Abstract
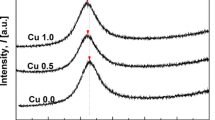
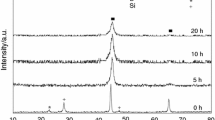
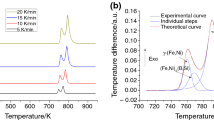
The present work demonstrates the results of crystallization kinetic of [(Fe0.9Ni0.1)77Mo5P9C7.5B1.5]100−xCux (x = 0.1 at.%) amorphous metallic alloy during non-isothermal annealing done by differential thermal analysis at various heating rates of 10, 20, and 40 K min−1 up to 1473 K. The results showed that by increasing the crystallization temperature, some crystalline phases including α-Fe, γ-Fe, FeNi2P, and Fe3C were formed. In addition, the volume fraction of crystalline phases increased from 9.2 to 20.2%, confirming the presence of crystalline phases by FE-SEM results. To calculate the activation energy (Eα), which is approximately independent of “α” in a wide range, some isoconversional methods such as Starink and Friedman were used for various crystallization steps. Moreover, the invariant kinetic parameters including IKP method and fitting models were used to calculate the empirical kinetic triplets [E, A, and g(α)]. IKP and Fitting methods are in a good agreement with each other to determine the kinetic mechanism at each crystallization stage. Therefore, to ensure the IKP results, the mechanism of four crystallization peaks was determined using a fitting method. Finally, it was found that the first, second, third, and fourth crystallization stages were controlled by A4, A4, A4, and P4 models, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue A, Wang X. Bulk amorphous FC20 (Fe–C–Si) alloys with small amounts of B and their crystallized structure and mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2000;48:1383–95.
Long ZL, Shao Y, Deng XH, Zhang ZC, Jiang Y, Zhang P, et al. Cr effects on magnetic and corrosion properties of Fe–Co–Si–B–Nb–Cr bulk glassy alloys with high glass-forming ability. Intermetallics. 2007;15:1453–8.
Guo SF, Chan KC, Xie SH, Yu P, Huang YJ, Zhang HJ. Novel centimeter-sized Fe-based bulk metallic glass with high corrosion resistance in simulated acid rain and seawater. J Non Cryst Solids. 2013;369:29–33.
Pang SJ, Zhang T, Asami K, Inoue A. Synthesis of Fe–Cr–Mo–C–B–P bulk metallic glasses with high corrosion resistance. Acta Mater. 2002;50:489–97.
Dan Z, Makino A, Hara N. Effects of P addition on corrosion properties of soft magnetic FeSiB alloys. Mater Trans. 2013;54:1691–6.
Han Y, Kong FL, Han FF, Inoue A, Zhu SL, Shalaan E, et al. New Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous alloys with high saturation magnetization and good corrosion resistance for dust core application. Intermetallics. 2016;76:18–25.
Jung HY, Stoica M, Yi S, Kim DH, Eckert J. Electrical and magnetic properties of Fe-based bulk metallic glass with minor Co and Ni addition. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;364:80–4.
Shen BL, Inoue A. Soft magnetic properties of bulk nanocrystalline Fe–Co–B–Si–Nb–Cu alloy with high saturated magnetization of 1.35 T. J Mater Res. 2004;19:2549–52.
Qi T, Li Y, Takeuchi A, Xie G, Miao H, Zhang W. Soft magnetic Fe25Co25Ni25(B, Si)25 high entropy bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics. 2015;66:8–12.
Lesz S, Kwapuliński P, Nabiałek M, Zackiewicz P, Hawelek L. Thermal stability, crystallization and magnetic properties of Fe–Co-based metallic glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125:1143–9.
Ferenc J, Kowalczyk M, Cie G. Magnetostrictive iron-based bulk metallic glasses for force sensors. IEEE Trans Magn. 2014;50:4–7.
Ramanan VRV. Metallic glasses in distribution transformer applications: an update. J Mater Eng. 1991;13:119–27.
Kim SW, Namkung J, Kwon O. Manufactor and industrial application of Fe-based metallic glasses. Mater Sci Forum. 2012;709:1324–30.
Makino A, Kubota T, Makabe M, Chang C, Inoue A. Fe-metalloid metallic glasses with high magnetic flux density and high glass-forming ability. Mater Sci Forum. 2007;565:1361–6.
