Summary
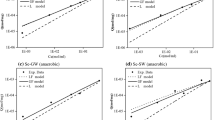
Sorption of radionuclides onto surrounding rocks play an important role in retarding the migration of radionuclides from a radioactive waste repository. The sorption isotherm model is usually used to describe the sorption behaviors and assess the sorption potential of radionuclides on rock. However, most of the studies to investigate the feasibility of isotherm models for the sorption of radionuclides are based on the assumption that the sorption energy is uniform and homogeneously distributed on the sorbent surfaces. In this study, two heterogeneity-based isotherms, Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm model (LF) and generalized-Freundlich isotherm model (GF), were used for the evaluation of the sorption characteristics of cesium on the selected Taiwan tuff and basalt. The sorption experiments in this study were carried out by batch method, and the experimental data were modeled by LF and GF heterogeneity-based isotherm models. The results showed that both of the LF and GF models could fit the data more perfectly than the Langmuir model. The heterogeneity of sorption onto tuff and basalt could be well characterized by the LF and GF models by means of the calculation and plotting of the affinity spectrum. The results showed that the sorption surface of tuff is more heterogeneous and complex than that of basalts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, SC., Juang, KW. & Jan, YL. Sorption of cesium on rocks using heterogeneity-based isotherm models. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 266, 101–105 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0876-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0876-5