Summary
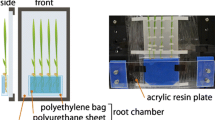
We present a new trial to measure real time water movement in a living plant using the positron emitting radionuclide, 15O. 15O was prepared by 14N(d,n)15O reaction and 10 ml of 15O labeled water (2 GBq) was supplied from the root of a soybean plant. To detect activity, an imaging plate (IP) as well as a BGO detector system were used. Since the half-life of 15O is extremely short, (T 1/2= 122 s), water uptake measurement was performed only for 20 minutes. In order to get [15O]waterimage, an IP was exposed to the plant for 1 minute for two times. Since the exposure to an IP requires dark condition, a BGO detector system was developed to measure [15O]waterunder light condition. A couple of BGO probes was set at the lowest stem and the gamma-rays (0.511 MeV) emitted from the radionuclide were measured through coincidence counting and compared with the radioactivity measured from an IP image. Using this system, we have found that the water uptake activity of the plant was drastically reduced under high humidity (99%) and dark condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanoi, K., Hojo, J., Nishioka, M. et al. New technique to trace [<Superscript>15</Superscript>O]water uptake in a living plant with an imaging plate and a BGO detector system. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263, 547–552 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0090-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0090-5