Wang G, Zhao DQ, Bai HY, Pan MX, Xia AL, Han BS, et al. Nanoscale periodic morphologies on the fracture surface of brittle metallic glasses. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;98:235501.
Wu Y, Li HX, Jiao ZB, Gao JE, Lu ZP. Size effects on the compressive deformation behaviour of a brittle Fe-based bulk metallic glass. Philos Mag Lett. 2010;90:403–12.
Lewandowski JJ, Wang WH, Greer AL. Intrinsic plasticity or brittleness of metallic glasses. Philos Mag Lett. 2005;85:77–87.
Rezaei-Shahreza P, Seifoddini A, Hasani S. Microstructural and phase evolutions: their dependent mechanical and magnetic properties in a Fe-based amorphous alloy during annealing process. J Alloys Compd. 2017;738:197–205.
Hofmann DC. Bulk metallic glasses and their composites: a brief history of diverging fields. J Mater. 2013;2013:1–8.
Zhang T, Liu F, Pang S, Li R. Ductile Fe-based bulk metallic glass with good soft-magnetic properties. Mater Trans. 2007;48:1157–60.
Guo SF, Qiu JL, Yu P, Xie SH, Chen W. Fe-based bulk metallic glasses: brittle or ductile? Appl Phys Lett. 2014;105:161901.
Gu XJ, Poon SJ, Shiflet GJ. Mechanical properties of iron-based bulk metallic glasses. J Mater Res. 2007;22:344–51.
Yang W, Liu H, Zhao Y, Inoue A, Jiang K, Huo J, et al. Mechanical properties and structural features of novel Fe-based bulk metallic glasses with unprecedented plasticity. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6233.
Li X, Kato H, Yubuta K, Makino A, Inoue A. Effect of Cu on nanocrystallization and plastic properties of FeSiBPCu bulk metallic glasses. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527:2598–602.
Naitoh Y, Bitoh T, Hatanai T, Makino A, Inoue A. Application of nanocrystalline soft magnetic Fe–M–B (M = Zr, Nb) alloys to choke coils. J Appl Phys. 1998;83:6332–4.
Yang X, Ma X, Li Q, Guo S. The effect of Mo on the glass forming ability, mechanical and magnetic properties of FePC ternary bulk metallic glasses. J Alloys Compd. 2013;554:446–9.
Dou L, Liu H, Hou L, Xue L, Yang W, Zhao Y, et al. Effects of Cu substitution for Fe on the glass-forming ability and soft magnetic properties for Fe-based bulk metallic glasses. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;358–359:23–6.
Bitoh T, Shibata D. Improvement of soft magnetic properties of [(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.20Si0.05]96Nb4 bulk metallic glass by B2O3 flux melting. J Appl Phys. 2008;103:07E702.
Stoica M, Roth S, Eckert J, Schultz L, Baró MD. Bulk amorphous FeCrMoGaPCB: preparation and magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater. 2005;290–291:1480–2.
Wang J, Li R, Hua N, Huang L, Zhang T. Ternary Fe–P–C bulk metallic glass with good soft-magnetic and mechanical properties. Scr Mater. 2011;65:536–9.
Zhang S, Sun D, Fu Y, Du H. Recent advances of superhard nanocomposite coatings: a review. Surf Coat Technol. 2003;167:113–9.
Joraid AA, El-oyoun MA, Alamri SN. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of amorphous Te51.3As45.7Cu3. Thermochim Acta. 2008;470:98–104.
Liavitskaya T, Vyazovkin S. Kinetics of thermal polymerization can be studied during continuous cooling. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2017;39:1700624.
Ke HB, Xu HY, Huang HG, Liu TW, Zhang P, Wu M, et al. Non-isothermal crystallization behavior of U-based amorphous alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2017;691:436–41.
Stanford VL, Vyazovkin S. Thermal decomposition kinetics of malonic acid in the condensed phase. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2017;56:7964–70.
Rezaei-Shahreza P, Seifoddini A, Hasani S. Non-isothermal kinetic analysis of nano-crystallization process in (Fe41Co7Cr15Mo14Y2C15)94B6 amorphous alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2017;652:119–25.
Wang X, Zeng M, Nollmann N, Wilde G, Wang J, Tang C. Thermal stability and non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of Pd82Si18 amorphous ribbon. AIP Adv. 2017;7:065206.
