Abstract
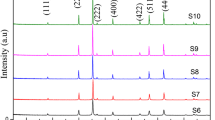
In this study, Mg–Mn–Al ferrite with a chemical composition of Mg0.8Mn0.2Al0.1Fe1.9O4 was synthesized via the sol–gel auto-combustion method. The effects of the sintering time and temperature on the magnetic properties and transmission behaviors were investigated in detail. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results revealed that the powders in the as auto-combusted state were in an amorphous state. Moreover, based on the differential thermal analysis (DTA) curve, the calcination temperature was calculated to be ~900 °C. According to the Archimedes equation, the highest density was obtained for the specimen sintered at 1250 °C for 5 h (94% of the theoretical density). In addition, permagraph results revealed the average magnetic properties of the mentioned samples are as follows: Hc = 7.0 Oe and Ms = 1400 G. According to vector network analyzer (VNA) results, the samples with qualified transmission behaviors showed low scattering parameters in a wide range of frequencies.

Highlights
-
Nanocrystalline Mg0.8Mn0.2Al0.1Fe1.9O4 was formed via a sol–gel auto-combustion method.
-
Microstructural, magnetic, and transmission behaviors (TB) were investigated.
-
The maximum density was obtained for the sample sintered at 1250 °C for 5 h (~4.08 g/cm3).
-
The TB of the samples was improved by increasing Ms.
-
The most favorable TB was obtained for the sample sintered at 1250 °C for 5 h.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pourzaki M, Kavkhani R, Kianvash A, Hajalilou A (2019) Structure, magnetic and transmission characteristics of the Co substituted Mg ferrites synthesized via a standard ceramic route. Ceram Int 45:5710–5716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.036
Shah MS, Ali K, Ali I et al. (2018) Structural and magnetic properties of praseodymium substituted barium-based spinel ferrites. Mater Res Bull 98:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.09.063
Krishna KR, Kumar KV, Ravinder D (2012) Structural and electrical conductivity studies in nickel-zinc ferrite. Adv Mater Phys Chem 02:185–191. https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2012.23028
Anu K, Hemalatha J (2019) Magnetic and electrical conductivity studies of zinc doped cobalt ferrite nanofluids. J Mol Liq 284:445–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.04.018
Hajalilou A, Mazlan SA (2016) A review on preparation techniques for synthesis of nanocrystalline soft magnetic ferrites and investigation on the effects of microstructure features on magnetic properties. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0217-2
Gan G, Zhang H, Li Q et al. (2018) Low loss, enhanced magneto-dielectric properties of Bi2O3 doped Mg-Cd ferrites for high frequency antennas. J Alloy Compd 735:2634–2639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.002
Agami WR (2018) Effect of neodymium substitution on the electric and dielectric properties of Mn-Ni-Zn ferrite. Phys B Condens Matter 534:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.01.021
Kalarus J, Kogias G, Holz D, Zaspalis VT (2012) High permeability-high frequency stable MnZn ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2788–2794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.04.011
Hasirci C, Karaagac O, Köçkar H (2019) Superparamagnetic zinc ferrite: a correlation between high magnetizations and nanoparticle sizes as a function of reaction time via hydrothermal process. J Magn Magn Mater 474:282–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.11.037
Akhtar MN, Saleem M, Khan MA (2018) Al doped spinel and garnet nanostructured ferrites for microwave frequency C and X- band applications. J Phys Chem Solids 123:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.08.007
Lwin N, Othman R, Sreekantan S, Ahmad Fauzi MN (2015) Study on the structural and electromagnetic properties of Tm-substituted Mg-Mn ferrites by a solution combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 385:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.03.046
Hajalilou A, Hashim M, Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi R, Masoudi MT (2015) Effect of milling atmosphere on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrite nanocrystalline. Chinese Phys B 24. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/24/4/048102
Dhiman RL, Taneja SP, Reddy VR (2008) Preparation and characterization of manganese ferrite aluminates. Adv Condens Matter Phys 2008:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/703479
Khishigdemberel I, Uyanga E, Hirazawa H, Sangaa D (2018) Influence of Cu dope on the structural behavior of MgFe2O4 at various temperatures Phys B Condens Matter 544:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.05.032
Kumar G, Chand J, Dogra A et al. (2010) Improvement in electrical and magnetic properties of mixed Mg-Al-Mn ferrite system synthesized by citrate precursor technique. J Phys Chem Solids 71:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2010.01.003
Maalam K El, Fkhar L, Mahhouti Z, et al. (2016) The effects of synthesis conditions on the magnetic properties of zinc ferrite spinel nanoparticles. J Phys Conf Ser 758. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/758/1/012008
Manouchehri S, Mohammadi Benehi ST, Yousefi MH (2016) Effect of aluminum doping on the structural and magnetic properties of mg-mn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation method. J Supercond Nov Magn 29:2179–2188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3546-7
Desai I, Nadagouda MN, Elovitz M et al. (2019) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic manganese ferrites. Mater Sci Energy Technol 2:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.01.009
Ramesh T, Shinde RS, Murthy SR (2011) Synthesis and characterization of NiCoMnCuFe1.96O4 for circulator application. J Magn Magn Mater 323:1593–1598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.12.010
Gul M, Akhtar K (2018) Synthesis and characterization of Al_doped manganese ferrite uniform particles for high-frequency applications. J Alloy Compd 765:1139–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.168
Hemeda OM, Mostafa NY, Abd Elkader OH, Ahmed MA (2014) Solubility limits in Mn-Mg ferrites system under hydrothermal conditions. J Magn Magn Mater 364:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.03.061
Babu KV, Kumar GVS, Satyanarayana G et al. (2018) Microstructural and magnetic properties of Ni1−xCuxFe2O4 (x = 0.05, 0.1 and 0.15) nano-crystalline ferrites J Sci Adv Mater Devices 3:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.04.003
