Abstract
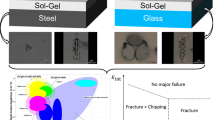
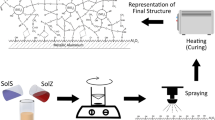
Sol–gel silica hybrid coatings from acid and base catalyzed sols were examined. The sol precursors were tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and methyltriethoxysilane (MTES). It is generally accepted that the type of catalyst has a significant impact on the micro-structure of the resulting polysilicates. Weakly branched polymers are formed in acid catalyzed sols and highly branched, compact, particle like polymers are formed in base catalyzed sols. The mechanical and chemical properties of sol–gel derived silica coatings from acid and base catalyzed sols were studied as a function of the heat treatment temperature and time. Hardness and elastic modulus were measured by micro indentation measurements. The chemical composition of both types of coatings was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang X, Qian M, Zeng X, Zhao Z et al (2008) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 45:103
Shilova OA, Hashkovsky SV, Tarasyuk EV (2003) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 26:1131
Chou TP, Chandrasekaran C, Cao GZ (2003) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 26:321
Datchary W, Mehner A, Zoch H-W, Lucca DA, Klopfstein MJ, Ghisleni R, Grimme D, Brinksmeier E (2005) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 35:245
Mehner A, Zoch H-W, Datchary W, Pongs G, Kunzmann H (2006) CIRP Ann 55(1):589
Mehner A, Dong J, Hoja T, Prenzel T, Mutlugünes Y, Brinksmeier E, Lucca DA, Klaiber F (2010) Key Eng Mater 438:65–72
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Sol-gel science: the Physics and Chemistry of sol-gel processing, Chap. 3. Academic Press Inc, San Diego
ller RK (1979) The chemistry of silica. Wiley, New York
Schmidt H (1984) Mat Res Soc Symp Proc 32:327
Villegas MA, Aparicio M, Duran A (1997) J Non Cryst Solids 218:146
Kozuka H, Kajimura M, Hirano T et al (2000) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 19:205
Menning M, Jonschker G, Schmidt H (1997) German Patent DE 197 14 949 A1
Mehner A, Datchary W, Bleil N, Zoch H-W, Klopfstein MJ, Lucca DA (2005) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 36:25
Pethica JB, Hutchings R, Oliver WC (1983) Philos Mag A 48:593
King RB (1987) Int J Solid and Struct 23:1657
Briggs D (1998) Surface analysis of polymers by XPS and static SIMS. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
L’Ecuyer JL, Brassard C, Cardinal C et al (1976) J Appl Phys 47:381
Bückle H (1959) Metallurgical Rev 4:49
Marschall DB, Noma T, Evans AG (1982) J Am Ceram Soc 65(10):175
Scherer GW (1997) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 8:353
Kim KD, Ondarec G (1995) J Mat Sci Let 14:455
Roy SS, McCann R, Papakonstantinou P et al (2005) Thin Solid Films 482:145
Lukaszewicz JP (1997) J Mater Sci 32:6063
Moulder JF, Stickle WF et al (1992) Handbook of x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer Corp, Minnesota
Lucca DA, Ghisleni R, Nastasi M et al (2007) Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 257:577
Sorarù GD, d’Andrea G, Glisenti A (1996) Mater Lett 27:1
Nocuń M, Leja E, Jedliński J, Najman J (2005) J Mol Struct 744–747:597
Almeida RM, Pantano CG (1990) J Appl Phys 68(8):4225
Socrates G (1980) Infrared characteristic group frequencies. Wiley, Chichester
Murtagh MT, Shahriari MR, Krihak M (1998) Chem Mater 10:3862
Acknowledgments
This work is part of the Transregional Collaborative Research Centre SFB/TR4 “Process Chains for the Replication of Complex Optical Elements”. The support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) through the SFB/TR4 and the National Science Foundation through Grant Nos. OISE-0352377 and OISE-0128050 is gratefully acknowledged. The Los Alamos National Laboratory portion of this work was supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, and the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies, a US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences user facility at Los Alamos National Laboratory (Contract DE-AC52-06NA25396) and Sandia National Laboratories (Contract DE-AC04-94AL85000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehner, A., Dong, J., Prenzel, T. et al. Mechanical and chemical properties of thick hybrid sol–gel silica coatings from acid and base catalyzed sols. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 54, 355–362 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2203-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2203-z