Abstract
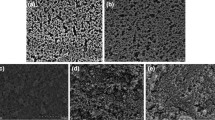
Asymmetric reverse osmosis membranes of cellulose acetate (CA) in presence of chitosan nanoparticles as anti-biofouling material were prepared using the phase-inversion technique. The effect of some preparation parameters on the membrane properties, e.g. polymer composition, evaporation time and annealing temperature were studied. FTIR, TGA, SEM and Contact angle were carried out to characterize the produced membranes. The water flux and salt rejection of the membranes were assessed using 35 g/L Nacl in a dead end filtration system. The results revealed that the addition of chitosan nanoparticles increased the water flux from 6 L/m2.h for blank (CA-0) to about 18 L/m2.h for (CA-2) membrane containing 2% chitosan nanoparticles with increment of salt rejection from 89 to 94%. For membrane with proper salt rejection it should be annealed at 80 °C prior to filtration test. The static adhesion test indicated enhancement in fouling resistance of the membrane containing chitosan nanoparticles to bacterial attack.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Etemadi H, Yegani R, Babaeipour V (2016) Study on the reinforcing effect of nanodiamond particles on the mechanical, thermal and antibacterial properties of cellulose acetate membranes. Diam Relat Mater 69:166–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2016.08.014
Baker RW (2004) Membrane technology and applications. Wiley, England
Abdelhamid AE, Khalil AM (2019) Polymeric membranes based on cellulose acetate loaded with candle soot nanoparticles for water desalination. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 56:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2018.1559698
Goetz LA, Jalvo B, Rosal R, Mathew AP (2016) Superhydrophilic anti-fouling electrospun cellulose acetate membranes coated with chitin nanocrystals for water filtration. J Memb Sci 510:238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.02.069
Powell LC, Hilal N, Wright CJ (2017) Atomic force microscopy study of the biofouling and mechanical properties of virgin and industrially fouled reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 404:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.11.010
Nagaraj V, Skillman L, Li D, Ho G (2018) Review – Bacteria and their extracellular polymeric substances causing biofouling on seawater reverse osmosis desalination membranes. J Environ Manage 223:586–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.088
Prihasto N, Liu QF, Kim SH (2009) Pre-treatment strategies for seawater desalination by reverse osmosis system. Desalination 249:308–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.09.010
Ben-Sasson M, Lu X, Bar-Zeev E, Zodrow KR, Nejati S, Qi G, Giannelis EP, Elimelech M (2014) In situ formation of silver nanoparticles on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membranes for biofouling mitigation. Water Res 62:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.05.049
Otitoju TA, Saari RA, Ahmad AL (2018) Progress in the modification of reverse osmosis (RO) membranes for enhanced performance. J Ind Eng Chem 67:52–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.07.010
Isawi H (2018) Development of thin-film composite membranes via radical grafting with methacrylic acid/ ZnO doped TiO2 nanocomposites. React Funct Polym 131:400–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.08.018
Abdelhamid AE, Elawady MM, El-Ghaffar MAA, Rabie AM, Larsen P, Christensen ML (2015) Surface modification of reverse osmosis membranes with zwitterionic polymer to reduce biofouling. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 15:999–1010. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2015.055
Marrez DA, Abdelhamid AE, Darwesh OM (2019) Eco-friendly cellulose acetate green synthesized silver nano-composite as antibacterial packaging system for food safety. Food Packag Shelf Life 20:100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100302
Elhalawany N, Wassel AR, Abdelhamid AE, Elfadl AA, Nouh S (2020) Novel hyper branched polyaniline nanocomposites for gamma radiation dosimetry. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02884-z
Abdelwahab NA, El-Nashar DE, El-Ghaffar MAA (2011) Polyfuran, polythiophene and their blend as novel antioxidants for styrene- butadiene rubber vulcanizates. Mater Des 32:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.06.003
Abd El-Ghaffar MA, El-Nashar DE, Youssef EAM (2003) Maleic acid/phenylene diamine adducts as new antioxidant amide polymers for rubber (NR and SBR) vulcanizates. Polym Degrad Stab 82:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(03)00161-7
Song HM, Zhu LJ, Zeng ZX, Xue QJ (2018) High performance forward osmosis cellulose acetate (CA) membrane modified by polyvinyl alcohol and polydopamine. J. Polym. Res. 25:159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1555-x
El-Shahat M, Abdelhamid AE, Abdelhameed RM (2020) Capture of iodide from wastewater by effective adsorptive membrane synthesized from MIL-125-NH2 and cross-linked chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 231:115742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115742
Wang X, Huang S, Wang Y, Wei P, Chen Y, Xia Y, Wang Y (2017) Eco-friendly cellulose acetate butyrate/poly(butylene succinate) blends: crystallization, miscibility, thermostability, rheological and mechanical properties. J. Polym. Res. 24:16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-1165-4
Wu H, Li T, Liu B, Chen C, Wang S, Crittenden JC (2018) Blended PVC/PVC-g-PEGMA ultrafiltration membranes with enhanced performance and antifouling properties. Appl Surf Sci 455:987–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.056
A. Ghaee, M. Shariaty-Niassar, J. Barzin, A.F. Ismail, Chitosan/Polyethersulfone Composite Nanofiltration Membrane for Industrial Wastewater Treatment, 2013.
