Abstract
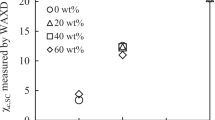
Asymmetric poly(L-lactide)/poly(D-Lactide) (PLLA/PDLA) blends were prepared by adding small amounts of PDLA into the PLLA matrix with the formation of stereocomplex crystallites (sc-crystallites). Rheological results indicated that the PLLA/PDLA melt at lower temperatures (<Tm,sc, the melting temperature of the formed stereocomplex crystallites) underwent the transition from liquid-like to solid-like viscoelastic behaviors with increasing of the PDLA concentration, which was related to the sc-crystallites reserved in the melt of asymmetric PLLA/PDLA blends. Dissolution experiment indicated the presence of sc-crystallites network structure in the PLLA/PDLA blends, and the size of the sc-crystallite junction particles network increased with increasing of the PDLA concentration. DSC and POM studies indicated that the PDLA concentration and the thermal treatment temperature had a significant influence on the PLLA crystallizability behavior. At low thermal treatment temperature (<T m,sc ), reserved sc-crystallites showed an obvious promoting effect for PLLA crystallization. With increasing of the thermal treatment temperature, its promoting effect decreased due to melting of the sc-crystallites. This result suggests the sc-crystallites played two roles: nucleation sites and cross-linking points, and the two roles had a competitive relationship with change of the thermal treatment temperature and the PDLA concentration.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai H, Liu H, Bai D, Zhang Q, Wang K, Deng H, Chen F, Fu Q (2014) Enhancing the melt stability of polylactide stereocomplexes using a solid-state cross-linking strategy during a melt-blending process. Polym Chem 5:5985–5993
Corneillie S, Smet M (2015) PLA architectures: the role of branching. Polym Chem 6:850–867
Rapoport N (2007) Physical stimuli-responsive polymeric micelles for anti-cancer drug delivery. Prog Polym Sci 32:962–990
Yang F, Murugan R, Ramakrishna S, Wang X, Ma Y-X, Wang S (2004) Fabrication of nano-structured porous PLLA scaffold intended for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials 25:1891–1900
Zeng J, Xu X, Chen X, Liang Q, Bian X, Yang L, Jing X (2003) Biodegradable electrospun fibers for drug delivery. J Control Release 92:227–231
Xu Y, Wang Y, Xu T, Zhang J, Liu C (2014) Crystallization kinetics and morphology of partially melted poly(lactic acid). Polym Test 37:179–185
Zeng X, Wu B, Wu L, Hu J, Bu Z, Li BG (2014) Poly(L-lactic acid)-block-poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) multiblock copolymers: from synthesis to thermo-mechanical properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:3550–3558
Xu Z, Niu Y, Yang L, Xie W, Li H, Gan Z, Wang Z (2010) Morphology, rheology and crystallization behavior of polylactide composites prepared through addition of five-armed star polylactide grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 51:730–737
Wang L, Jing X, Cheng H, Hu X, Yang L, Huang Y (2012) Rheology and crystallization of long-chain branched poly(L-lactide)s with controlled branch length. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:10731–10741
Wang L, Jing X, Cheng H, Hu X, Yang L, Huang Y (2012) Blends of linear and long-chain branched poly(L-lactide)s with high melt strength and fast crystallization rate. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:10088–10099
Brutman JP, Delgado PA, Hillmyer MA (2014) Polylactide vitrimers. ACS Macro Lett 3:607–610
Xie M, Wang L, Ge J, Guo B, Ma PX (2015) Strong electroactive biodegradable shape memory polymer networks based on star-shaped polylactide and aniline trimer for bone tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:6772–6781
Fischer AM, Wolf FK, Frey H (2012) Long-chain branched poly(Lactide)s based on polycondensation of AB2-type macromonomers. Macromol Chem Phys 213:1349–1358
Ishida K, Furuhashi Y, Yoshie N (2014) Synthesis of Diels–Alder network polymers from bisfuranic terminated poly (L-lactide) and tris-maleimide. Polym Degrad Stabil 110:149–155
Chakoli AN, He J, Chayjan MA, Huang Y, Zhang B (2015) Irradiation of poly(L-lactide) biopolymer reinforced with functionalized MWCNTs. RSC Adv 5:55544–55549
Zhang D, Kandadai MA, Cech J, Roth S, Curran SA (2006) Poly(L-lactide)(PLLA)/multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) composite: characterization and biocompatibility evaluation. J Phys Chem B 110:12910–12915
Jing Z, Shi X, Zhang G, Qin J (2015) Synthesis, stereocomplex crystallization and properties of poly (L-lactide)/four-armed star poly (D-Lactide) functionalized carbon nanotubes nanocomposites. Polym Adv Technol 26:223–233
