Abstract
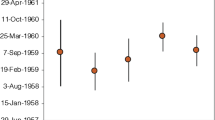
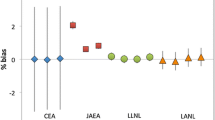
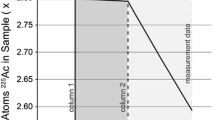
Plutonium (Pu) metal samples from an interlaboratory exchange exercise and simulated swipe samples were dated using plutonium–uranium (Pu–U) and plutonium–americium (Pu–Am). Metal data were evaluated for consistency and the swipe data against its source material. Metal ages based on 239Pu versus 235U and 240Pu versus 236U agreed to within a few percent, while the 238Pu–234U and 241Pu–241Am measurements had larger uncertainties. Swipe ages compared favorably with the material’s known history. Neptunium (237Np) analyses were examined in the context of the 241Pu–241Am–237Np system to estimate whether Np can provide insights on material from which Am, Np, and U were removed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tandon L, Kuhn K, Decker D, Porterfield D, Laintz K, Wong A, Holland M, Peterson DS. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-009-0215-3
Moody KJ (1995) Technical report. U.S. UCRL-ID-120253
Wallenius M, Meyer K (2000) Fresenius J Anal Chem 366:234
Marsh S, Ortiz M, Abernathy R, Rein J (1974) Los Alamos report 5568
Callis E, Abernathy R (1991) Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Proc 103:93105
Lycke W, De Bievre P, Damen R, Gallet M, Hendrickx F, Rosman K (1987) Proceedings of an international symposium on nuclear material safeguards, vol 1. p 115
Callis EL, Saponara NM, Noll PD Jr (1997) Chemical Science and Technology Division (CST), Division Review Poster Session, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico, U.S.A. June 19, 1997
Mahan C, Bonchin S, Figg D, Gerth D, Collier C (2000) J Anal At Spectrom 15:929
Tandon L, Kuhn K, Porterfield D, Temer D, Decker D, Hastings B Los Alamos Controlled Publication 08-0580
Donohue D (1998) J Alloys Compd 11:271
Faure G (1986) Principles of isotope geology. Wiley, New York, p 291
Chart of the nuclides, General Electric Co., San Jose, 1989
Katz J, Seaborg G, Morss L (1986) The chemistry of the actinide elements, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London, p 499
Moody K, Hutcheon I, Grant P (2005) Nuclear forensic analysis. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, p 237
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the technical and support staff of the various laboratories whose work contributed to this publication. This program is administered by LANL under the auspices of the U.S. Dept. of Energy. The Nuclear Weapons Pit Manufacturing Program provided financial support. LANL is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, for the U.S. Dept. of Energy under contract no. DE-AC52-06NA25396. This publication is LA-UR 09-02059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spencer, K.J., Tandon, L., Gallimore, D. et al. Refinement of Pu parent–daughter isotopic and concentration analysis for forensic (dating) purposes. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 282, 549–554 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0287-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0287-0