Abstract
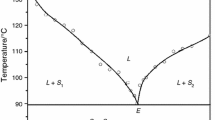
Solid–liquid phase equilibrium data of three binary organic systems, namely, 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde (HB)—4-bromo-2-nitroanilne (BNA), benzoin (BN)—resorcinol (RC) and urea (U)—1,3-dinitrobenzene (DNB), were studied by the thaw–melt method. While the former two systems show the formation of simple eutectic, the third system shows the formation of a monotectic and a eutectic with a large immiscibility region where two immiscible liquid phases are in equilibrium with a liquid of single phase. Growth kinetics of the pure components, the monotectic and the eutectics, studied by measuring the rate of movement (v) of solid–liquid interface in a thin U-tube at different undercoolings (ΔT) suggests the applicability of the Hillig–Turnbull’s equation: v = u (ΔT)n, where v and n are the constants depending on the nature of the materials involved. The thermal properties of materials such as heat of mixing, entropy of fusion, roughness parameter, interfacial energy, and excess thermodynamic functions were computed from the enthalpy of fusion values, determined by differential scanning calorimeter (Mettler DSC-4000) system. The role of solid–liquid interfacial energy on morphologic change of monotectic growth has also been discussed. The microstructures of monotectic and eutectics were taken which showed lamellar and federal features.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herlach DM, Cochrane RF, Egry I, Fecht HJ, Greer AL. Containerless processing in the study of metallic melts and their solidification. Int Mater Rev. 1993;38:273–347.
Predel B. Constitution and thermodynamics of monotectic alloys: a survey. J Phase Equilibr. 1997;18(4):327–37.
Trivedi R, Kurz W. Dendritic growth. Int Mater Rev. 1994;39(2):49–74.
Majumdar B, Chattopadhyay K. The Rayleigh instability and the origin of rows of droplets in the monotectic microstructure of zinc–bismuth alloys. Met Trans A. 1996;27(A):2053–7.
Ji H-Z, Meng X-C, Zhao H-K. (Solid + liquid) equilibrium of (4-chloro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione + 5-chloro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione). J Chem Eng Data. 2010;55:2590–3.
Gupta P, Agrawal T, Das SS, Singh NB. Solvent free reactions, Reactions of nitrophenols in 8-hydroxyquinoline–benzoic acid eutectic melt. J Therm Anal Calorim. doi:10.1007/s10973-010-1255-1.
Fu J, Rice JW, Suuberg EM. Phase behavior and vapor pressures of the pyrene + 9,10-dibromoanthracene system. Fluid Phase Equilibria. 2010;298:219–24.
Peters CA, Wammer KH, Knightes CD. Multicomponent NAPL solidification thermodynamics. Transp Porous Media. 2000;38:57–77.
Rice JW, Suuberg EM. Thermodynamic study of (anthracene + aenzo[a]pyrene) solid mixtures. J Chem Thermodyn. 2010;42:1356–60.
Farges JP. Organic conductors. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.; 1994.
Gunter P. Nonlinear optical effects and materials. Berlin: Springer; 2000. p. 540.
Singh NB, Henningsen T, Hopkins RH, Mazelsky R, Hamacher RD, Supertzi EP, Hopkins FK, Zelmon DE, Singh OP. Nonlinear optical characteristics of binary organic system. J Cryst Growth. 1993;128:976–80.
Dwivedi Y, Kant S, Rai RN, Rai SB. Efficient white light generation from 2,3-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-quinoxaline complex. Appl Phys B. 2010;101:639–42.
Choi J, Aggarwal MD, Wang WS, Penn BG, Frazier DO. Binary organic single crystals for nonlinear optical application. J Korean Phys Soc. 1998;32:S433–5.
Rai RN, Lan CW. Crystal structure and properties of new organic nonlinear optical material. J Mater Res. 2002;17(7):1587–91.
Derby B, Favier JJ. A criterion for the determination of monotectic structure. Acta Met. 1983;7:1123–30.
Ecker A, Frazier DO, Alexander JID. Fluid flow in solidifying monotectic alloys. Metall Trans. 1989;20A:2517–27.
Dean JA. Lange’s handbook of chemistry. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1985.
Sharma KP, Rai RN. Novel organic monotectic alloy and its thermal, physicochemical, and microstructural studies. J Mater Sci. 2011;46:1551–6.
Rai RN. Phase diagram, optical, nonlinear optical, and physicochemical studies of the organic monotectic system: pentachloropyridine-succinonotrile. J Mater Res. 2004;19(5):1348–55.
Rai US, Rai RN. Physical chemistry of organic eutectic and monotectic: hexamethylbenzene-succinonitrile system. Chem Mater. 1999;11(11):3031–6.
Kant S, Rai RN. Solid–liquid equilibrium and thermochemical studies of organic analogue of metal-nonmetal system: succinonitrile-pentachloronitrobenzene. Thermochim Acta. 2011;512:49–54.
Rai US, Rai RN. Physical chemistry of organic eutectics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1998;53:883–93.
Rai RN, Mudunuri SR, Reddi RSB, Satuluri VSA Kumar, Ganeshmoorthy S Gupta PK. Crystal growth and nonlinear optical studies of m-dinitrobenzene doped urea. J Cryst Growth. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2011.02.019.
Hillig WB, Turnbull D. Theory of Crystal growth in undercooled pure liquids. J Chem Phys. 1956;24:914.
Winegard WC, Majka S, Thall BM, Chalmers B. Eutectic solidification in metals. Can J Chem. 1951;29:320–7.
Rai RN, Rai US. Solid–liquid equilibrium and thermochemical properties of organic eutectic in a monotectic system. Thermochim Acta. 2000;363:23–8.
Rai US, Rai RN. Physical chemistry of the organic analog of metal–metal eutectic and monotectic alloys. J Cryst Growth. 1998;191:234–42.
Singh N, Singh Narsingh B, Rai US, Singh OP. Structure of eutectic melts; binding organic systems. Thermochim Acta. 1985;95:291–3.
Rai RN, Rai US, Varma KBR. Thermal, miscibility gap and microstructural studies of organic analog of metal-nonmetal system: p-dibromobenzene-succinonitrile. Thermochim Acta. 2002;387:101–7.
Eustathopoulos N, Nicholas MG, Drevet B. Wettability at high temperatures. Pergamon, Oxford: Pergamon Materials Series; 1999.
Christian JW. The theory of phase transformation in metals and alloys. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1965. p. 992.
Kaukler WF, Frazier DO. Observations of a monotectic solidification interface morphology. J Cryst Growth. 1985;71:340–5.
Singh NB, Rai US, Singh OP. Chemistry of eutectic and monotectic; phenanthrene-succinonitrile system. J Cryst Growth. 1985;71:353–60.
Hunt JD, Jackson KA. Binary eutectic solidification. Trans Met Soc AIME. 1966;236:843–52.
Chadwick GA. Monotectic solidification. Br J Appl Phys. 1965;16:1095–7.
Cahn JW. Critical point wetting. J Chem Phys. 1977;66:3667–72.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Board of Research in Nuclear Science, Department of Atomic Energy, Mumbai, India for thier financial support, and the Head, Department of Chemistry for providing the necessary infrastructure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddi, R.S.B., Satuluri, V.S.A.K., Rai, U.S. et al. Thermal, physicochemical and microstructural studies of binary organic eutectic systems. J Therm Anal Calorim 107, 377–385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1478-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1478-9