Sci. 2013;71:163–71.
Balla HH, Abdullah S, Faizal WM, Zulkifli R, Sopian K. Numerical study of the enhancement of heat transfer for hybrid CuO–Cu nanofluids flowing in a circular pipe. J Oleo Sci. 2013;62(7):533–9.
Takabi B, Salehi S. Augmentation of the heat transfer performance of a sinusoidal corrugated enclosure by employing hybrid nanofluid. Adv Mech Eng. 2014;6:147059.
Takabi B, Gheitaghy AM, Tazraei P. Hybrid water-based suspension of Al2O3 and Cu nanoparticles on laminar convection effectiveness. J Thermophys Heat Transfer. 2016;30:523–32.
Rashad AM, Chamkha AJ, Ismael MA, Salah T. Magnetohydrodynamics natural convection in a triangular cavity filled with a Cu–Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid with localized heating from below and internal heat generation. J Heat Transfer. 2018;140(7):072502.
Benkhedda M, Boufendi T, Tayebi T, et al. Convective heat transfer performance of hybrid nanofluid in a horizontal pipe considering nanoparticles shapes effect. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140:411–25.
Moghadassi A, Ghomi E, Parvizian F. A numerical study of water based Al2O3 and Al2O3–Cu hybrid nanofluid effect on forced convective heat transfer. Int J Therm Sci. 2015;92:50–7.
Sundar LS, Singh MK, Sousa AC. Enhanced heat transfer and friction factor of MWCNT–Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2014;52:73–83.
Alsabery AI, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ, Hashim I. Mixed convection of Al2O3–water nanofluid in adouble lid-driven square cavity with a solid inner insert using Buongiorno’s two-phase model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;119:939–61.
Sheremet M, Oztop H, Pop I, Abu-Hamdeh N. Analysis of entropy generation in natural convection of nanofluid inside a square cavity having hot solid block: Tiwari and Das’ model. Entropy. 2015;18(1):9.
Rahman MM, Mamun MAH, Saidur R. Analysis of magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection and joule heating in lid-driven cavity having a square block. J Chin Inst Eng. 2011;34(5):585–99.
Mahapatra PS, De S, Ghosh K, Manna NK, Mukhopadhyay A. Heat transfer enhancement and entropy generation in a square enclosure in the presence of adiabatic and isothermal blocks. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl. 2013;64:577–96.
Sivaraj C, Sheremet M. MHD natural convection in an inclined square porous cavity with a heat conducting solid block. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;426:351–60.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. Entropy generation analysis due to MHD natural convection flow in a cavity occupied with hybrid nanofluid and equipped with a conducting hollow cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:2165–79.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. Entropy generation analysis during MHD natural convection flow of hybrid nanofluid in a square cavity containing a corrugated conducting block. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow. 2019;30(3):1115–36.
Corcione M. Empirical correlating equations for predicting the effective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofluids. Energy Convers Manag. 2011;52(1):789–93.
Maxwell JC. A treatise on electricity and magnetism. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1881.
Patankar SV. Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1980.
House JM, Beckermann C, Smith TF. Effect of a centered conducting body on natural convection heat transfer in an enclosure. Numer Heat Transf. 1990;18(2):213–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tayebi, T., Chamkha, A.J. Effects of various configurations of an inserted corrugated conductive cylinder on MHD natural convection in a hybrid nanofluid-filled square domain. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 1399–1411 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10206-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10206-y