Abstract
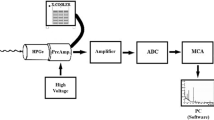
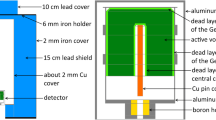
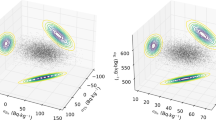
Low-level gamma-ray spectrometry with large volume HPGe detectors has been widely used in analysis of environmental radionuclides. The reasons are excellent energy resolution and high efficiency that permits selective and non-destructive analyses of several radionuclides in composite samples. Although the most effective way of increasing the sensitivity of a gamma-ray spectrometer is to increase counting efficiency and the amount of the sample, very often the only possible way is to decrease the detector’s background. The typical background components of a low-level HPGe detector, not situated deep underground, are cosmic radiation (cosmic muons, neutrons and activation products), radioactivity of construction materials, radon and its progenies. A review of Monte Carlo simulations of background components of HPGe detectors, and their characteristics in coincidence and anti-Compton mode of operation are presented and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Heusser, in: Low-Level Measurements of Radioactivity in the Environment, M. Garcia-Leon, R. Garcia-Tenorio (Eds), World Scientific, Singapore, 1994, p. 69.
P. P. Povinec, in: Low-level Measurements of Radioactivity in the Environment, M. Garcia-Leon, M. Garcia-Tenorio (Eds), World Scientific, Singapore, 1994, p. 113.
P. Vojtyla, J. Beer, P. Štavina, Nucl. Instr. Meth., B86 (1994) 380.
G. Heusser, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci., 45 (1995) 543.
S. Niese, M. Koehler, B. Gleisberg, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 233 (1998) 167.
H. Neder, G. Heusser, M. Laubenstein, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 53 (2000) 191.
S. Neumaier, D. Arnold, J. Boehm, E. Funck, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 53 (2000) 173.
P. Vojtyla, P. P. Povinec, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 53 (2000) 185.
T. M. Semkow, P. P. Parekh, C. D. Schwenker, A. J. Khan, A. Bari, J. F. Colaresi, O. K. Tench, G. David, W. Guryn, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 57 (2002) 213.
P. P. Povinec, in: Marine Radioactivity, H. D. Livingston (Ed.), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2004, p. 237.
P. P. Povinec, J.-F. Comanducci, I. Levy-Palomo, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 61 (2004) 85.
P. P. Povinec, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 261 (2005) 413.
P. Theodorsson, Measurement of Weak Radioactivity, World Scientific, Singapore, 1996, p. 333.
M. Laubenstein, M. Hult, J. Gasparo, D. Arnold, S. Neumaier, G. Heusser, M. Koehler, P. P. Povinec, J.-L. Reyss, M. Schwaiger, P. Theodorsson, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 61 (2004) 167.
M. Hult, M. J. Martinez Canet, M. Koehler, J. Das Neves, P. N. Johnston, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 53 (2000) 225.
K. Komura, Y. Hamajima, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 61 (2004) 185.
S. Pagava, A. A. Burchuladze, T. Robakidze, L. Rusetski, D. Tsintsadze, P. P. Povinec, M. Chudy, J. Stanicek, in: Rare Nuclear Processes, P. P. Povinec (Ed.), World Scientific, Singapore, 1992, p. 300.
G. Heusser, M. Laubenstein, H. Neder, in: Radionuclides in the Environment, P. P. Povinec, J. A. Sanchez-Cabeza (Eds), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006, p. 495.
K. Debertin, R. G. Helmer, Gamma and X-Ray Spectrometry with Semiconductor Detectors, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1998.
P. P. Povinec, Isotopenpraxis, 18 (1982) 423.
I. Zvara, P. Povinec, I. Sykora, Pure Appl. Chem., 66 (1994) 2537.
CERN, GEANT Detector Description and Simulation Tool, CERN Program Library Office, CERN, Geneva, 1990.
P. Vojtyla, Nucl. Instr. Meth., B100 (1995) 87.
P. Vojtyla, Nucl. Instr. Meth., B111 (1996) 163.
P. Vojtyla, P. P. Povinec, in: Radionuclides in the Environment, P. P. Povinec, J. A. Sanchez-Cabeza (Eds), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006, p. 529.
J. Stanicek, P. P. Povinec, Nucl. Instr. Meth., B17 (1986) 462.
P. P. Povinec, J.-F. Comanducci, I. Levy-Palomo, F. Avaullee, in: Radionuclides in the Environment, P. P. Povinec, J. A. Sanchez-Cabeza (Eds), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006, p. 538.
I. Sykora, P. P. Povinec, Nucl. Instr. Meth., B17 (1986) 467.
V. Hlinka, S. Usacev, P. P. Povinec, M. Chudy, Acta Univ. Comen. Phys., 18 (1977) 109.
I. Sykora, P. P. Povinec, Acta Physica Univ. Comen., 31 (1990) 83.
I. Sykora, M. Durcik, J. Stanicek, P. P. Povinec, in: Rare Nuclear Processes, P. P. Povinec (Ed.), World Scientific, Singapore, 1992, p. 321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Povinec, P.P. Low-level gamma-ray spectrometry for environmental samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 276, 771–777 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-008-0631-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-008-0631-9