Abstract
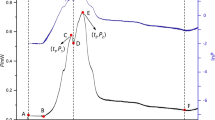
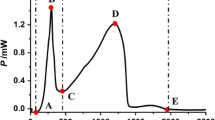
The root of Wikstroemia indica has been widely used in China as folk medicine for the treatment for arthritis, whooping cough, cancer, and bacillosis. However, the constituents which have antibacterial activity were not clarified yet. In this study, the antibacterial effect of five extracts from W. indica on Escherichia coli was evaluated by microcalorimetry coupled with agar dilution method. The ethanol extract of W. indica was isolated with organic solvents of different polarities including petroleum (P.E.) extract, chloroform (CHCl3) extract, ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract, n-butylalcohol (nBuOH) extract, and residue extract. The metabolic profiles of E. coli growth at 37 °C were measured by microcalorimetry. According to the principal component analysis, k 1, k 2, and P 1 were obtained from heat flow power–time (HFP–time) curve. The agar dilution method was performed to verify the results of thermodynamics. The results of microcalorimetric experiment indicated that EtOAc fraction demonstrated the strongest antibacterial activity with half-inhibitory concentration of 92.4 μg mL−1. Meanwhile, similar results were gained from the common method of agar diffusion, which suggested that EtOAc extract could be further developed as antibacterial bioactive fraction of W. indica. Altogether, microcalorimetry is a useful technique to provide sufficient quantitative information and evaluate the antimicrobial effect with its sensitive.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kato A, Hashimoto Y, Kidokoro M. (+)-Nortrachelogenin a new pharmacologically active lignan from Wikstroemia indica. J Nat Prod. 1979;42:159–62.
Wang LY, Unehara T, Kitanaka S. Anti-inflammatory activity of new guaiane type sesquiterpene from Wikstroemia indica. Chem Pharm Bull. 2005;53:137–9.
Hu K, Kobayashi H, Dong A, Iwasaki S, Yao X. Antifungal antimitotic and anti-HIV-1 agents from the roots of Wikstroemia indica. Planta Med. 2000;66:564–7.
Nunome S, Ishiyama A, Kobayashi M, Otoguro K, Kiyohara H, Yamada H, Omura S. In vitro antimalarial activity of biflavonoids from Wikstroemia indica. Planta Med. 2004;70:76–8.
Yang ZY, Du ZM. Study on antibacterial effect of Wikstroemia indica decoction. Journal of Harbin Pharmaceutical. 2006;40:362–4.
Braissant O, Wirz D, Gopfert B, Daniels AU. Use of isothermal microcalorimetry to monitor mi crobial activities. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010;303:1–8.
Wang J, Cheng DH, Zeng N, Xia HL, Fu Y, Yan D, Zhao YL, Xiao XH. Microcalorimetric study of the effect of Benzoinum and Styrax on the growth of Escherichia coli. Nat Prod Res. 2011;25:457–63.
Ding L, Li X, Liu P, Li SQ, Lv JL. Study of the Action of Se and Cu on the Growth Metabolism of Escherichia coli by Microcalorimetry. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2010;137:364–72.
Zheng QF, Zhao YL, Wang JB, Liu TT, Zhang B. Spectrum-effect relationships between UPLC fingerprints and bioactivities of crude secondary roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux (Fuzi) and its three processed products on mitochondrial growth coupled with canonical correlation analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;153:615–23.
Zhao YL, Wang JB, Zhang P, Li RS, Xiao XH. Microcalorimetric study of the opposing effects of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1 on the growth of mice splenic lymphocytes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;104:357–63.
Dai CM, Wang JB, Peng C, Xiao XH. Investigation of anti-microbial activity of catechin on Escherichia coli growth by microcalorimetry. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;30:284–8.
Kong WJ, Jin C, Xiao XH, Zhao YL, Li ZL, Zhang P, Liu W, Li XF. Comparative study of effects of two bile acid derivatives on Staphylococcus aureus by multiple analytical methods. J Hazard Mater. 2010;179:742–7.
Vor T, Dyckmans J, Flessa H, Beese F. Use of microcalorimetry to study microbial activity during the transition from oxic to anoxic conditions. Biol Fert Soils. 2002;36:66–71.
Li X, Liu Y, Wu J, Liang HG, Qu SS. Microcalorimetric study of Staphylococcus aureus growth affected by selenium compounds. Thermochim Acta. 2002;387:57–61.
Liu SX, Zhao YL, Zeng N, Liu TT, Zhang YM, Han B, Li JY, Wang LF, Wang RL, Gong M, Li YG, Xiao XH. Anti-bacterial effect of four extracts from leaves of Dracontomelon dao on Escherichia coli growth using microcalorimetry coupled with principal component analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:491–7.
Pierce KM, Hope JL, Johnson KJ, Wright BW, Synovec RE. Classification of gasoline data obtained by gas chromatography using a piecewise alignment algorithm combined with feature selection and principal component analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1096:101–10.
Kong WJ, Wang JB, Xing XY, Jin C, Xiao XH, Zhao YL, Zhang P, Zang QC, Li ZL. Screening for novel antibacterial agents based on the activities of compounds on metabolism of Escherichia coli: a microcalorimetric study. J Hazard Mater. 2011;185:346–52.
Li JX, Wang JY, Zhang LL, Yan D, Wang RL, Li BC, Xiao XH. Microcalorimetric investigation on the interaction of six alkaloids from Rhizoma Coptidis. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 2013;48:1807–11.
Xie CL, Tang HK, Song ZH, Qu SS. Microcalorimetric study of bacterial growth. Thermochim Acta. 1988;123:33–41.
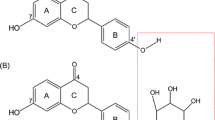
Lu CL, Zhu L, Piao JH, Jiang JG. Chemical compositions extracted from Wikstroemia indica and their multiple activities. Pharmaceutical Biol. 2012;50:225–31.
Trampuz A, Salzmann S, Antheaume J, Daniels AU. Microcalorimetry: a novel method for detection of microbial contamination in platelet products. Transfusion. 2007;47:1643–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Qu, F., Wang, J. et al. Antibacterial effect of different extracts from Wikstroemia indica on Escherichia coli based on microcalorimetry coupled with agar dilution method. J Therm Anal Calorim 123, 1583–1590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4999-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4999-9