Abstract
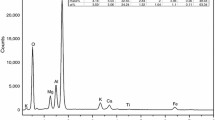
In this work, CaCl2·6H2O/sepiolite was successfully designed and synthesized as a novel form-stable composite phase change material by vacuum impregnation method, using sepiolite as a sustainer and CaCl2·6H2O as phase change material. Scanning electron microscope and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy measurements display that CaCl2·6H2O is filled into the porous structure of sepiolite by physical interactions. Phase transformation behavior and thermal stability were revealed from differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis, respectively. Results show that the melting enthalpy of the composite phase change material containing 70% CaCl2·6H2O can achieve 87.9 J g−1, and the composite PCM has a good thermal stability in the temperature range from 25 to 100 °C. Meanwhile, the crystal structure of CaCl2·6H2O is maintained in the porous structure of sepiolite observed by X-ray diffraction. It means that sepiolite reduces the super-cooling of CaCl2·6H2O which ensures the good phase change behavior of the composites. These results exhibit that the CaCl2·6H2O/sepiolite composite phase change material possesses high latent heat. Moreover, low cost of the sepiolite enables the composites to be a good candidate for latent heat storage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang WD, Zhang GD, Sun HX, Chen PS, Zhu ZQ, Li A. Graphene–nickel/n-carboxylic acids composites as form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Sol Energ Mat Sol C. 2015;132:425–30.
Chen CZ, Liu WM, Wang HW, Peng KL. Synthesis and performances of novel solid–solid phase change materials with hexahydroxy compounds for thermal energy storage. Appl Energ. 2015;152:198–206.
Qiu XL, Song GL, Chu XD, Li XZ, Tang GY. Microencapsulated n-alkane with p(n-butyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) shell as phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy. 2013;91:212–20.
Sarı A, Alkan C, Biçer A, Altuntas A, Bilgin C. Micro/nanoencapsulated n-nonadecane with poly (methyl methacrylate) shell for thermal energy storage. Energ Convers Manage. 2014;86:614–21.
Krupa I, Nógellová Z, Špitalský Z, Malíková M, Sobolčiak P, Abdelrazeq HW, Ouederni M, Karkri M, Janigová L, Al-Maadeed MASA. Positive influence of expanded graphite on the physical behavior of phase change materials based on linear low-density polyethylene and paraffin wax. Thermochim Acta. 2015;614:218–25.
Qiu XL, Lu LX, Han PG, Tang GY, Song GL. Fabrication, thermal property and thermal reliability of microencapsulated paraffin with ethyl methacrylate-based copolymer shell. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:1291–9.
Ferrer G, Solé A, Barreneche C, Martorell I, Cabeza LF. Review on the methodology used in thermal stability characterization of phase change materials. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2015;50:665–85.
Yuan YP, Zhang HQ, Zhang N, Sun QR, Cao XL. Effect of water content on the phase transition temperature, latent heat and water uptake of PEG polymers acting as endothermal-hydroscopic materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:699–708.
Akeiber H, Nejat P, Majid MZA, Wahid MA, Jomehzadeh F, Famileh IZ, Calautit JK, Hughes BR, Zaki SA. A review on phase change material (PCM) for sustainable passive cooling in building envelopes. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2016;60:1470–97.
Li G, Zhang BB, Li X, Zhou Y, Sun QG, Yun Q. The preparation, characterization and modification of a new phase change material: CaCl2· 6H2O–MgCl2·6H2O eutectic hydrate salt. Sol Energ Mat Sol C. 2014;126:51–5.
Jradi M, Gillott M, Riffat S. Simulation of the transient behaviour of encapsulated organic and inorganic phase change materials for low-temperature energy storage. Appl Therm Eng. 2013;59(1):211–22.
Tyagi VV, Buddhi D. Thermal cycle testing of calcium chloride hexahydrate as a possible PCM for latent heat storage. Sol Energ Mat Sol C. 2008;92(8):891–9.
Zhou ZH, Zhang ZM, Zuo J, Huang K, Zhang LY. Phase change materials for solar thermal energy storage in residential buildings in cold climate. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2015;48:692–703.
Singh SP, Bhat V. Applications of organic phase change materials for thermal comfort in buildings. Rev Chem Eng. 2014;30(5):521–38.
Zeng JL, Zheng SH, Yu SB, Zhu FR, Gan J, Zhu L, Xiao ZL, Zhu XY, Zhu Z, Sun LX, Cao Z. Preparation and thermal properties of palmitic acid/polyaniline/exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets form-stable phase change materials. Appl Energ. 2014;115:603–9.
Zeng JL, Zhu FR, Yu SB, Xiao ZL, Yan WP, Zheng SH, Zhang L, Sun LX, Cao Z. Myristic acid/polyaniline composites as form stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Sol Energ Mat Sol C. 2013;114:136–40.
Jiang DH, Li AG, Shi FE, Ren RS. Mineral sepiolite energy-saving residential materials. Adv Mater Res. 2011;178:185–90.
Hibino T, Tsunashima A, Yamazaki A, Otsuka R. Model calculation of sepiolite surface areas. Clay Clay Miner. 1995;43(4):391–6.
Rodríguez A, Ovejero G, Mestanza M, García J. Removal of dyes from wastewaters by adsorption on sepiolite and pansil. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2010;49(7):3207–16.
Zhang KL, Pan JN, Tang CK, Shen J, Peng G, Qiu D. Study on adsorption of octenylsuccinate by sepiolite. Desalin Water Treat. 2016;57(19):8765–75.
Mora M, Carmona MA, Jiménez-Sanchidrián C, López MI, Ruiz JR. Sepiolite as environmental friendly and reusable catalyst for the selective synthesis of (E)-nitrostyrenes. React Kinet Mech Cat. 2010;99(2):303–9.
Frost RL, Ding Z. Controlled rate thermal analysis and differential scanning calorimetry of sepiolites and palygorskites. Thermochim Acta. 2003;397(1):119–28.
Miura A, Nakazawa K, Takei T, Kumada N, Kinomura N, Ohki R, Koshiyama H. Acid-, base-, and heat-induced degradation behavior of Chinese sepiolite. Ceram Int. 2012;38(6):4677–84.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51102230, 51462006), and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 2014GXNSFAA118401, 2013GXNSFBA019244).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, W., Zhang, H., Xia, Y. et al. Preparation and thermophysical properties of a novel form-stable CaCl2·6H2O/sepiolite composite phase change material for latent heat storage. J Therm Anal Calorim 131, 57–63 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6170-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6170-2