Abstract
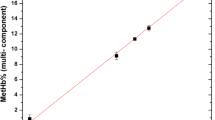
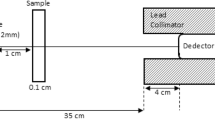
The objective of the proposed work is focused on measuring iron concentration directly in whole blood as tool for estimating hemoglobin and anemic conditions in patients across the world. The investigated method depends on theory of photon attenuation through transmission of low energy in whole blood sample. The mathematical expressions for calculating hemoglobin and iron deficit on blood using photon attenuation are derived. Calculations are carried out for estimating concentration of iron in blood samples taken from children, adults and old patients and therefore measuring their hemoglobin and iron deficit from normal values. Theoretical mass attenuation coefficient values were obtained using the XCOM program. A high-resolution gamma-ray spectrometry based on high purity germanium detector was employed to measure attenuation of strongly collimated monoenergetic gamma beam through blood samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anemia detection methods in low-resources settings. A manual for health workers. http://www.path.org. Accessed 25 Jan 2014
Malhotra M (2002) Anemia linked to poor outcomes for pregnant women and their babies. Int J Gynecol Obstet 79:93–100
World Health Organization (2008) Worldwide prevalence of anemia 1993–2005
Pundir CS, Chawla S (2014) Determination of glycated hemoglobin with special emphasis on biosensing methods. Anal Biochem 444:47–56
Pang S, Liu S, Su X (2014) A novel fluorescence assay for the detection of hemoglobin based on the G-quadruplex/hemin complex. Talanta 118:118–122
Ranganathan H, Gunasekaran N (2006) Simple method for estimation of hemoglobin in human blood using color analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 10(4):657–662
Medhat ME (2012) Gamma absorption technique in elemental analysis of composite materials. Ann Nucl Energy 47:204–209
Shivaramu (2002) Effective atomic numbers for photon energy absorption and photonattenuation of tissues from human organs. Med Dosim 27:1–9
Berger MJ, Hubbell JH, Seltzer SM, Chang J, Coursey JS, Sukumar R, Zucker DS, Olsen K (2010) XCOM: photon cross sections database, NIST standard reference database (XGAM). http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xcom/index.cfm. Accessed 25 Jan 2014
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank all members in the Institute of High Energy Physics (IHEP) during hosting my postdoctoral fellowship funded by Chinese Academy of Science (CAS), China. I would like to thank also Mrs. Jing Yu and Li Nan nurses from Beijing Universe Hospital for supporting blood samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medhat, M.E. A new method for detecting hemoglobin directly in whole blood using photon attenuation techniques. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300, 437–443 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-2992-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-2992-6