Mansour SF (2011) Structural and magnetic investigations of sub-nano Mn-Mg ferrite prepared by wet method. J Magn Magn Mater 323:1735–1740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.09.012
Bierlich S, Reimann T, Gellersen F et al. (2019) Sintering, microwave properties, and circulator applications of textured Sc-substituted M-type ferrite thick films. J Eur Ceram Soc 39:3077–3081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.04.014
Tsay CY, Liang SC, Lei CM, Chang CC (2016) A comparative study of the magnetic and microwave properties of Al3+ and In3+ substituted Mg-Mn ferrites. Ceram Int 42:4748–4753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.154
Singh M, Sud SP (2001) Controlling the properties of magnesium-manganese ferrites. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol 83:180–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5107(01)00514-1
Liu H, Li A, Ding X et al. (2019) Magnetic induction heating properties of Mg1−xZnxFe2O4 ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method Solid State Sci 93:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.05.005
Azadmanjiri J (2007) Preparation of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles from chemical sol-gel combustion method and the magnetic properties after sintering. J Non Cryst Solids 353:4170–4173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.06.046
De-León-Prado LE, Cortés-Hernández DA, Almanza-Robles JM, et al. (2017) Synthesis and characterization of nanosized MgxMn1−xFe2O4 ferrites by both sol-gel and thermal decomposition methods. J Magn Magn Mater 427:230–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.036
Ramarao K, Rajesh Babu B, Kishore, Babu B et al. (2018) Composition dependence of structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Co substituted magnesium ferrite. Phys B Condens Matter 528:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.10.072
Mali AV, Wandre TM, Sanadi KR et al. (2016) Synthesis, characterization and electrical properties of novel Mn substituted MgAl2O4 synthesized by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:613–619.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3796-3
Hossain MS, Hoque SM, Liba SI, Choudhury S (2017) Effect of synthesis methods and a comparative study of structural and magnetic properties of zinc ferrite. AIP Adv 7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5009925
Ali MA, Khan MNI, Chowdhury F-U-Z et al. (2015) Effect of sintering temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 ferrite: synthesized from nanocrystalline powders. JPCS 1718:2–11
Kinsler P, McCall MW (2015) The futures of transformations and metamaterials. Photonics Nanostruct - Fundam Appl 15:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.photonics.2015.04.005
Smith DR, Vier DC, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2005) Electromagnetic parameter retrieval from inhomogeneous metamaterials. Phys Rev E - Stat Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys 71:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.71.036617
Alizad Farzin Y, Mirzaee O, Ghasemi A (2016) Synthesis behavior and magnetic properties of Mg-Ni co-doped Y-type hexaferrite prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion method. Mater Chem Phys 178:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.04.082
Bindra Narang S, Kaur P, Bahel S, Singh C (2016) Microwave characterization of Co-Ti substituted barium hexagonal ferrites in X- band. J Magn Magn Mater 405:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.12.044
Liu Y, Wei SC, Wang YJ et al. (2013) Characterization of (Mg, La) substituted Ni-Zn spinel ferrite. Phys Procedia 50:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2013.11.009
Seyyed Ebrahimi SA, Azadmanjiri J (2007) Evaluation of NiFe2O4 ferrite nanocrystalline powder synthesized by a sol-gel auto-combustion method J Non Cryst Solids 353:802–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2006.12.044
Adli RG, Kianvash A, Hosseini MG et al. (2018) Mechanochemically synthesized NiCo2O4/Vulcan/PANI nanocomposite and investigation of its electrochemical behavior as a supercapacitor. Ceram Int 44:20049–20057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.279
Hajalilou A, Hashim M, Ebrahimi-Kahizsangi R et al. (2014) Synthesis of titanium carbide and TiC-SiO2 nanocomposite powder using rutile and Si by mechanically activated sintering. Adv Powder Technol 25:1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2014.02.008
Ghaffari Adli R, Kianvash A, Hosseini MG et al. (2019) Facile and scalable synthesis of ultrafine MnCo2O4 nanoparticles via mechanical alloying as supercapacitive materials. Jom 71:2396–2404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03486-9
Hajalilou A, Mazlan SA, Shameli K (2016) A comparative study of different concentrations of pure Zn powder effects on synthesis, structure, magnetic and microwave-absorbing properties in mechanically-alloyed Ni-Zn ferrite. J Phys Chem Solids 96–97:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2016.05.001
Rafeekali K, Maheem M, Mohammed EM (2015) Effect of sintering temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. NPCM 4:194–198
Rafferty A, Prescott T, Brabazon D (2008) Sintering behaviour of cobalt ferrite ceramic. Ceram Int 34:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2006.07.012
Zabotto FL, Gualdi AJ, Eiras JA (2012) Influence of the sintering temperature on the magnetic and electric properties of NiFe2O4 ferrites. Mater Res 15:428–433. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392012005000043
Ahmed MA, EL-Khawlani AA (2009) Enhancement of the crystal size and magnetic properties of Mg-substituted Co ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1959–1963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.12.021
Hajalilou, A, Kamari, HM, Shameli, K (2017). Dielectric and electrical characteristics of mechanically synthesized Ni-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 708-813-826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.030
Chagas EF, Ponce AS, Prado RJ, et al. (2014) Thermal effect on magnetic parameters of high-coercivity cobalt ferrite. J Appl Phys 116. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4890033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavkhani, R., Pourzaki, M., Kianvash, A. et al. Effect of sintering temperature and soaking time on the magnetic properties and transmission behavior of nano crystalline Mg0.8Mn0.2Al0.1Fe1.9O4. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 99, 444–454 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05454-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05454-1