Abstract
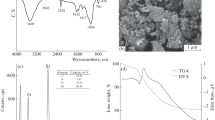
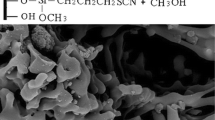
This manuscript reported sol–gel derived organic–inorganic hybrid sorbent for the removal of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions from aqueous solutions. The hybrid sorbent (S2/SiO2) had been synthesized by a simple co-condensation of bis[3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl]disulfide and tetraethoxysilane via sol–gel transformation. The S2/SiO2 was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, elemental analysis and thermogravimetric analysis. The influences of different adsorption parameters, such as pH value of solution, contact time and initial concentrations of metal ions on the adsorption amount of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ were examined. The optimum pH for adsorption was found to be in the range of 3.7–8.5. The adsorption rates of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ by S2/SiO2 were rapid. Ho’s pseudo-second-order model best described the kinetics of the adsorption reaction. The adsorption process of metals followed Langmuir isotherm model, and the experimental values of maximum adsorption capacities for Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ were 26.8, 56.7 and 13.3 mg g−1, respectively. The positive values of ΔH o suggested endothermic nature of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ adsorption on S2/SiO2 sorbent. Increase in entropy of adsorption reaction was shown by the positive values of ΔS o and the negative values of ΔG o indicating that the adsorption was spontaneous in nature.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baptista Neto JA, Smith BJ, McAllister JJ (2000) Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments in a near shore environment, Jurujuba Sound, Southeast Brazil. Environ Pollut 109:1–9
Zhuang P, Zou H, Shu W (2009) Biotransfer of heavy metals along a soil-plant-insect-chicken food chain: field study. J Environ Sci 21:849–853
Esalah JO, Weber ME, Vera JH (1999) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by precipitation with sodium di-(n-octyl) phosphinate. Sep Purif Technol 18:25–36
Qdais HA, Moussa H (2004) Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by membrane processes: a comparative study. Desalination 164:105–110
Vinodh R, Padmavathi R, Sangeetha D (2011) Separation of heavy metals from water samples using anion exchange polymers by adsorption process. Desalination 267:267–276
Pan B, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L, Zhang Q, Zheng S (2009) Development of polymeric and polymer-based hybrid adsorbents for pollutants removal from waters. Chem Eng J 151:19–29
Doğan M, Turhan Y, Alkan M, Namli H, Turan P, Demirbaş Ö (2008) Functionalized sepiolite for heavy metal ions adsorption. Desalination 230:248–268
Saeed A, Akhter MW, Iqbal M (2005) Removal and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solution using papaya wood as a new biosorbent. Sep Purif Technol 45:25–31
Pandey S, Mishra SB (2011) Sol–gel derived organic–inorganic hybrid materials: synthesis, characterizations and applications. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 59:73–94
Chevalier PM, Corriu RJP, Moreau JJE, Man MWC (1997) Chemistry of hybrid organic-inorganic access to silica materials through chemical selectivity. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 8:603–607
Chung Y-S, Lee B, Choo K-H, Choi S-J (2011) Removal of perrhenate anions in aqueous solutions using anion-exchange organic/inorganic hybrid nanoporous beads. J Ind Eng Chem 17:114–119
Prakash S, Kumar M, Tripathi BP, Shahi VK (2010) Sol–gel derived poly(vinyl alcohol)-3-(2-aminoethylamino) propyl trimethoxysilane: cross-linked organic–inorganic hybrid beads for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 162:28–36
Zou H, Wu S, Shen J (2008) Polymer/silica nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem Rev 108:3893–3957
Ma Y, Kanezashi M, Tsuru T (2010) Preparation of organic/inorganic hybrid silica using methyltriethoxysilane and tetraethoxysilane as co-precursors. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 53:93–99
Bois L, Bonhommé A, Ribes A, Pais B, Raffin G, Tessier F (2003) Functionalized silica for heavy metal ions adsorption. Colloids Surf A 221:221–230
Aguado J, Arsuaga JM, Arencibia A, Lindo M, Gascón V (2009) Aqueous heavy metals removal by adsorption on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica. J Hazard Mater 163:213–221
Chen D, Huang C, He M, Hu B (2009) Separation and preconcentration of inorganic arsenic species in natural water samples with 3-(2-aminoethylamino) propyltrimethoxysilane modified ordered mesoporous silica micro-column and their determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 164:1146–1151