Waheed S, Ahmad A, Khan SM, Gul SE, Jamil T, Islam A, Hussain T (2014) Synthesis, characterization, permeation and antibacterial properties of cellulose acetate/polyethylene glycol membranes modified with chitosan. Desalination 351:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.07.019
Arthanareeswaran G, Kumar SA (2010) Effect of additives concentration on performance of cellulose acetate and polyethersulfone blend membranes. J Porous Mater 17:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-009-9319-y
Zhang A, Zhang Y, Pan G, Xu J, Yan H, Liu Y (2017) In situ formation of copper nanoparticles in carboxylated chitosan layer: Preparation and characterization of surface modified TFC membrane with protein fouling resistance and long-lasting antibacterial properties. Sep Purif Technol 176:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.12.006
Liu C, Bai R (2006) Preparing highly porous chitosan/cellulose acetate blend hollow fibers as adsorptive membranes: Effect of polymer concentrations and coagulant compositions. J Memb Sci 279:336–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.019
Kong M, Chen XG, Xing K, Park HJ (2010) Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int J Food Microbiol 144:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.012
Bagheripour E, Moghadassi AR, Hosseini SM, Ray MB, Parvizian F, Bruggen Van der B (2018) Highly hydrophilic and antifouling nanofiltration membrane incorporated with water-dispersible composite activated carbon/chitosan nanoparticles. Chem Eng Res Des 132:812–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.02.027
Worthley CH, Constantopoulos KT, Ginic-Markovic M, Markovic E, Clarke S (2013) A study into the effect of POSS nanoparticles on cellulose acetate membranes. J Memb Sci 431:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.12.025
Vercellino T, Morse A, Tran P, Song L, Hamood A, Reid T, Moseley T (2013) Attachment of organo-selenium to polyamide composite reverse osmosis membranes to inhibit biofilm formation of S. aureus and E. coli. Desalination 309:291–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.10.020
Liu PS, Chen Q, Wu SS, Shen J, Lin SC (2010) Surface modification of cellulose membranes with zwitterionic polymers for resistance to protein adsorption and platelet adhesion. J Memb Sci 350:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.01.015
El-Sayed AA, Amr A, Kamel OMHM, El-Saidi MMT, Abdelhamid AE (2020) Eco-friendly fabric modification based on AgNPs@Moringa for mosquito repellent applications. Cellulose 8:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03355-8
Li F, Fei P, Cheng B, Meng J, Liao L (2019) Synthesis, characterization and excellent antibacterial property of cellulose acetate reverse osmosis membrane via a two-step reaction. Carbohydr Polym 216:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.026
Moghazy RM, Labena A, Husien S, Mansor ES, Abdelhamid AE (2020) Neoteric approach for efficient eco-friendly dye removal and recovery using algal-polymer biosorbent sheets: Characterization, factorial design, equilibrium and kinetics. Int J Biol Macromol 157:494–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.165
Liu C, Bai R (2005) Preparation of chitosan/cellulose acetate blend hollow fibers for adsorptive performance. J Memb Sci 267:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.06.001
Ghaseminezhad SM, Barikani M, Salehirad M (2019) Development of graphene oxide-cellulose acetate nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane for seawater desalination. Compos Part B Eng 161:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.10.079
Ngo TMP, Nguyen TH, Dang TMQ, Tran TX, Rachtanapun P (2020) Characteristics and antimicrobial properties of active edible films based on pectin and nanochitosan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062224
Kusworo TD, Budiyono AL, Wibowo AI, Harjanto GD, Yudisthira AD, Iswanto FB (2014) Cellulose acetate membrane with improved perm-selectivity through modification dope composition and solvent evaporation for water softening. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 7:3852–3859. https://doi.org/10.19026/rjaset.7.742
Su J, Yang Q, Teo JF, Chung TS (2010) Cellulose acetate nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for forward osmosis processes. J Memb Sci 355:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2010.03.003
Manjikian S (1967) Desalination Membranes from Organic Casting Solutions. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 6:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/i360021a004
Weng R, Chen L, Lin S, Zhang H, Wu H, Liu K, Cao S, Huang L (2017) Preparation and characterization of antibacterial cellulose/chitosan nanofiltration membranes. Polymers (Basel). 9:116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9040116
Zidan TA, Abdelhamid AE, Zaki EG (2020) N-Aminorhodanine modified chitosan hydrogel for antibacterial and copper ions removal from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 158:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.180
Ardila N, Daigle F, Heuzey MC, Ajji A (2017) Antibacterial activity of neat chitosan powder and flakes. Molecules 22(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010100
Pan C, Qian J, Fan J, Guo H, Gou L, Yang H, Liang C (2019) Preparation nanoparticle by ionic cross-linked emulsified chitosan and its antibacterial activity. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 568:362–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.02.039
Acknowledgement
The author would like to thank National research Centre for contribution in completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
High lights: (1) Cellulose acetate membranes were prepared via phase-inversion technique; (2) The membranes blended with chitosan nano-particles showed enhanced water flux and salt rejection properties; (3) The cellulose membranes modified with chitosan nano-particles exhibited remarkable antifouling properties to bacterial attack.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Ghaffar, M.A.A., Elawady, M.M., Rabie, A.M. et al. Enhancing the RO performance of cellulose acetate membrane using chitosan nanoparticles. J Polym Res 27, 337 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02319-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02319-7