Abstract
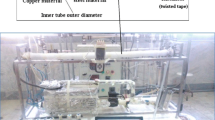
In this article, thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol–water-based TiO2 nanofluids has been modeled by artificial neural network. For this purpose, thermal conductivity of nanofluids with volume fractions of 0.2–1 % has been collected in temperatures of 30–70 °C. These data were modeled by artificial neural networks. So two common types of neural networks were used, and the results were compared with each other. One of these networks was multilayer perceptron, and the other one was radial basis approximation. Finally, an experimental relationship was suggested for calculating thermal conductivity of this nanofluid and the results were compared with the results of radial basis neural network. This comparison shows that neural networks are very powerful in modeling the nanofluids experimental data and are able to follow the patterns of these data with a high precision.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghadimi A, Saidur R, Metselaar H.S.C. A review of nanofluid stability properties and characterization in stationary conditions. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:4051–4068.
Azwadi N, Sidik C, Mohammed HA, Alawi OA, Samion S. A review on preparation methods and challenges of nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;54:115–125.
Munkhbayar B, Tanshen MR, Jeoun J, Chung H, Jeong H. Surfactant-free dispersion of silver nanoparticles into MWCNT-aqueous nanofluids prepared by one-step technique and their thermal characteristics. Ceram Int. 2013;39:6415–25.
Kumar SA, Meenakshi KS, Narashimhan BRV, Srikanth S, Arthanareeswaran G. Synthesis and characterization of copper nanofluid by a novel one-step method. Mater Chem Phys. 2009;113:57–62.
Ponmani S, William JKM, Samuel R, Nagarajan R, Sangwai JS. Formation and characterization of thermal and electrical properties of CuO and ZnO nanofluids in xanthan gum. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2014;443:37–43.
Hemmat Esfe M, Yan W-M, Akbari M, Karimipour A, Hassani M. Experimental study on thermal conductivity of DWCNT-ZnO/water-EG nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;68:248–51.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S. Experimental investigation and proposed correlations for temperature- dependent thermal conductivity enhancement of ethylene glycol based nanofluid containing ZnO nanoparticles. J Heat Mass Transf Res. 2014;1:47–54.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Biglari M, Rostamian H. Experimental investigation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-Al2O3/water: A statistical approach. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;69:29–33.
Hemmat Esfe M, Hassani Ahangar MR, Rejvani M, Toghraie D, Hajmohammad MH. Designing an artificial neural network to predict dynamic viscosity of aqueous nanofluid of TiO2 using experimental data. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;75:192–6.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Yan W-M, Afrand M, Sina N. Study on thermal conductivity of water-based nanofluids with hybrid suspensions of CNTs/Al2O3 nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:1–6.
Hemmat Esfe M, Afrand M, Yan W, Yarmand H, Toghraie D, Dahari M. Effects of temperature and concentration on rheological behavior of MWCNTs/SiO2(20-80)-SAE40 hybrid nano-lubricant. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:133–138.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Asadi A, Karimipour A, et al. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of Mg (OH) 2-ethylene glycol nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120:1145–9.
Hemmat Esfe M, Naderi A, Akbari M, Afrand M, Karimipour A. Evaluation of thermal conductivity of COOH-functionalized MWCNTs/water via temperature and solid volume fraction by using experimental data and ANN methods. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015;121:1273–8.
Rayatzadeh HR, Saffar-Avval M, Mansourkiaei M, Abbassi A. Effects of continuous sonication on laminar convective heat transfer inside a tube using water–TiO2 nanofluid. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2013;48:8–14.
Buonomo B, Manca O, Marinelli L, Nardini S. Effect of temperature and sonication time on nanofluid thermal conductivity measurements by nano-flash method. Appl Therm Eng. 2015;91:181–90.
Mahbubul IM, Shahrul IM, Khaleduzzaman SS, Saidur R, Amalina MA, Turgut A. Experimental investigation on effect of ultrasonication duration on colloidal dispersion and thermophysical properties of alumina–water nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;88:73–81.
Zawrah MF, Khattab RM, Girgis LG, El Daidamony H, Abdel Aziz RE. Stability and electrical conductivity of water-base Al2O3 nanofluids for different applications. HBRC J. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.hbrcj.2014.12.001.
Hemmat M, Akbar A, Arani A, Rezaie M, Yan W, Karimipour A, et al. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:189–95.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Wongwises S, Toghraie D. An experimental study on the effect of diameter on thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Fe/water nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1817–24.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Mahian O, Wongwises S, Hemmat M, Saedodin S, et al. Efficiency of ferromagnetic nanoparticles suspended in ethylene glycol for applications in energy devices: Effects of particle size, temperature, and concentration. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;58:138–146.
Hemmat Esfe M, Afrand M, Karimipour A, Yan W-M, Sina N. An experimental study on thermal conductivity of MgO nanoparticles suspended in a binary mixture of water and ethylene glycol. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;67:173–5.
Estellé P, Halelfadl S, Maré T. Lignin as dispersant for water-based carbon nanotubes nanofluids: impact on viscosity and thermal conductivity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;57:8–12.
Xia G, Jiang H, Liu R, Zhai Y. Effects of surfactant on the stability and thermal conductivity of Al2O3/de-ionized water nanofluids. Int J Therm Sci. 2014;84:118–24.
Hemmat Esfe M, Afrand M, Wongwises S, Naderi A, Asadi A, Rostami S. Applications of feedforward multilayer perceptron artificial neural networks and empirical correlation for prediction of thermal conductivity of Mg(OH)2–EG using experimental data. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;67:46–50.
Hemmat Esfe M, Afrand M, Yan W-M, Akbari M. Applicability of artificial neural network and nonlinear regression to predict thermal conductivity modeling of Al2O3–water nanofluids using experimental data. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:246–249.
Hemmat Esfe M, Wongwises S, Naderi A, Asadi A, Safaei MR, Rostamian H, Dahari M, Karimipour A. Thermal conductivity of Cu/TiO2–water/EG hybrid nanofluid: experimental data and modeling using artificial neural network and correlation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:100–104.
Hemmat Esfe M, Rostamian H, Afrand M, Karimipour A, Hassani M. Modeling and estimation of thermal conductivity of MgO–water/EG (60:40) by artificial neural network and correlation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;68:98–103.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Sina N, Afrand M. Designing an artificial neural network to predict thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of ferromagnetic nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;68:50–7.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Naderi A, Alirezaie A, Karimipour A, Wongwises S. Modeling of thermal conductivity of ZnO-EG using experimental data and ANN methods. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;63:35–40.
Hojjat M, Etemad SGG, Bagheri R, Thibault J. Thermal conductivity of non-Newtonian nanofluids : Experimental data and modeling using neural network. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:1017–23.
Chandra Sekhara Reddy M, Vasudeva Rao V. Experimental studies on thermal conductivity of blends of ethylene glycol-water-based TiO2 nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;46:31–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemmat Esfe, M. Designing an artificial neural network using radial basis function (RBF-ANN) to model thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol–water-based TiO2 nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim 127, 2125–2131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5725-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5725-y