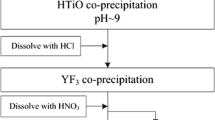
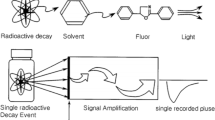
Abstract
A derivation of the Bateman equation combined with successive liquid scintillation counting measurements was used to rapidly determine accurate individual activities of 90Sr and 90Y in samples containing both isotopes regardless of the sample age. This method does not require chemical separation of Sr from Y or waiting for secular equilibrium to take place. Accurate data can be obtained within 3 half-lives of 90Y ingrowth (i.e. within 5 days), associated uncertainties with this method are comparable to those obtained with traditional techniques that include separations. This novel technique allows for decreased sample processing cost and time, without reducing data quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chadwick MB, Herman M, Oblozinsky P et al (2011) ENDF/B-VII. 1 nuclear data for science and technology: cross sections, covariances, fission product yields and decay data. Nucl Data Sheets 112:2887–2996
Baum EM, Ernesti MC, Knox HD, Miller TR, Watson AM (2009) Nuclides and isotopes chart of the nuclides, 17th edn. Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory
Bowen WQ, Cottee M, Hobbs C (2012) Multilateral cooperation and the prevention of nuclear terrorism: pragmatism over idealism. Int Aff 88:349–368
Charbonneau L, Benoit J-M, Jovanovic S et al (2014) A nuclear forensic method for determining the age of radioactive cobalt sources. Anal Methods 6:983–992
Eby N, Hermes R, Charnley N, Smoliga JA (2010) Trinitite-the atomic rock. Geol Today 26:180–185
Fedchenko V (2014) The role of nuclear forensics in nuclear security. Strateg Anal 38:230–247
Jones AE, Turner P, Zimmerman C, Goulermas JY (2014) Classification of spent reactor fuel for nuclear forensics. Anal Chem 86:5399–5405
Boulyga SF (2011) Mass spectrometric analysis of long-lived radionuclides in bio-assays. Int J Mass Spectrom 307:200–210
Boulyga SF, Becker JS (2002) Isotopic analysis of uranium and plutonium using ICP-MS and estimation of burn-up of spent uranium in contaminated environmental samples. J Anal At Spectrom 17:1143–1147
Public health statement: strontium. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/tp159-c1-b.pdf. Accessed 1 Feb 2019
Froidevaux P, Geering JJ, Valley JF (2006) 90Sr in deciduous teeth from 1950 to 2002: the Swiss experience. Sci Total Environ 367:596–605
Mangano JJ, Gould JM, Sternglass EJ et al (2003) An unexpected rise in strontium-90 in US deciduous teeth in the 1990s. Sci Total Environ 317:37–51
Alvarez A, Navarro N, Salvador S (1995) New method for 90Sr determination in liquid samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 191:315–322
ASTM International (2013) ASTM D5811-08(2013) standard test method for strontium-90 in water. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Wang JJ (2013) A quick liquid scintillation counting technique for analysis of 90Sr in environmental samples. Appl Radiat Isot 81:169–174
Environmental Protection Agency (2010) Rapid radiochemical methods for selected radionuclides in water for environmental restoration following homeland security events. Montgomery, AL
Grate JW, Strebin R, Janata J et al (1996) Automated analysis of radionuclides in nuclear waste: rapid determination of 90Sr by sequential injection analysis. Anal Chem 68:333–340
Holmgren S, Tovedal A, Jonsson S et al (2014) Handling interferences in 89Sr and 90Sr measurements of reactor coolant water: a method based on strontium separation chemistry. Appl Radiat Isot 90:94–101
Kameo Y, Katayama A, Fujiwara A et al (2007) Rapid determination of 89Sr and 90Sr in radioactive waste using Sr extraction disk and beta-ray spectrometer. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 274:71–78
Kiba T, Mizukami S (1958) Rapid separation of radioactive strontium extraction with TTA-hexone. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 31:1007–1013
Lee JS, Park UJ, Son KJ, Han HS (2009) One column operation for 90Sr/90Y separation by using a functionalized-silica. Appl Radiat Isot 67:1332–1335
Mateos JJ, Gomez E, Garcias F et al (2000) Rapid 90Sr/90Y determination in water samples using a sequential injection method. Sect Title Water 53:139–144
Maxwell SL, Culligan BK (2009) Rapid method for determination of radiostrontium in emergency milk samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279:757–760
Holmgren S, Tovedal A, Björnham O, Ramebäck H (2016) Time optimization of 90Sr determinations: sequential measurement of multiple samples during ingrowth of 90Y. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 110:150–154
O’Hara MJ, Burge SR, Grate JW (2009) Automated radioanalytical system for the determination of Sr-90 in environmental water samples by Y-90 Cherenkov radiation counting. Anal Chem 81:1228–1237
Olfert JM, Dai X, Kramer-Tremblay S (2014) Rapid determination of 90Sr/90Y in water samples by liquid scintillation and Cherenkov counting. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:263–267
Pan J, Emanuele K, Maher E, Lin ZC, Healey S, Regan P (2016) Analysis of radioactive strontium-90 in food by Čerenkov liquid scintillation counting. Appl Radiat Isot 126:214–218
Tarancón A, Alonso E, Garc JF, Rauret G (2002) Sr/90 Y determination by Cerenkov, liquid scintillation and plastic scintillation techniques. Anal Chim Acta 471:135–143
Tayeb M, Dai X, Corcoran EC, Kelly DG (2014) Evaluation of interferences on measurements of 90Sr/90Y by TDCR Cherenkov counting technique. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:409–414
Tsroya S, Dolgin B, German U et al (2013) Fast determination of 90Sr/90Y activity in milk by Cherenkov counting. Appl Radiat Isot 82:332–339
Vaca F, Manjón G, Garcia-León M (1998) Efficiency calibration of a liquid scintillation counter for 90Y cherenkov counting. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A Accel Spectrom Detect Assoc Equip 406:267–275
Bateman H (1910) The solution of a system of differential equations occuring in the theory of radioactive transformations. Proc Cambridge Philos Soc Math Phys Sci 15:423–427
Zhengshui H, Ying P, Wanwu M, Xun F (1995) Purification of organophosphorus acid extractants. Solvent Extr Ion Exch 13:965–976
Friend MT, Wall NA (2017) Hafnium(IV) complexation with oxalate at variable temperatures. Radiochim Acta 105:379–388
Swearingen KJ, Omoto T, Wall N (2017) Analysis of organic and high dissolved salt content solutions using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 37:1231–1236
Eikenberg J, Beer H, Rüthi M, Zumsteg I, Vetter A (2006) Precise determination of Sr-89 and 90-Sr 90-Y in various metrics. The LSC 3-window approach. In: Chatupnik S, Schonhofer F, Noakes J (eds) LSC 2005, advances in liquid scintillation spectrometry, pp 237–249
L’Annunziata M (2012) Handbook of radioactivity analysis. Academic Press, London
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, Basic Research Award #HDTRA1-12-1-0015, to Washington State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swearingen, K.J., Wall, N.A. Fast and accurate simultaneous quantification of strontium-90 and yttrium-90 using liquid scintillation counting in conjunction with the Bateman equation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 320, 71–78 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06444-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06444-6