Abstract
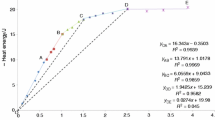
Isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry was adopted as a novel characterization method to investigate the polymerization processes of silica when the combination of silica sol and potassium sodium silicate was stirred at 25.0, 35.0, and 45.0 °C. Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters were simultaneously obtained. The enthalpy change was greater at each higher temperature. The reaction orders (m, n) instantaneously varied, up and down in an alternate manner. At 25.0, 35.0, and 45.0 °C, the rate constants were different; the maximum rate constant occurred at 25.0 °C. These phenomena reflect a two-stage oligomeric mechanism of silica monomers. The measurements of particle size showed the complex chemical composition of aqueous silicates, which can be qualitatively designated by the particle size distribution in two parts. The results further indicate that the colloidal particles in the mixed silica sol and silicates first dissolved. Then the “active” silica in the silicates redeposited to make a distinct particle size distribution influenced by K+ and Na+ ions as well as by temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- M :
-
The molar ratio of silica to alkali metal oxide in silicates
- Q T :
-
Total enthalpy change for a mixing reaction when it has gone to completion (J)
- ΔH :
-
Changes in enthalpy (kJ mol−1)
- A mol :
-
The initial number of moles of CH83–125 silica sol (mol)
- B mol :
-
The initial number of moles of potassium sodium silicate (mol)
- [A]0 :
-
The initial molar concentration of CH83–125 silica sol (mol dm−3)
- [B]0 :
-
The initial molar concentration of potassium sodium silicate (mol dm−3)
- V :
-
The total volume of CH83–125 silica sol and potassium sodium silicate (dm3)
- Φ:
-
Heat flow (mW)
- q :
-
Heat output (J)
- k :
-
Rate constant ((mol dm−3)1−m−n s−1)
- m :
-
The reaction order of CH83–125 silica sol
- n :
-
The reaction order of potassium sodium silicate
References
Jiao GF, Pu M, Liu MJ, Chen BH. Establishment and applications of selective aggregation model of silica sol particles. Mater Lett. 2007;61:4314–7.
Tsai MS, Wu WC. Aluminum modified colloidal silica via sodium silicate. Mater Lett. 2004;58:1881–4.
García-Cerda LA, Mendoza-González O, Pérez-Robles JF, González-Hernández J. Structural characterization and properties of colloidal silica coatings on copper substrates. Mater Lett. 2002;56:450–3.
Coradin T, Livage J. Aqueous silicates in biological sol-gel applications: new perspectives for old precursors. Acc Chem Res. 2007;40:819–26.
Conrad CF, Icopini GA, Yasuhara H, Bandstra JZ, Brantley SL, Heaney PJ. Modeling the kinetics of silica nanocolloid formation and precipitation in geologically relevant aqueous solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2007;71:531–42.
Perry CC, Keeling-Tucker T. Biosilicification: the role of the organic matrix in structure control. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2000;5:537–50.
Vogelsberger W, Opfermann J, Wank U, Schulze H, Rudakoff G. On the determination of kinetic parameters of sol formation by rheological measurements. Colloids Surf A. 1993;78:99–108.
Yang LN, Qiu SJ, Xu F, Sun LX, Zhao ZB, Liang JG, et al. Microcalorimetric investigation of the growth of the Escherichia coli DH5α in different antibiotics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;89:875–9.
Chen JR, Wu SH, Lin SY, Hou HY, Shu CM. Utilization of microcalorimetry for an assessment of the potential for a runaway decomposition of cumene hydroperoxide at low temperatures. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:127–33.
Chen XJ, Feng WS, Miao W, Yu YH, Shen YF, Wan CY, et al. A microcalorimetric assay of Tetrahymena thermophila for assessing tributyltin acute toxicity. J Therm Anal Cal. 2008;94:779–84.
Hansen LD. Calorimetric measurement of the kinetics of slow reactions. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2000;39:3541–9.
Wadsö I. Isothermal microcalorimetry: current problems and prospects. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;64:75–84.
Wadsö I, Wadsö L. Systematic errors in isothermal micro- and nanocalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;82:553–8.
O’Neill MAA, Gaisford S, Beezer AE, Skaria CV, Sears P. A comparison of the performance of calorimeters: application of a test and reference reaction. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;84:301–6.
Alig I, Lellinger D, Oehler H, Adamovsky SA, Schick C. Microcalorimetry for characterization of film formation and cure of coatings and adhesives. Prog Org Coat. 2008;61:166–75.