Buhani Narsito, Nuryono KunartiES (2010) Production of metal ion imprinted polymer from mercapto–silica through sol–gel process as selective adsorbent of cadmium. Desalination 251:83–89
Lee B, Kim Y, Lee H, Yi J (2001) Synthesis of functionalized porous silicas via templating method as heavy metal ion adsorbents: the introduction of surface hydrophilicity onto the surface of adsorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 50:77–90
Fan H-T, Sun T (2012) Selective removal of iron from aqueous solution using ion imprinted cyanato-functionalized silica gel sorbents. Sep Sci Technol 47:507–512
Blitz IP, Blitz JP, Guńko VM, Sheeran DJ (2007) Functionalized silicas: structural characteristics and adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Colloids Surf A 307:83–92
Li Z-C, Fan H-T, Zhang Y, Chen M-X, Yu Z-Y, Cao X-Q, Sun T (2011) Cd(II)-imprinted polymer sorbents prepared by combination of surface imprinting technique with hydrothermal assisted sol–gel process for selective removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 171:703–710
Moreira JC, Pavan LC, Gushikem Y (1990) Adsorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), Hg(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions on a 2-mercaptobenzimidazole-modified silica gel. Mikrochim Acta 102:107–115
Hao N, Han L, Yang Y, Wang H, Webley PA, Zhao D (2010) A metal-ion-assisted assembly approach to synthesize disulfide-bridged periodical mesoporous organosilicas with high sulfide contents and efficient adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 256:5334–5342
Chiu P-J, Vetrivel S, Chiang AST, Kao H-M (2011) Synthesis and characterization of cubic periodic mesoporous organosilicas with a high loading of disulfide groups. New J Chem 35:489–494
Quirarte-Escalante CA, Soto V, De La Cruz W, Porras GR, Manríquez R, Gomez-Salaza S (2009) Synthesis of hybrid adsorbents combining sol–gel processing and molecular imprinting applied to lead removal from aqueous streams. Chem Mater 21:1439–1450
Wu Q, Liao J, Yin Q, Li Y (2008) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of ordered macroporous silicas functionalized with organosulfur groups. Mater Res Bull 43:1209–1217
Teng M, Wang H, Li F, Zhang B (2011) Thioether-functionalized mesoporous fiber membranes: sol–gel combined electrospun fabrication and their applications for Hg2+ removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 355:23–28
Deng B, Wang C-C, Li Q-G, Xu A-W (2009) Highly ordered lamellar mesostructure of nanocrystalline PbSO4 prepared by hydrothermal treatment. J Phys Chem C 113:18473–18479
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetensk Handl 24:1–39
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second-order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Freundlich HMF (1906) Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Khan AA, Singh RP (1987) Adsorption thermodynamics of carbofuran on Sn(IV) arsenosilicate in H+, Na+ and Ca2+ forms. Colloids Surf 24:33–42
Koroki M, Saito S, Hashimoto H, Yamada T, Aoyama M (2010) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by the culm of bamboo grass treated with concentrated sulfuric acid. Environ Chem Lett 8:59–61
Huang Y-H, Hsueh C-L, Cheng H-P, Su L-C, Chen C-Y (2007) Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption of Cu(II) onto waste iron oxide. J Hazard Mater 144:406–411
Venkatraman BR, Parthasarathy S, Kasthuri A, Pandian P, Arivoli S (2009) Adsorption of chromium ions by acid activated low cost carbon-Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. E J Chem 6:S1–S11
Arivolia S, Thenkuzhali M, Prasath PMD (2009) Adsorption of rhodamine B by acid activated carbon-Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Orbital 1:138–155
Lisha KP, Maliyekkal SM, Pradeep T (2010) Manganese dioxide nanowhiskers: a potential adsorbent for the removal of Hg(II) from water. Chem Eng J 160:432–439
Şölener M, Tunali S, Özcan AS, Özcan A, Gedikbey T (2008) Adsorption characteristics of lead(II) ions onto the clay/poly(methoxyethyl)acrylamide (PMEA) composite from aqueous solutions. Desalination 223:308–322
Acknowledgments
The Project was sponsored by the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (grant no. 21107076), by the doctoral scientific research foundation of Liaoning Province of China (grant no. 20111048) and by program for Liaoning excellent talents in university of China (grant no. LJQ2012032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, HT., Su, ZJ., Fan, XL. et al. Sol–gel derived organic–inorganic hybrid sorbent for removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solution. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 64, 418–426 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2872-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2872-x