Abstract
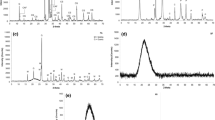
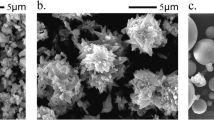
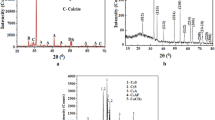
The effect of nano-metakaolin (NMK) addition on hydration characteristics of fly ash (FA) blended cement mortar was experimentally investigated. The amorphous or glassy silica, which is the major component of a pozzolan, reacts with the calcium hydroxide liberated during calcium silicate hydration. It is believable to add FA and NMK particles in order to make high performance concrete. The physico-mechanical properties of FA blended cement mortars made with different percentages of NMK were investigated. The experimental results showed that the compressive and flexural strengths of mortars containing NMK are higher than those of FA blended cement mortar at 60 days of hydration age. It is demonstrated that the nanoparticles enhances strength than FA. In addition, the hydration process was monitored using scanning electron microscopy and thermal gravimetric analysis (TG). The results of these examinations indicate that NMK behaves not only as a filler to improve microstructure, but also as an activator to promote the pozzolanic reaction.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM C 618-85. Standard specifications for fly ash and raw or calcined natural pozzolan for use as mineral admixture in Portland cement concrete. Philadelphia: ASTM; 1985.
Ahmaruzzaman M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2010;36:327–63.
Saraswathy V, Muralidharan S, Thangavel K, Srinivasan S. Influence of activated fly ash on corrosion-resistance and strength of concrete. Cem Concr Compos. 2003;25:673–80.
Ganjian E, Pouya HS. The effect of Persian Gulf tidal zone exposure on durability of mixes containing silica fume and blast furnace slag. Constr Build Mater. 2009;23:644–52.
Wang S, Liamazos E, Baxter L, Fonseca F. Durability of biomass fly ash concrete: freezing and thawing and rapid chloride permeability tests. Fuel. 2008;87:359–64.
Pacewska B, Blonkowski G, Wiliska I. Investigation of the influence of different fly ashes on cement hydration. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;86:179–86.
Monteiro PJM, Kirchheim AP, Chae S, Fischer P, MacDowell AA, Schaible E, Wenk HR. Characterizing the nano and micro structure of concrete to improve its durability. Cem Concr Compos. 2009;31:577–84.
Li H, Xiao H, Yuan J, Ou J. Microstructure of cement mortar with nano-particles. Composites B. 2004;35:185–9.
Shih J, Chang T, Hsiao T. Effect of nanosilica on characterization of Portland cement composite. Mater Sci Eng A. 2006;424:266–74.
Morsy MS, Aglan H. Development and characterization of nanostructured-perlite-cementitious surface compounds. J Mater Sci. 2007;42(24):10196–202.
Shebl SS, Allie L, Morsy MS, Aglan HA. Mechanical behavior of activated nano silicate filled cement binders. J Mater Sci. 2009;44:1600–6.
Kosmatka SH, Kerkhoff B, Panarese WC. Design and control of concrete mixtures. Skokie: Portland Cement Association; 2002.
Amin MS, Abo-El-Enein SA, Abdel Rahman A, Alfalous K. Artificial pozzolanic cement pastes containing burnt clay with and without silica fume. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:1105–15.
He X, Shi X. Chloride permeability and microstructure of Portland cement mortars incorporating nanomaterials. In: Transportation research record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, No. 2070. Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, Washington, DC, 2008, pp. 13–21.
Morsy MS, Al-Salloum YA, Abbas H, Alsayed SH. Behavior of blended cement mortars containing nano-metakaolin at elevated temperatures. Constr Build Mater. 2012;35:900–5.
Björnström J, Martinelli A, Matic A, Börjesson L, Panas I. Accelerating effects of colloidal nano-silica for beneficial calcium–silicate–hydrate formation in cement. Chem Phys Lett. 2004;392(1–3):242–8.
Li H, Zhang M, Ou J. Abrasion resistance of concrete containing nano-particles for pavement. Wear. 2006;260:1262–6.
Li G. Properties of high-volume fly ash concrete incorporating nano-SiO2. Cem Concr Res. 2004;34:1043–9.
Shih J-Y, Chang Ta-P, Hsiao T-C. Effect of nanosilica on characterization of Portland cement composite. Mater Sci Eng. 2006;24:266–74.
Jo BW, Kim CH, Tae G, Park JB. Characteristics of cement mortar with nano-SiO2 particles. Cem Concr Compos. 2007;21:1351–5.
Park CK, Nohb MH, Park TH. Rheological properties of cementitious materials containing mineral admixtures. Cem Concr Res. 2005;35:842–9.
Qing Y, Zenan Z, Deyu K, Rongshen C. Influence of nano-SiO2 addition on properties of hardened cement paste as compared with silica fume. Constr Build Mater. 2007;21:539–45.
ASTM C 150-04, Standard Specification for Portland Cement.
Henning O, El-Didamony H, Hanna KM, Wiss Z. Hochsch Archit. Weimar: Banwes; 1972.
ASTM C642 - 13 Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete.
Jain J, Neithalath N. Analysis of calcium leaching behaviour of plain and modified cement pastes in pure water. Cem Concr Compos. 2009;31:176–85.
Saad M, Abo-El-Enein SA, Hanna GB, Kotkata MF. Effect of temperature on physical and mechanical properties of concrete containing silica fume. Cem Concr Res. 1996;26(5):669–75.
Acknowledgements
The Authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding of this research through the research group project No. RGP-VPP-104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsy, M.S., Al-Salloum, Y., Almusallam, T. et al. Effect of nano-metakaolin addition on the hydration characteristics of fly ash blended cement mortar. J Therm Anal Calorim 116, 845–852 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3512-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3512-6