Abstract
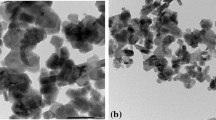
The reactivity of MgO obtained from calcination of magnesium carbonate at different temperatures has been investigated by means of hydration in a constant relative humidity environment at 40°C for periods up to 24 days. Natural magnesite and AR grade basic MgCO3 calcined in the range of 500–1000°C was characterised in terms of surface area, crystallite size, morphology, and hydration rate.
It was found that the hydration rate is dependent on the surface area and crystallite size where temperature was the main variable affecting them. The most reactive MgO was produced at the lowest calcination temperature with the highest surface area and the smallest crystallite size. The basic MgO specimens showed higher degree of hydration compared to the natural MgO specimens due to the smaller surface area and larger crystallite size. The low MgO content of the starting natural magnesite is also attributable to the lower reactivity. This preliminary study serves as a mean to investigate potential utilisation of reactive MgO as a supplementary cementitious material in eco-friendly cements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AN Copp (1998) Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 77 107 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjsl2rurY%3D
M Frith T Buffrey I Strawbridge (1998) Br. Ceram. Trans. 97 29 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitVSrsbY%3D
DA Kramer (2001) Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 80 81 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlvVertr0%3D
RI Razouk RS Mikhail (1955) J. Phys. Chem. 59 636 Occurrence Handle10.1021/j150529a015 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG2MXns1ansg%3D%3D
Standard Practice for Maintaining Constant Relative Humidity by Means of Aqueous Solutions, ASTM International, 1996, ASTM E104-85.
RW Cheary A Coelho (1992) J. Appl. Crystallogr. 25 109 Occurrence Handle10.1107/S0021889891010804 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XhvVGis70%3D
BS Girgis LG Girgis (1969) J. Appl. Chem. 19 292 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3cXmsVGh Occurrence Handle10.1002/jctb.5010191003
VSS Birchal SDF Rocha VST Ciminelli (2000) Miner. Eng. 13 1629 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00146-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosl2ls7w%3D
RI Razouk RS Mikhail (1958) J. Phys. Chem. 62 920 Occurrence Handle10.1021/j150566a006 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG1MXhvFU%3D
GL Smitheson NN Bakhshi (1969) Can. J. Chem. Eng. 47 508 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3cXmsFyr Occurrence Handle10.1002/cjce.5450470602
W Feitknecht H Braun (1967) Helv. Chim. Acta 50 2040 Occurrence Handle10.1002/hlca.19670500738 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF2sXlt1Wqs78%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Thomas, P.S., Ray, A.S. et al. A TG analysis of the effect of calcination conditions on the properties of reactive magnesia. J Therm Anal Calorim 88, 145–149 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8106-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8106-0