Abstract
This work reports the effects of two reducing atmospheres (N2 + H2 and carbon) on the luminescent, morphological, and structural properties of Sr4Al14O25:Eu2+ (1 mol%), Dy3+ (2 mol%), Cr3+ (1–4 mol%) [SALO:Eu, Dy, Cr] phosphors. They were synthesized by a combustion method followed by an annealing treatment in a reducing atmosphere. According to scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images, the samples annealed in both types of reducing atmospheres present microparticles with irregular shape. An increase of Cr concentration from 1 to 4 mol% produced microparticles with higher porosity. X-ray diffraction patterns demonstrated that the orthorhombic phase was maintained in all the samples synthesized with different Cr concentrations or reducing atmospheres. Two main emission bands centered at 490 and 693 nm were observed in the SALO:Eu, Dy, Cr phosphors under excitation at 375 nm. In general, the annealing under carbon atmosphere produced the strongest luminescent emission and the longest phosphorescence times in SALO:Eu, Dy, Cr phosphors. When the Cr concentration is increased from 1 to 4 mol%, the phosphorescence times for the NIR and VIS bands were drastically reduced from ≈1830 to 40–60 s. The phosphorescence intensity was favored by the presence of defects such as oxygen vacancies (Vo) and Dy3+–Vo traps, which were formed after the introduction of Dy3+ and Cr3+ ions in the SALO host. The presence of these defects was confirmed by absorbance measurements. The annealing in carbon atmosphere is simpler than that in H2 + N2 atmosphere and leads to enhanced luminescent properties of SALO:Eu, Dy, Cr phosphors.

Highlights
-
The luminescent properties of SALO:Eu, Dy, Cr strongly depend on the reduced reductive atmosphere.
-
Threefold NIR persistence time enhancement is obtained under carbon reductive atmosphere treatment.
-
NIR luminescent intensity increases under carbon reductive atmosphere treatment.
-
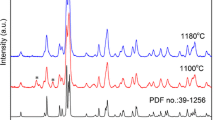
The structural properties of SALO:Eu, Dy, Cr do not depend on the used reductive atmosphere.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia W, Yuan H, Lu L, Liu H, Yen W (1998) J Lumin 76:424–428
Chai Y, Zhang P, Zheng Z (2008) Phys B: Condens Matter 403:4120–4122
Aitasalo T, Hölsä J, Jungner H, Lastusaari M, Niittykoski J (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:4589–4598
Matsuzawa T, Aoki Y, Takeuchi N, Murayama Y (1996) Electrochem Soc 143:2670–2673
Jia D (2003) Opt Mater 22:65–69
Shankar V, Chander H, Divi H, Ghosh P (2003) US Patent 0183807 A1:1–4
Lin Y, Tang Z, Zhang Z (2001) Mater Lett 51:14–18
García Solé J, Bausá L, Jaque D (2005) An introduction to the optical spectroscopy of inorganic solids. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., England
Hemmer E, Venkatachalam N, Hyodo H, Hattori A, Ebina Y, Kishimoto H, Soga K (2013) Nanoscale 5:1–22
Marciniak L, Bednarkiewocks A (2017) 243:388–393
Xiu J, Murata D, Katayama Y, Ueda J (2017) J Mater Chem B 5:6385–6393
Ekambaram S, Patil KC, Maaza M (2005) J Alloy Compd 393:81–92
Luitel HN, Watari T, Chand R, Torikai T, Yada M (2013) J Mater 2013:1–10
Kaya S, Karacaoglu E, Karasu B (2012) Ceram Int 38:3701–3706
Lai T, Chang C, Yang C, Das S, Lu C (2013) Ceram Int 39(2013):159–163
Wang J, Ma Q, Wang Y, Shen H, Yuan Q (2017) Nanoscale 9:6204–6218
Xiang H, Cheng J, Ma X, Zhou X, Chruma J (2013) ChemSoc Rev 42:6128–6185
Gao S, Chen D, Li Q, Ye J, Jiang H (2014) Sci Rep 4:1–6
Chihara T, Umezawa M, Miyata K, Sekiyama S, Hosokawa N, Okubo K, Kamimura M, Soga K (2019) Sci Rep 9:12806
Li Y, Gecevicius M, Qiu J (2016) Chem Soc Rev 45:2090–2136
Sharma S, Gourier D, Viana B, Maldiney T, Teston E, Scherman D, Richard C (2014) Opt Mat 36:1901–1906
Lécuyer T, Teston E, Ramirez-Garcia G, Maldiney T, Viana B, Seguin J (2016) Theranostics 6:2488–2524
Lin X, Song L, Chen S, Chen X, Wei J, Li J, Huang G, Yang H (2017) Appl Mat Interf 9:41181–41187
Bessiére A, Sharma S, Basavaraju N, Priolkar K, L Binet, Viana B (2014) Chem Mater 26:1365−1373
Zhong R, Zhang J, Zhang X, Lu S (2006) Appl Phys Lett 88:2019161–2019163
Luitel H, Watari T, Torikai T, Yada M (2009) Opt Mat 31:1200–1204
Teng Y, Zhou Y, Khisro Y, Zhou Y (2014) Qiu J Mat Chem Phys 147:772–776
Huyan S, Deng L, Wu Z, Zhao K, Sun J, Wu L, Zhao Y, Yuan H, Gooch M, Lv B, Zhu Chen Y, Chu C (2019) Sci Rep 9:1–7
Monshi A, Foroughi M, Monshi M (2012) World J Nano Sci Eng 2:154–160
Guo H, Wang Y, Li G, Liu J, Li Y (2016) RSC Adv 1:1–8
Xingdong L, Wangen S (2007) Rare Met 26:305–310
Brito H, Hölsä J, Laamanen L, Lastusaari M, Malkamäki M, Rodrigues L (2012) Opt Mat Expr 2:371–381
Rezende M, Araujo R, Valerio M, Jackson R (2010) J Phys 249:012042
Li X, Hua Y, Ma H, Deng B, Jia G, Xu G (2015) RSC Adv 1:1–11
Kumar G, Liu D, Tian Y, Brik M, Sardar D (2015) Opt Mat 50:199–203
Yahia Z, Bayaklya HN, Shafia M, Paintera S, Taylora V, Greene J, Ros K (2014) Complex Met 1:46–51
Rao V, Prasad P, Babua M, Rao P, Satyanarayana T, Santos L, Veeraiah N (2018) Biomol Spect 188:516–524
Yang Y, Wang Y (2017) Yin Appl Surf Sci 420:399–406
Guo D, Qian Y, Su Y, Shi H, Li P, Wu J, Wang S, Cui C, Tang H (2017) AIP Adv 7:1–6
Aitasalo T, Deren P, Holsa J, Jungner H, Krupa J, Lastusaari M, Legendziewicz J, Niittykoski J, Strek W (2003) J Sol Stat Chem 171:114–122
Singh V, Chakaradhar R, Rao J, Kim D (2008) Phosphors, Sol Stat Sci 10:1525–1532
Dorenbos P (2004) J Lumin 108:301–305
Acknowledgements
MG-R thanks conacyt for the PhD scholarship. JO thanks the financial support of CONACYT through the CATEDRAS-CONACYT program. Authors also appreciate the technical work performed by Christian Albor for the SEM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guzmán-Rocha, M., Oliva, J., Diaz-Torres, L.A. et al. Effect of the reducing atmospheres on the photoluminescent and phosphorescent properties of Sr4Al14O25:Eu2+, Dy3+, Cr3+ phosphors. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 95, 423–431 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05299-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05299-8