Summary
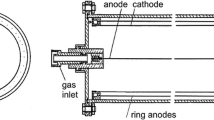
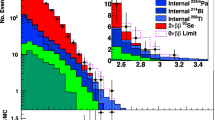
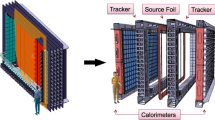
Recent developments in radiometrics and mass spectrometry techniques for ultra-sensitive analysis of radionuclides in the marine environment are reviewed. In the radiometrics sector the dominant development has been the utilization of large HPGe detectors in underground laboratories with anti-cosmic or anti-Compton shielding for the analysis of short and medium-lived radionuclides in the environment. In the mass spectrometry sector, applications of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) for the analysis of long-lived radionuclides in the environment are the most important recent achievements. The recent developments do not only considerably decrease the detection limits for several radionuclides (up to several orders of magnitude), but they also enable to decrease sample volumes so that sampling, e.g., of the water column can be much easier and more effective. A comparison of radiometrics and mass spectrometry results for the analysis of radionuclides in the marine environment shows a reasonable agreement - within quoted uncertainties, for wide range of activities and different sample matrices analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Povinec, P. Ultra-sensitive radionuclide spectrometry: Radiometrics and mass spectrometry synergy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263, 413–417 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0070-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0070-9