Seiffodini A, Zaremehrjardi S. Effects of heat treatment on crystallization behavior, microstructure and the resulting microhardness of a (Fe0.9Ni0.1)77Mo5P9C7.5B1.5 bulk metallic glass composite. J Non Cryst Solids. 2016;432:313–8.
Askari-paykani M, Ahmadabadi MN, Seiffodini A. The effect of liquid phase separation on the Vickers microindentation shear bands evolution in a Fe-based bulk metallic glass. Mater Sci Eng A. 2013;585:363–70.
Starink MJ. Activation energy determination for linear heating experiments: deviations due to neglecting the low temperature end of the temperature integral. J Mater Sci. 2006;42:483–9.
Starink M. The determination of activation energy from linear heating rate experiments: a comparison of the accuracy of isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta. 2003;404:163–76.
Friedman HL. Kinetics of thermal degradation of char-forming plastics from thermogravimetry. Application to a phenolic plastic. J Polym Sci Part C Polym Symp. 2007;6:183–95.
Lesnikovich AI, Levchik SV. A method of finding invariant values of kinetic parameters. J Therm Anal. 1983;27:89–93.
Hasani S, Shamanian M, Shafyei A, Behjati P, Szpunar JAA. Non-isothermal kinetic analysis on the phase transformations of Fe–Co–V alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2014;596:89–97.
Rezaei-Shahreza P, Seifoddini A, Hasani S. Thermal stability and crystallization process in a Fe-based bulk amorphous alloy: the kinetic analysis. J Non Cryst Solids. 2017;471:286–94.
Hasani S, Panjepour M, Shamanian M. Non-isothermal kinetic analysis of oxidation of pure aluminum powder particles. Oxid Met. 2013;81:299–313.
Ledeti A, Olariu T, Caunii A, Vlase G, Circioban D, Baul B, et al. Evaluation of thermal stability and kinetic of degradation for levodopa in non-isothermal conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:1881–8.
Prajapati R, Kasyap S, Patel AT, Pratap A. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of Zr52Cu18Ni14Al10Ti6 metallic glass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:21–33.
Uzun N, Colak AT, Emen FM, Cilgı GK. The thermal and detailed kinetic analysis of dipicolinate complexes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:1735–44.
Campostrini R, Mahmoud A, Leoni M, Scardi P. Activation energy in the thermal decomposition of MgH2 powders by coupled TG–MS measurements. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:225–40.
Criado JM. The use of the IKP method for evaluating the kinetic parameters and the conversion function of the thermal dehydrochlorination of PVC from non-isothermal data. Polym Degrad Stab. 2004;84:311–20.
Singh A, Sharma TC, Kishore P. Thermal degradation kinetics and reaction models of 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-based plastic-bonded explosives containing fluoropolymer matrices. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129:1403–14.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Aghili S, Panjepour M, Meratian M. Kinetic analysis of formation of boron trioxide from thermal decomposition of boric acid under non-isothermal conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:2443–55.
Gorbachev VM, Lad KN, Savalia RT, Pratap A, Dey GK, Banerjee S. A solution of the exponential integral in the non-isothermal kinetics for linear heating. J Therm Anal. 1975;8:349–50.
Hasani S, Panjepour M, Shamanian M. Effect of atmosphere and heating rate on mechanism of MoSi2 formation during self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:1073–81.
Souri D, Shahmoradi Y. Calorimetric analysis of non-crystalline TeO2–V2O5–Sb2O3. Determination of crystallization activation energy, Avrami index and stability parameter. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129:601–7.
Hasani S, Panjepour M, Shamanian M. A study of the effect of aluminum on MoSi2 formation by self-propagation high-temperature synthesis. J Alloys Compd. 2010;502:80–6.
Gong P, Yao K, Zhao S. Cu-alloying effect on crystallization kinetics of Ti41Zr25Be28Fe6 bulk metallic glass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121:697–704.
Coats AW, Redfern JP. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature. 1964;201:68–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaafari, Z., Seifoddini, A., Hasani, S. et al. Kinetic analysis of crystallization process in [(Fe0.9Ni0.1)77Mo5P9C7.5B1.5]100−xCux (x = 0.1 at.%) BMG. J Therm Anal Calorim 134, 1565–1574 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7372-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7372-y