Abstract
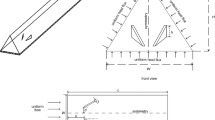
In this research, a numerical simulation is performed to investigate thermal and viscous irreversibilities for Al2O3–water nanofluid inside a duct equipped with porous baffles. The effects of different parameters including Reynolds number, Darcy number, solid volume fraction of nanoparticles, and the number of baffle were investigated on thermal and viscous entropy generation rates and Bejan number. The results indicated that the viscous and thermal entropy generations decrease by increasing the number of baffles for N > 4. The reductions in the viscous and thermal entropy generations are 32 and 14%, respectively as the number of baffles increases in the range of 4–16. Moreover, the thermal entropy generation is dominant term in most part of the duct except along the centerline of the duct in the space between bottom and top baffles where the velocity gradients are intense.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Baffle height (m)
- A :
-
Surface (m2)
- B c :
-
Boltzmann constant (–)
- Be :
-
Bejan number (–)
- C F :
-
Forchheimer coefficient (–)
- C P :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure (J kg−1 K−1)
- d f :
-
Molecular diameter of base fluid (nm)
- d p :
-
Nanoparticle diameter (nm)
- Da :
-
Darcy number (= K/H2) (–)
- H :
-
Width the duct (m)
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- K :
-
Permeability (m2)
- l BF :
-
Mean free path of water (–)
- L 1 :
-
Distance of baffle from input of the duct (m)
- L 2 :
-
Distance of baffle from output of the duct (m)
- N :
-
Number of baffle (–)
- N g :
-
Dimensionless local volumetric entropy generation rate (–)
- N t :
-
Dimensionless total entropy generation rate (–)
- \(p\) :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number (= υf/αf) (–)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number (= ρfUinH/μf) (–)
- S :
-
Baffle spacing (m)
- S g :
-
Entropy generation rate (W m−3 K−1)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u, v :
-
Velocity component in x and y directions, respectively (m s−1)
- x, y :
-
Rectangular coordinates components (m)
- w :
-
Baffle thickness (m)
- λ :
-
Binary parameter (–)
- δ :
-
Distance between particles (nm)
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- ε :
-
Porosity (–)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of the fluid (kg m−3)
- φ :
-
Solid volume fraction (–)
- B:
-
Brownian
- eff:
-
Effective
- f:
-
Fluid
- in:
-
Inlet
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- p:
-
Porous
- s:
-
Solid
- w:
-
Wall
References
Menasria F, Zedairia M, Moummi A. Numerical study of thermohydraulic performance of solar air heater duct equipped with novel continuous rectangular baffles with high aspect ratio. Energy. 2017;133:593–608.
Amirahmadi S, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Minimization of exergy losses in a trapezoidal duct with turbulator, roughness and beveled corners. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;107:533–43.
Sheikholeslami M, Gorji-Bandpy M, Ganji DD. Review of heat transfer enhancement methods: focus on passive methods using swirl flow devices. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2015;49(49):444–69.
Bovand M, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop penalty in porous solar heaters: numerical simulations. Sol Energ. 2016;123:145–59.
Zade NM, Akar S, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Thermo-hydraulic analysis for a novel eccentric helical screw tape insert in a three dimensional tube. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;110:413–21.
Li P, Liu Z, Liu W, Chen G. Numerical study on heat transfer enhancement characteristics of tube inserted with centrally hollow narrow twisted tapes. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;88:481–91.
Ellahi R. Special issue on recent developments of nanofluids. Appl Sci. 2018;8:192.
Shirvan KM, Ellahi R, Mamourian M, Moghiman M. Effect of wavy surface characteristics on heat transfer in a wavy square cavity filled with nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:1110–8.
Ellahi R, Tariq MH, Hassan M, Vafai K. On boundary layer magnetic flow of nano-Ferroliquid under the influence of low oscillating over stretchable rotating disk. J Mol Liq. 2017;229:339–45.
Esfahani JA, Akbarzadeh M, Rashidi S, Rosen MA, Ellahi R. Influences of wavy wall and nanoparticles on entropy generation in a plate heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;109:1162–71.
Rashidi S, Esfahani JA, Ellahi R. Convective heat transfer and particle motion in an obstructed duct with two side-by-side obstacles by means of DPM model. Appl Sci. 2017;7:431.
Hassn M, Zeeshan A, Majeed A, Ellahi R. Particle shape effects on ferrofuids flow and heat transfer under influence of low oscillating magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;443:36–44.
Ijaz N, Zeeshan A, Bhatti AM, Ellahi R. Analytical study on liquid-solid particles interaction in the presence of heat and mass transfer through a wavy channel. J Mol Liq. 2018;250:80–7.
Zeeshan A, Shehzad N, Ellahi R. Analysis of activation energy in Couette-Poiseuille flow of nanofluid in the presence of chemical reaction and convective boundary conditions. Results Phys. 2018;8:502–12.
Santra AK, Sen S, Chakraborty N. Study of heat transfer due to laminar flow of copper–water nanofluid through two isothermally heated parallel plates. Int J Therm Sci. 2009;48:391–400.
Bovand M, Rashidi S, Ahmadi G, Esfahani JA. Effects of trap and reeflct particle boundary conditions on particle transport and convective heat transfer for duct flow-A two-way coupling of Eulerian–Lagrangian model. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;108:368–77.