Pelmenschikov A, Strandh H, Pettersson LGM, Leszczynski J. Lattice resistance to hydrolysis of Si−O−Si bonds of silicate minerals: ab initio calculations of a single water attack onto the (001) and (111) β-cristobalite surfaces. J Phys Chem B. 2000;104:5779–83.
Iler RK. The chemistry of silica. New York: Wiley; 1979.
Willson RJ, Beezer AE, Hills AK, Mitchell JC. The imidazole catalysed hydrolysis of triacetin: a medium term chemical calibrant for isothermal microcalorimeters. Thermochim Acta. 1999;325:125–32.
Gaisford S, Hills AK, Beezer AE, Mitchell JC. Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of isothermal microcalorimetric data: applications to consecutive reaction schemes. Thermochim Acta. 1999;328:39–45.
Hills AK, Beezer AE, Mitchell JC, Connor JA. Sources of error, and their correction, in the analysis of isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetric data: applications of a newly developed test reaction. Thermochim Acta. 2001;380:19–26.
Beezer AE. An outline of new calculation methods for the determination of both thermodynamic and kinetic parameters from isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry. Thermochim Acta. 2001;380:205–8.
O’Neill MAA, Beezer AE, Deal RM, Morris AC, Mitchell JC, Orchard JA, et al. Survey of the effect of fill volume on the values for the enthalpy and rate constant derived from isothermal microcalorimetry: applications of a newly developed test reaction. Thermochim Acta. 2003;397:163–9.
Harrison CC, Loton N. Novel routes to designer silicas: studies of the decomposition of (M+)2[Si(C6H4O2)3·xH2O. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1995;91(23):4287–97.
Rodríguez-Añón J, Proupín-Castiñeiras J, Villanueva-López M, Núñez-Fernández O. Development of an experimental procedure to analyse the ‘soil health state’ by microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Cal. 2007;87:15–9.
Willson RJ, Beezer AE, Mitchell JC, Loh W. Determination of thermodynamic and kinetic parameters from isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry: applications to long-term-reaction studies. J Phys Chem. 1995;99:7108–13.
Beezer AE, Morris AC, O’Neill MAA, Willson RJ, Hills AK, Mitchell JC, et al. Direct determination of equilibrium thermodynamic and kinetic parameters from isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:1212–5.
Willson RJ, Beezer AE. A mathematical approach for the calculation of reaction order for common solution phase reactions. Thermochim Acta. 2003;402:75–80.
O’Neill MAA, Beezer AE, Morris AC, Urakami K, Willson RJ, Connor JA. Solid-state reactions from isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry: theoretical approach and evaluation via simulated data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;73:709–14.
Beezer AE, Willson RJ, Mitchell JC, Hills AK, Gaisford S, Wood E, et al. Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters from isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry. Pure Appl Chem. 1998;70:633–8.
Bishop AD, Bear JL. The thermodynamics and kinetics of the polymerization of silicic acid in dilute aqueous solution. Thermochim Acta. 1972;3:399–409.
Trinh TT, Jansen APJ, van Santen RA. Mechanism of oligomerization reactions of silica. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:23099–106.
Tossell JA. Theoretical study on the dimerization of Si(OH)4 in aqueous solution and its dependence on temperature and dielectric constant. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2005;69:283–91.
Kinrade SD. Oxygen-17 NMR study of aqueous potassium silicates. J Phys Chem. 1996;100:4760–4.
Löbbus M, Vogelsberger W, Sonnefeld J, Seidel A. Current considerations for the dissolution kinetics of solid oxides with silica. Langmuir. 1998;14:4386–96.
Vogelsberger W, Seidel A, Breyer T. Kinetics of sol particle formation as a function of pH studied by viscosity measurements in silica solutions. Langmuir. 2002;18:3027–33.
Gaboriaud F, Nonat A, Chaumont D, Craievich A, Hanquet B. 29Si NMR and small-angle X-ray scattering studies of the effect of alkaline ions (Li+, Na+, and K+) in silico-alkaline sols. J Phys Chem B. 1999;103:2091–9.
Provis JL, Duxson P, Lukey GC, Separovic F, Kriven WM, van Deventer JSJ. Modeling speciation in highly concentrated alkaline silicate solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2005;44:8899–908.
Tsai MS, Huang PY, Wu WC. The study of formation process of colloidal silica. Mater Res Bull. 2005;40:1609–16.
Tsai MS, Huang PY, Yang CH. Formation mechanisms of colloidal silica via sodium silicate. J Nanopart Res. 2006;8:943–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50673080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Zhang, C., Wu, L. et al. Studies of mechanism of silica polymerization reactions in the combination of silica sol and potassium sodium waterglass via isothermal heat conduction microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim 101, 959–964 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-0697-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-0697-9