Abstract
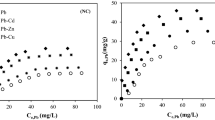
Fishbone as a main backfill material of permeable reactive barrier to remediate groundwater contaminated with Co and Sr was investigated through single- and bi-solute competitive sorptions. The single-solute sorption data were fitted by Freundlich, Langmuir and Dubinin-Radushkevich models. The coefficients of determination (R 2 > 0.91) indicated that all models fitted well. Maximum sorption capacities (q mL ) of Co and Sr predicted by the Langmuir model were 0.55 mmol/g and 0.50 mmol/g, respectively. The bi-solute competitive sorption of the metals was analyzed by the Langmuir, competitive Langmuir, Sheindorf-Rebhun-Sheintuch (SRS) and P-factor models. The sorbed amount of one solute in bi-solute system decreased due to competition with the other solute. Langmuir model parameters for single- (q mL and b L ) and bi-solute (q * mL and b * L ) competitive sorptions were compared to analyze the effect of competition between the metals. The competitive Langmuir, SRS and P-factor models predicted the bi-solute competitive sorption data well (R 2 > 0.93).






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b L :
-
Langmuir model constant (L/mmol)
- b L,i :
-
Langmuir model constant of a solute i in single-solute sorption (L/mmol)
- b * L,i :
-
Langmuir model constant of a solute i in bi-solute competitive sorption (L/mmol)
- C :
-
Aqueous-phase equilibrium concentration (mmol/L)
- C 0 :
-
Initial concentration (mmol/L) of metal in aqueous solution
- C m,i :
-
Aqueous-phase equilibrium concentration (mmol/L) of a solute i in multi-solute competitive sorption
- CLM:
-
Competitive Langmuir model
- E :
-
Mean free energy (kJ/mol) in Dubinin-Radushkevich model
- K F :
-
Freundlich sorption coefficient [(mmol/g)/(mmol/L)\( ^{{N_{F} }} \)]
- K F,i :
-
Freundlich sorption coefficient obtained from a single-solute system [(mmol/g)/(mmol/L)\( ^{{N_{F} }} \)]
- N d :
-
The number of data points
- N F :
-
Exponent in Freundlich model
- N F,i :
-
Exponent in Freundlich model obtained from a single-solute system
- P :
-
The number of parameters
- P i :
-
P-factor model parameter
- q :
-
Solid-phase equilibrium concentration (mmol/g)
- q i,exp :
-
Solid-phase equilibrium concentration of the experimental data (mmol/g)
- q i,pred :
-
Solid-phase equilibrium concentration of theoretically predicted points (mmol/g)
- q m,i :
-
Solid-phase equilibrium concentration of a solute i in multi-solute competitive sorption (mmol/g)
- q mD :
-
Maximum sorption capacity of Dubinin-Radushkevich model (mmol/g)
- q mL :
-
Maximum sorption capacity of Langmuir model (mmol/g)
- q mL,i :
-
Maximum sorption capacity of solute i in single-solute sorption predicted by Langmuir model (mmol/g)
- q * mL,i :
-
Maximum sorption capacity of solute i in bi-solute competitive sorption predicted by Langmuir model (mmol/g)
- R:
-
Gas constant, 8.314 (J/mole/K)
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- R L :
-
Separation factor
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- rss:
-
Residual sum of squares
- SSE:
-
Sum of squared errors
- T:
-
Absolute temperature (K)
- α:
-
SRS model coefficient
- α i,j :
-
Dimensionless competition coefficient for the sorption of solute i in the presence of solute j predicted by SRS model
- β:
-
Dubinin-Radushkevich model parameter (mol2/J2)
- ε:
-
Polanyi potential (J/mol)
References
ASTDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (2004) Toxicological profile for cobalt. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service
ASDTR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (2004) Toxicological profile for strontium. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service
Conca JL, Wright J (2006) Appl Geochem 21:1288–1300
Morrison SJ, Metzler DR, Dwyer BP (2002) J Contam Hydrol 56:99–116
El-Kamash AM (2008) J Hazard Mater 151:432–445
Simon F-G, Biermann V, Segebade C, Hedrich M (2004) Sci Total Environ 326:249–256
Admassu W, Breese T (1999) J Hazard Mater 69:187–196
Dimović S, Smičiklas I, Plećaš I, Antonović D, Mitrić M (2009) J Hazard Mater 164:279–287
Smičiklas I, Dimović S, Plećaš I, Mitrić M (2006) Water Res 40:2267–2274
Simon F-G, Segebade C, Hedrich M (2003) Sci Total Environ 307:231–238
Versada J, Hradil D, Řanda Z, Jelínek E, Štulík K (2005) Appl Clay Sci 30:53–66
USEPA (2007) Method 9081: cation-exchange capacity of soils (sodium acetate), Test methods for the evaluation of solid waste: laboratory manual physical chemical methods, SW-846, Washington, DC, USEPA, Office of Solid Waste
Smiciklas I, Dimovic S, Sljivic M, Plecas I (2008) J Environ Sci Health Part A 43:210–217
Wolff-Boenisch D, Traina SJ (2006) Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:4356–4366
Kundu S, Gupta AK (2006) Chem Eng J 122:93–106
Sheindorf C, Rebhun M, Sheintuch M (1881) J Colloid Interf Sci 79:136–142
Srivastava VC, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Chem Eng J 117:79–91
Valderrama C, Barios JI, Rarran A, Cortina JL (2010) Water Air Soil Pollut 210:421–434
Choy KKH, Proter JF, Mckay G (2000) J Chem Eng Data 45:575–584
Corami A, Mignardi S, Ferrini V (2008) J Colloid Interf Sci 317:402–408
Ma B, Shin WS, Oh S, Park Y-J, Choi S-J (2010) Sep Sci Technol 45:453–462
Changtawong V, Harvey NW, Bashkin VN (2003) Water Air Soil Pollut 148:111–125
Lazić S, Vuković Ž (1991) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 149:161–168
McKay G, Blair HS, Gardner JR (1982) J Appl Polym Sci 27:3040–3057
Wang LM, Chen J, Ewing RC (2004) Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 8:405–418
Handley-Sidhu S, Renshaw JC, Moriyama S, Stolpe B, Mennan C, Bagheriasl S, Yong P, Stamboulis A, Paterson-Beedle M, Sasaki K, Pattrick RAD, Lead JR, Macaskie LE (2011) Environ Sci Technol 45:6985–6990
Lazarević S, Janković-Častvan I, Tanasković D, Pavićević V, Janaćković Dj, Petrović R (2008) J Environ Eng 134:683–688
Rosskopfová O, Galamboš M, Rajec P (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287:715–722
Gómez del Río JA, Morando PJ, Cicerone DS (2004) J Environ Manage 71:169–177
Park Y, Shin WS, Choi S-J (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292:837–852
Khan SA, Rehman RU, Khan MA (1995) Waste Manag 15:641–650
Bhattacharyya KG, Gupta SS (2007) Sep Sci Technol 42:3391–3418
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (grant number: M20709005401-07B0900-40110). The authors would like to acknowledge the Korea Basic Science Institute (Daegu) and Kyungpook National University Center for Scientific Instrument for SEM–EDS, XRF and XRD analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y., Shin, W.S. & Choi, SJ. Removal of cobalt and strontium from groundwater by sorption onto fishbone. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295, 789–799 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1959-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1959-8