Abstract
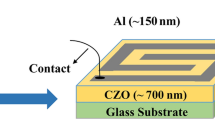
The electrical, optical and humidity sensor properties of nanostructured ZnO samples were investigated. The structural properties of Sn doped ZnO samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction and atomic force microscopy. It was found that the all samples have a hexagonal crystal structure. The electrical conductivity of the samples indicates that undoped and Sn doped ZnO samples exhibit the semiconducting behavior. The optical absorption method was used to determine the optical band gaps of the samples. The optical band gap and activation energy values of the ZnO samples were changed with Sn doping. The ZnO based on quartz crystal microbalance humidity sensors were prepared and sensing properties of the sensors were changed with Sn doping. The response time required to reach 70 % is about 13–16 s, while the recovery time from 70 to 30 % RH is about 13–15 s. The fast response of the sensors is due to easy diffusion of water molecules between ZnO nanopowders. The prepared sensors have a high reproducibility and sensitivity for humidity sensing applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamazoe N, Shimizu Y (1986) Sens Actuators 10:379–398
Dessler AE, Sherwood SC (2009) A matter of humidity. Science 323:1020–1021
Chu J, Peng XY, Feng P, Sheng Y, Zhang JT (2013) Sens Actuators B 178:508–513
Huang H, Zhou J, Chen S, Zeng L, Huang Y (2004) Sens Actuators B 101:316–321
Zhang J, Hu JQ, Zhu FR, Gong H, O’Shea SJ (2002) Sens. Actuators B Chem 87:159–167
Teresa M, Sergio P, Nogueira T, Oliveira JP (2000) Sens Actuators B 68:218
Nanto H, Tsubakino S, Habara M, Kondo K, Morita T, Douguchi Y, Nakazumi H, Waite R (1996) Sens Actuators B 34:312
Henkel K, Opera A, Paloumpa I, Appel G, Schmeiber D, Kamieth P (2001) Sens Actuators B 76:124
Nanto H, Dougami N, Mukai T, Habara M, Kusano E, Kinbara A, Ogawa T, Oyabu T (2000) Sens Actuators B 66:16
Klingshirn C (2007) Phys Status Solidi B 9:3027–3073
Erol A, Okur S, Comba B, Mermer O, Arıkan MC (2010) Sens Actuators B 145:174–180
Arnold MA, Avouris P, Pan ZW, Wang ZL (2003) J Phys Chem B 107:659–663
Erol A, Okur S, Comba B, Mermer O, Arıkan C (2005) Sens Actuators B Chem 107:379
Qi Q, Zhang T, Yu Q, Wang R, Zeng Y, Liu L, Yang H (2008) Sens Actuators B 133:638–643
Zhang Y, Ke Yu, Ouyang S, Luo L, Hongmei H, Zhang Q, Zhu Z (2005) Phys B 368:94–99
Wang X-H, Ding Y-F, Zhang J, Zhu Z-Q, You S-Z, Chen S-Q, Zhu J (2006) Sens Actuators B 115:421–427
Ateş T, Tatar C, Yakuphanoglu F (2013) Sens Actuators 190:153
Wu GS, Xie T, Yuan XY, Li Y, Yang L, Xiao YH, Zhang LD (2005) Solid State Commun 134:485–489
Ilican S, Caglar M, Caglar Y (2010) Appl Surf Sci 256:7204–7210
Zhou X, Zhang J, Jiang T, Wang X, Zhu Z (2007) Sens Actuators A Phys 135:209–214
Neogi SK, Ghosh R, Paul GK, Bera SK, Bandyopadhyay S (2009) J Alloy Compd 487:269–273
Srinivasan G, Kumar J (2008) J Cryst Growth 310:1841–1846
Tauc J (1974) Amorphous and liquid semiconductors. Plenum Press, New York
Aydın C, Abd El Sadek MS, Zheng K, Yahia IS, Yakuphanoglu F (2013) Opt Laser Technol 48:447–452
Yakuphanoglu F (2010) J Alloy Compd 507:184–189
Ilican S, Caglar Y, Caglar M, Yakuphanoglu F (2006) Physica E 35:131–138
Yakuphanoglu F, Ilican S, Caglar M, Caglar Y (2010) Superlattice Microstruct 47:732–743
Sun ZP, Liu L, Zhang L, Jia DZ (2006) Nanotechnology 17:2266–2270
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under Grant No. (363-258-D1435). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hendi, A.A., Alorainy, R.H. & Yakuphanoglu, F. Humidity sensing characteristics of Sn doped Zinc oxide based quartz crystal microbalance sensors. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 72, 559–564 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3473-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3473-7