Summary
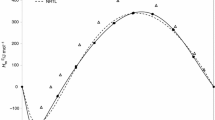
Experimental excess molar enthalpies and excess molar volumes of the ternary system x 1MTBE+x 21-propanol+(1-x 1-x 2) hexane and the involved binary mixtures have been determined at 298.15 K and atmospheric pressure. Excess molar enthalpies were measured using a standard Calvet microcalorimeter, and excess molar volumes were determined from the densities of the pure liquids and mixtures, using a DMA 4500 Anton Paar densimeter. The UNIFAC group contribution model (in the versions of Larsen et al., and Gmehling et al.) has been employed to estimate excess enthalpies values. Several empirical expressions for estimating ternary properties from experimental binary results were applied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mato, M., Cebreiro, S., Verdes, P. et al. Thermodynamic properties of the ternary system MTBE+1-propanol+hexane. J Therm Anal Calorim 80, 303–309 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-0651-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-0651-4