Mousavi SS, Hooman K. Heat and fluid flow in entrance region of a channel with staggered baffles. Energ Convers Manag. 2006;47:2011–9.
Promvonge P, Jedsadaratanachai W, Kwankaomeng S. Numerical study of laminar flow and heat transfer in square channel with 30° inline angled baffle turbulators. Appl Therm Eng. 2010;30:1292–303.
Rashidi S, Eskandarian M, Mahian O, Poncet S. Combination of nanofluid and inserts for heat transfer enhancement-Gaps and challenges. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7070-9.
Targui N, Kahalerras H. Analysis of a double pipe heat exchanger performance by use of porous baffles and nanofluids. Int J Mech Aeros Indus Mechatron Eng. 2014;8:1546–51.
Goudarzi K, Jamali H. Heat transfer enhancement of Al2O3-EG nanofluid in a car radiator with wire coil inserts. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;118:510–7.
Rashidi S, Akbarzadeh M, Karimi N, Masoodi R. Combined effects of nanofluid and transverse twisted-baffles on the flow structures, heat transfer and irreversibilities inside a square duct—a numerical study. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;130:135–48.
Akar S, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Second law of thermodynamic analysis for nanofluid turbulent flow around a rotating cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1189–200.
Ebrahimi A, Rikhtegar F, Sabaghan A, Roohi E. Heat transfer and entropy generation in a microchannel with longitudinal vortex generators using nanofluids. Energy. 2016;101:190–201.
Rashidi S, Zade NM, Esfahani JA. Thermo-fluid performance and entropy generation analysis for a new eccentric helical screw tape insert in a 3D tube. Chem Eng Process. 2017;117:27–37.
Akbarzadeh M, Rashidi S, Karimi N, Omar N. First and second laws of thermodynamics analysis of nanofluid flow inside a heat exchanger duct with wavy walls and a porous insert. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7044-y.
Maskaniyan M, Nazari M, Rashidi S, Mahian O. Natural convection and entropy generation analysis inside a channel with a porous plate mounted as a cooling system. Therm Sci Eng Prog. 2018;6:186–93.
Torabi M, Zhang K, Yang G, Wang J, Wu P. Heat transfer and entropy generation analyses in a channel partially filled with porous media using local thermal non-equilibrium model. Energy. 2015;82:922–38.
Torabi M, Dickson C, Karimi N. Theoretical investigation of entropy generation and heat transfer by forced convection of copper-water nanofluid in a porous channel—local thermal non-equilibrium and partial filling effects. Powder Technol. 2016;301:234–54.
Valipour MS, Rashidi S, Masoodi R. Magnetohydrodynamics flow and heat transfer around a solid cylinder wrapped with a porous ring. J Heat Transf. 2014;136:062601–9.
Rashidi A, Fathi H, Brilakis I. Innovative stereo vision-based approach to generate dense depth map of transportation infrastructure. Transp Res Rec J Transp Res Board. 2011;2215:93–9.
Rashidi A, Rashidi-Nejad H, Maghiar M. Productivity estimation of bulldozers using generalized linear mixed models. KSCE J Civil Eng. 2014;18(6):1580–9.
Rashidi A, Sigari MH, Maghiar M, Citrin D. An analogy between various machinelearning techniques for detecting construction materials in digital images. KSCE J Civil Eng. 2016;20(4):1178–88.
Rashidi A, Jazebi F, Brilakis I. Neurofuzzy genetic system for selection of construction project managers. J Constr Eng Manag. 2011;137(1):17–29.
Albojamal A, Vafai K. Analysis of single phase, discrete and mixture models, in predicting nanofluid transport. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:225–37.
Lee DY, Vafai K. Analytical characterization and conceptual assessment of solid and fluid temperature differentials in porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1999;42:423–35.
Valipour MS, Masoodi R, Rashidi S, Bovand M, Mirhosseini M. A numerical study on convection around a square cylinder using Al2O3-H2O nanofluid. Therm Sci. 2014;18(4):1305–14.
Zhou S-Q, Ni R. Measurement of the specific heat capacity of water-based Al2O3 nanofluid. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92(9):093123.
Masoumi N, Sohrabi N, Behzadmehr A. A new model for calculating the effective viscosity of nanofluids. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2009;42(5):055501.
Chon CH, Kihm KD, Lee SP, Choi SU. Empirical correlation finding the role of temperature and particle size for nanofluid (Al2O3) thermal conductivity enhancement. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;87(15):153107.
Patankar SV. Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. New York: Hemisphere; 1980.
Heyhat MM, Kowsary F, Rashidi AM, Momenpour MH, Amrollahi A. Experimental investigation of laminar convective heat transfer and pressure drop of water-based Al2O3 nanofluids in fully developed flow regime. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2013;44:483–9.
Davari A, Maerefat M. Numerical analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in entrance and fully developed regions of a channel with porous baffles. J Heat Transf. 2016;138:062601.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, under Grant No. 45933.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamsabadi, H., Rashidi, S. & Esfahani, J.A. Entropy generation analysis for nanofluid flow inside a duct equipped with porous baffles. J Therm Anal Calorim 135, 1009–1019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7350-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7350-4