Abstract
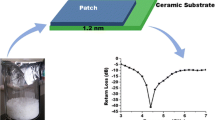
This study reports the characterization, fabrication, and performance of global positioning systems (GPS) patch antennas as a function of calcium (Ca) concentration and dielectric constant (ɛ r ). Zn(1−x)CaxAl2O4 (x = 0.00, 0.05, 0.10, 0.20, 0.25, and 0.30) thin films were prepared through a sol–gel method. The effects of added Ca on the nanostructures and dielectric properties of ZnAl2O4 ceramics were investigated. The addition of Ca increased the crystallite size, grain size, and surface morphology, thereby increasing the density and dielectric constant. As the Ca content increased, the ɛ r values linearly increased. However, the Q u values decreased (at x = 0.25 to x = 0.25) after achieving the optimum values at x = 0.20. Finally, GPS patch antennas were successfully fabricated using the Zn(1−x)CaxAl2O4 material. The patch antenna sizes decreased as ɛ r increased from 2.88 × 4.37 cm (ɛ r ≈ 8.52) to 2.88 × 4.37 cm (ɛ r ≈ 10.16). The performance (return loss analysis) and operating frequencies of the GPS patch antennas were measured using the PNA series network analyzer. Results show that the patch antenna resonates at frequency of 1.570 GHz and produces a return loss bandwidth between −16.6 and −27.5 dB. The optimal performance of GPS patch antenna with ɛ r ≈ 9.95, Q u ≈ 6,186, and return loss = −27.5 dB was obtained from specimen using Zn0.80Ca0.20Al2O4 (x = 0.20) ceramics.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang C-L, Chen J-Y, Wang Y-H (2009) J Alloy Compd 478:842–846
Huang C-L, Chen J-Y, Tseng Y-W (2010) Mater Sci Eng B 167:142–146
Lei W, Lu W-Z, Zhu J-H, Ye X (2009) Ceram Int 35:277–280
Tseng C-F, Tsai P-S (2013) Ceram Int 39:75–79
Sebastian MT (2008) In: Jordan Hill (ed). Dielectric materials for wireless communication, vol, First Edition edn. UK Elsevier Ltd, Oxford
Tsunooka T, Androu M, Higashida Y, Sugiura H, Ohsato H (2003) J Eur Ceram Soc 23:2573–2578
Kim JC, Kim MH, Lim JB, Nahm S, Paik JH, Kim JH (2007) J Am Ceram Soc 90:641–644
Wang X, Lei W, Lu W (2009) Ferroelectrics 388:80–87
Wu J-M, Lu W-Z, Lei W, Wang X-C (2011) Mater Res Bull 46:1485–1489
Silva AAD, Goncalves ADS, Davolos MR (2009) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 49:101–105
Surendran KP, Santha N, Mohanan P, Sebastian MT (2004) Eur Phys J B Condens Matter Complex Syst 41:301–306
Lei W, Lu WZ, Wang XH, Liang F, Wang J (2011) J Am Ceram Soc 94:20–23
Lei W, Lu WZ, Zhu JH, Wang XH (2007) Mater Lett 61:4066–4069
Lei W, Lu W-Z, Liu D, Zhu J-H (2009) J Am Ceram Soc 92:105–109
Lei W, Lu W-Z, Zhu J-H, Liang F, Liu D (2008) J Am Ceram Soc 91:1958–1961
Huang C-L, Yang T-J, Huang C-C (2009) J Am Ceram Soc 92:119–124
Kurajica S, Tkalčec E, Gržeta B, Iveković D, Mandić V, Popović J, Kranzelić D (2011) J Alloy Compd 509:3223–3228
Martins RF, Serra OA (2010) J Braz Chem Soc 21:1395–1398
Barros BS, Melo PS, Kiminami RHGA, Costa ACFM, Sá GF, Alves S Jr (2006) J Mater Sci 41:4744–4748
Huang CL, Chen JY, Li BJ (2009) J Alloy Compd 484:494–497
Chen YC (2011) Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control IEEE Trans 58:2531–2538
Tian X, Wan L, Pan K, Tian C, Fu H, Shi K (2009) J Alloy Compd 488:320–324
Charinpanitkul T, Poommarin P, Wongkaew A, Kim K-S (2009) J Ind Eng Chem 15:163–166
de Souza LKC, Zamian JR, da Rocha Filho GN, Soledade LEB, dos Santos IMG, Souza AG, Scheller T, Angélica RS, da Costa CEF (2009) Dyes Pigments 81:187–192
Zawadzki M, Staszak W, López Suárez FE, Illán Gómez MJ, Bueno López A (2009) Appl Catal A Gen 371:92–98
Kumar RT, Selvam NCS, Ragupathi C, Kennedy LJ, Vijaya JJ (2012) Powder Technol 224:147–154
Kim JS, Kim JS, Park HL (2004) Solid State Commun 131:735–738
Beier MJ, Hansen TW, Grunwaldt JD (2009) J Catal 266:320–330
Nikumbh AK, Adhyapak PV (2010) Powder Technol 202:14–23
Zhang H, Fang L, Elsebrock R, Yuan RZ (2005) Mater Chem Phys 93:450–454
Jamal E, Kumar D, Anantharaman MR (2011) Bull Mater Sci 34:251–259
Abdullah H, Jalal W, Zulfakar M (2014) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 69:429–440
Xavier CS, Sczancoski JC, Cavalcante LS, Paiva-Santos CO, Varela JA, Longo E, Li MS (2009) Solid State Sci 11:2173–2179
Nazir S, Ikram N, Amin B, Tanveer M, Shaukat A, Saeed Y (2009) J Phys Chem Solids 70:874–880
Arya GS, Negi NS (2013) J Phys D Appl Phys 46:095004
Koops CG (1951) Phys Rev 81:121–124
Wagner KW (1913) Ann Phys 345:817–855
Subramanian MA, Shannon RD, Chai BHT, Abraham MM, Wintersgill MC (1989) Phys Chem Miner 16:741–746
Kingery W, Bowen H, Uhlmann D (1976) Introduction to ceramics. Willey, New York
Huang C-L, Tasi C-F, Chen Y-B, Cheng Y-C (2008) J Alloy Compd 453:337–340
Chen Y-B (2011) J Alloy Compd 509:2285–2288
Sotoudeh H-H, Joseph C, Sooseok O, Ju-Ung J, Noh-Joon P, Dae-Hee P (2009) J Electr Eng Technol 4:282–286
Balanis CA (2005) Antenna theory analysis and design, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Huang CL, Tseng CF, Yang WR, Yang TJ (2008) J Am Ceram Soc 91:2201–2204
Acknowledgments
This project is carried out in Photonic Technology Laboratory, Institute of Microengineering and Nanoelectronics (IMEN), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jalal, W.N.W., Abdullah, H., Zulfakar, M.S. et al. GPS patch antenna performance by modification of Zn(1−x)CaxAl2O4-based microwave dielectric ceramics. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71, 477–489 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3397-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3397-2