Abstract
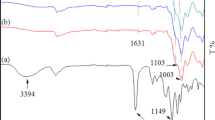
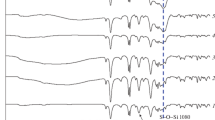
The sol–gel derived chemically combined organic–inorganic nanocomposites were synthesized from poly(etheramide) and tetraethoxysilane. Reaction of a mixture of 4-aminophenyl ether and 1,3-phenyldiamine with terephthaloyl chloride (TPC) in dimethylacetamide (DMAc) produced the amide chains. These chains were modified with carbonyl chloride end groups using a slight excess of diacid chloride and were then reacted with aminophenyl trimethoxysilane (APTMOS), where the amine group reacted with carbonyl chloride end groups. Hydrolysis/condensation of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) and alkoxy groups present in APTMOS developed bonding between the polyamide chains and inorganic silica network generated in situ. By changing the relative proportions of the polymer solution and the amount of TEOS, the composition of hybrid films was varied. Thin hybrid films with various concentrations of silica network obtained after evaporation of the solvent were subjected to mechanical, dynamic mechanical thermal and morphological measurements. The results indicate a gradual increase in the modulus (3.84 GPa) and tensile strength (121 MPa) up to 15-wt.% silica relative to the pure polyamide. The elongation at break point and toughness gradually decrease with addition of silica content. These hybrids were found to be thermally stable up to a temperature of 500 °C. The weight retained above 800 °C was roughly proportional to amount of silica in the matrix. The glass transition temperature and the storage moduli increased with increasing silica concentration. The maximum increase in the T g value (358 °C) was observed with 15-wt.% silica. Scanning electron micrographs indicated the uniform distribution of silica in the composites with an average particle size ranging from 9 to 47 nm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Sol–gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol–gel processing. Academic Press, Boston
Klein LC (1988) Sol–gel technology for thin films, performs, electronics and specialty shapes. Noyes, Park Ridge, NJ
Brinker CJ, Mecartney ML, Sanchez C (1986), (1988) Better ceramics through chemistry, vols II and III. Material research society, Pittsburgh
Hench LL, West JK (1990) Chem Rev 90:33
Mark JE (1992) J Appl Polym Sci Appl Polym Symp 50:273
Mark JE (1991) J Inorg Organomet Polym 1:431
Mark JE, Wang S, Ahmad Z (1995) Macromol Chem Symp 98:731
Schmidt H (1990) Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 180:961
Baney RH, Gillion LR, Hirano SI, Schmidt HK (1992) Submicron multiphase materials, vol 27. Material research society, Pittsburgh
Schmidt H (1994) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 1:217
Schmidt H (1984) Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 32:327
Phillip G, Schmidt H (1984) J Non-Cryst Solids 63:283
Schmidt H, Seiferling B (1986) Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 73:739
Sur GS, Mark JE (1985) Eur Polym J 21(2):1051
Tamami B, Betrabet C, Wilkes GL (1993) Polym Bull 30:39
Wang B, Wilkes GL (1994) J Macromol Sci Pure Appl Chem A31(2):249
Wen J, Vasudevan VJ, Wilkes GL (1995) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 5:115
Huang HH, Oler B, Wilkes GL (1987) Macromolecules 20:1322
Wang B, Wilkes GL (1991) J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem Ed 29:905
Brennan AB, Rodrigues DE, Wang B, Wilkes GL (1992) In: Hench LL, West JK (eds) Chemical processing of advanced materials. Wiley, New York
Betrabet CS, Wilkes GL (1995) Chem Mater 7:535
Ahmad Z, Wang S, Mark JE (1993) ACS Div Polym Chem Polym Prepr 34(2):745
Ahmad Z, Sarwar MI, Mark JE (1997) J Mater Chem 7(2):259
Ahmad Z, Sarwar MI, Mark JE (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 63:1345
Ahmad Z, Sarwar MI, Krug H, Schmidt H (1997) Int J Polym Mater 39:127
Ahmad Z, Sarwar MI, Wang S, Mark JE (1997) Polymer 38(17):4523
Ahmad Z, Sarwar MI, Mark JE (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 70:297
Ahmad Z, Sarwar MI, Krug H, Schmidt H (1997) Die Angew Makromol Chemie 248:139
Sarwar MI, Zulfiqar S, Ahmad Z (2007) Colloid Polym Sci (Online first)
Sarwar MI, Zulfiqar S, Ahmad Z (2007) Polym. Compos (In press)
Sarwar MI, Zulfiqar S, Ahmad Z (2007) Polym Int (Online first)
Sarwar MI, Zulfiqar S, Ahmad Z (2007) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 44:41
Mascia L, Kioul A (1994) J Mater Sci Lett 13(9):641
Wang S, Ahmad Z, Mark JE (1994) Polym Mater Sci Eng 70(1):305
Wang S, Ahmad Z, Mark JE (1994) Chem Mater 6:943
Ahmad Z, Wang S, Mark JE (1994) Polym Mater Sci Eng 70(1):303
Chen JP, Ahmad Z, Wang S, Mark JE, Arnold FE (1995) In: Mark JE, Lee CY-C, Bianconi PA (eds) Hybrid organic–inorganic composites. ACS Symp Ser 585, Washington, DC, pp 297
Zulfiqar S, Ahmad Z, Ishaq M, Saeed S, Sarwar MI (2007) J Mater Sci 42:93
Kausar A, Zulfiqar S, Shabbir S, Ishaq M, Sarwar MI (2007) Polym Bull 59:457
Mark JE, Jiang C-Y, Tang M-Y (1984) Macromolecules 17:2613
Brennan AB, Wilkes GL (1991) Polymer 32:733
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are due to Professor Dr. Gerhard Wegner and Dr. Ingo Lieberwirth of Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Mainz, Germany, for providing the SEM measurement facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarwar, M.I., Zulfiqar, S. & Ahmad, Z. Poly (ether amide) and silica nanocomposites derived from sol–gel process. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 45, 89–95 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-007-1640-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-007-1640-9