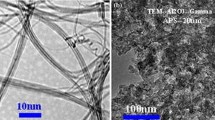
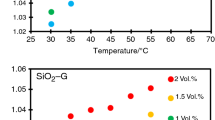
Abstract
In the current work, after generating experimental data points for different volume fraction of nanoparticles (\(\phi\)) and different temperatures, an algorithm to find the best neuron number in the hidden layer of artificial neural network (ANN) method is proposed to find the best architecture and then to predict the thermal conductivity (\(k_{\text{nf}}\)) of SiO2/water–ethylene glycol (50:50) nanofluid. This ANN is a feed-forward network with Levenberg–Marquardt for the learning algorithm. Regarding the experimental data points, a third-order function is obtained. In the fitting method, the mean square error is 2.7547e−05, and the maximum value of error is 0.0125. The correlation coefficient of the fitting method is 0.9919. This surface also shows the behavior of nanofluid based on the \(\phi\) and temperatures, and finally, the results of these methods have been compared. It can be seen that for 8 neuron numbers, the correlation coefficient for all outputs of ANN is 0.993861.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruhani B, Toghraie D, Hekmatifar M, Hadian M. Statistical investigation for developing a new model for rheological behavior of ZnO–Ag (50%–50%)/water hybrid Newtonian nanofluid using experimental data. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2019;525:741–75.
Moradi A, Toghraie D, Isfahani AHM, Hosseinian A. An experimental study on MWCNT–water nanofluids flow and heat transfer in double-pipe heat exchanger using porous media. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08076-0.
Keyvani M, Afrand M, Toghraie D, Reiszadeh M. An experimental study on the thermal conductivity of cerium oxide/ethylene glycol nanofluid: developing a new correlation. J Mol Liq. 2018;266:211–7.
Saeedi HA, Akbari M, Toghraie D. An experimental study on rheological behavior of a nanofluid containing oxide nanoparticle and proposing a new correlation. Physica E: Low-dimensional Syst Nanostruct. 2018;99:285–93.
Akhgar A, Toghraie D. An experimental study on the stability and thermal conductivity of water-ethylene glycol/TiO2-MWCNTs hybrid nanofluid: developing a new correlation. Powder Technol. 2018;338:806–18.
Deris Zadeh A, Toghraie D. Experimental investigation for developing a new model for the dynamic viscosity of silver/ethylene glycol nanofluid at different temperatures and solid volume fractions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:1449–61.
Afshari A, Akbari M, Toghraie D, Eftekhari Yazdi M. Experimental investigation of rheological behavior of the hybrid nanofluid of MWCNT–alumina/water (80%)–ethylene-glycol (20%). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1001–15.
Ahmadi Esfahani M, Toghraie D. Experimental investigation for developing a new model for the thermal conductivity of silica/water-ethylene glycol (40%–60%) nanofluid at different temperatures and solid volume fractions. J Mol Liq. 2017;232:105–12.
Hemmat Esfe M, Rostamian H, Afrand M, Karimipour A, Hassani M. Modeling and estimation of thermal conductivity of MgO–water/EG (60:40) by artificial neural network and correlation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;68:98–103.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Naderi A, Alirezaie A, Karimipour A, Wongwises S, Goodarzi M, Dahari M. Modeling of thermal conductivity of ZnO-EG using experimental data and ANN methods. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;63:35–40.
Afrand M, Toghraie D, Sina N. Experimental study on thermal conductivity of water-based Fe3O4 nanofluid: development of a new correlation and modeled by artificial neural network. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;75:262–9.
Afrand M, Najafabadi KN, Sina N, Safaei MR, Kherbeet AS, Wongwises S, Dahari M. Prediction of dynamic viscosity of a hybrid nano-lubricant by an optimal artificial neural network. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:209–14.
Hemmat Esfe M, Hajmohammad H, Toghraie D, Rostamian H, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Multi-objective optimization of nanofluid flow in double tube heat exchangers for applications in energy systems. Energy. 2017;137:160–71.
Hemmat Esfe M, Yan W, Afrand M, Sarraf M, Toghraie D, Dahari M. Estimation of thermal conductivity of Al2O3/water (40%)–ethylene glycol (60%) by artificial neural network and correlation using experimental data. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;74:125–8.
Hemmat Esfe M, Hassani Ahangar MR, Rejvani M, Toghraie D, Hadi Hajmohammad M. Designing an artificial neural network to predict dynamic viscosity of aqueous nanofluid of TiO2 using experimental data. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;75:192–6.
Tajik Jamal-Abadi M, Zamzamian AH. Optimization of thermal conductivity of Al2O3 nanofluid by using ANN and GRG methods. Int J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013;9:177–84.
Tahani M, Vakili M, Khosrojerdi S. Experimental evaluation and ANN modeling of thermal conductivity of graphene oxide nanoplatelets/deionized water nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:358–65.
Khosrojerdi S, Vakili M, Yahyaei M, Kalhor K. Thermal conductivity modeling of graphene nanoplatelets/deionized water nanofluid by MLP neural network and theoretical modeling using experimental results. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;74:11–7.
Hemmat Esfe M, Motahari K, Sanatizadeh E, Afrand M, Rostamian H, Hassani Ahangar MR. Estimation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-water in low temperature by artificial neural network and correlation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:376–81.
Aghayar R, Maddah H, Faramarzi AR, Mohammadiun H, Mohammadiun M. Comparison of the experimental and predicted data for thermal conductivity of iron oxide nanofluid using artificial neural networks. Nanomed Res J. 2016;1:15–22.
Afrand M, Hemmat Esfe M, Abedini E, Teimouri H. Predicting the effects of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and temperature on the thermal conductivity of water using artificial neural network and experimental data. Phys E. 2017;87:242–7.
Zhao N, Li Z. Experiment and artificial neural network prediction of thermal conductivity and viscosity for alumina–water nanofluids. Materials. 2017;10:552–60.
Hemmat Esfe M, Esfandeh S, Afrand M, Rejvani M, Rostamian SH. Experimental evaluation, new correlation proposing and ANN modeling of thermal properties of EG based hybrid nanofluid containing ZnODWCNT nanoparticles for internal combustion engines applications. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;133:452–63.
Aghayari R, Maddah H, Ahmadi MH, Yan W, Ghasemi N. Measurement and artificial neural network modeling of electrical conductivity of CuO/glycerol nanofluids at various thermal and concentration conditions. Energies. 2018;11:1190–8.
Kannaiyan S, Boobalan C, Castro Nagarajan F, Sivaraman S. Modeling of thermal conductivity and density of alumina/silica in water hybrid nanocolloid by the application of artificial neural networks. Chin J Chem Eng. 2019;27:726–36.
Zendehboudi A, Saidur R. A reliable model to estimate the effective thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2019;55:397–411.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostami, S., Toghraie, D., Esfahani, M.A. et al. Predict the thermal conductivity of SiO2/water–ethylene glycol (50:50) hybrid nanofluid using artificial neural network. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 1119–1128 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09426-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09426-z