Yang JH, Lin SH, Lee YD (2012) Preparation and characterization of poly(L-lactide)–graphene composites using the in situ ring-opening polymerization of PLLA with graphene as the initiator. J Mater Chem 22:10805–10815
Gu J, Li N, Tian L, Lv Z, Zhang Q (2015) High thermal conductivity graphite nanoplatelet/UHMWPE nanocomposites. RSC Adv 5:36334–36339
Zheng X, Zhou S, Li X, Weng J (2006) Shape memory properties of poly(D, L-lactide)/hydroxyapatite composites. Biomaterials 27:4288–4295
Ignjatović N, Tomić S, Dakić M, Miljković M, Plavšić M, Uskoković DS (1999) Properties of hydroxyapatite/poly-L-lactide composite biomaterials. Biomaterials 20:809–816
Raquez JM, Habibi Y, Murariu M, Dubois P (2013) Polylactide (PLA)-based nanocomposites. Prog Polym Sci 38:1504–1542
Liu H, Bai D, Bai H, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2015) Constructing stereocomplex structure at the interface for remarkably accelerating matrix crystallization and enhancing mechanical properties of poly(L-lactide)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites. J Mater Chem A 3:13835–13847
Yin HY, Wei XF, Bao RY, Dong QX, Liu ZY, Yang W, Xie BH, Yang MB (2015) Enantiomeric poly(D-lactide) with a higher melting point served as a significant nucleating agent for poly(L-lactide). Cryst Eng Comm 17:4334–4342
Jing Z, Shi X, Zhang G, Lei R (2015) Investigation of poly(lactide) stereocomplexation between linear poly(L-lactide) and PDLA-PEG-PDLA tri-block copolymer. Polym Int 64:1399–1407
Shao J, Sun J, Bian X, Cui Y, Li G, Chen X (2012) Investigation of poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: 3-armed poly(L-lactide) blended with linear and 3-armed enantiomers. J Phys Chem B 116:9983–9991
Tsuji H (2005) Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications. Macromol Biosci 5:569–597
Tsuji H, Ikada Y (1999) Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. XI. Mechanical properties and morphology of solution-cast films. Polymer 40:6699–6708
Yamane H, Sasai K, Takano M, Takahashi M (2004) Poly(D-lactic acid) as a rheological modifier of poly(L-lactic acid): shear and biaxial extensional flow behavior. J Rheol 48:599–609
Inkinen S, Stolt M, Sodergard A (2011) Effect of blending ratio and oligomer structure on the thermal transitions of stereocomplexes consisting of D-lactic acid oligomer and poly(L-lactide). Polym Adv Technol 22:1658–1664
Wei XF, Bao R, Cao Z, Yang W, Xie B, Yang M (2014) Stereocomplex crystallite network in asymmetric PLLA/PDLA blends: formation, structure, and confining effect on the crystallization rate of homocrystallites. Macromolecules 47:1439–1448
Ma, P.; Shen, T.; Xu, P.; Dong, W.; Lemetra, P.J.; Chen, M. superior Performance of fully bio-based poly(lactide) via stereocomplexation-induced phase separation: structure versus property. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2015, 3, 1470–1478
Cartier L, Okihara T, Ikada Y, Tsuji H, Puiggali J, Lotz B (2000) Epitaxial crystallization and crystalline polymorphism of polylactides. Polymer 41:8909–8919
Pei A, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2010) Functionalized cellulose nanocrystals as biobased nucleation agents in poly(L-lactide)(PLLA)–crystallization and mechanical property effects. Compos Sci Technol 70:815–821
Sun Y, He C (2012) Synthesis and stereocomplex crystallization of poly(lactide)–graphene oxide nanocomposites. ACS Macro Lett 1:709–713
Baimark Y, Srihanam P (2015) Influence of chain extender on thermal properties and melt flow index of stereocomplex PLA. Polym Test 45:52–57
Pan P, Han L, Bao J, Xie Q, Shan G, Bao Y (2015) Competitive stereocomplexation, homocrystallization, and polymorphic crystalline transition in poly(L-lactic acid)/poly(D-lactic acid) racemic blends: molecular weight effects. J Phys Chem B 119:6462–6470
Li Y, Han C, Bian J, Han L, Dong L, Gao G (2012) Rheology and biodegradation of polylactide/silica nanocomposites. Polym Composite 33:1719–1727
Raffa P, Stuart MCA, Broekhuis AA, Picchioni F (2014) The effect of hydrophilic and hydrophobic block length on the rheology of amphiphilic diblock polystyrene-b-poly(sodium methacrylate) copolymers prepared by ATRP. J Colloid Interf Sci 428:152–161
Jing Z, Shi X, Zhang G, Li J (2015) Rheology and crystallization behavior of PLLA/TiO2-g-PDLA composites. Polym Adv Technol 26:528–537
Narita J, Katagiri M, Tsuji H (2013) Highly enhanced accelerating effect of melt-recrystallized stereocomplex crystallites on poly(L-lactic acid) crystallization, 2-effects of poly(D-lactic acid) concentration. Macromol Mater Eng 298:270–282
Coppola S, Acierno S, Grizzuti N, Vlassopoulos D (2006) Viscoelastic behavior of semicrystalline thermoplastic polymers during the early stages of crystallization. Macromolecules 39:1507–1514
Li Y, Xin S, Bian Y, Dong Q, Han C, Xu K, Dong L (2015) Stereocomplex crystallite network in poly(D, L-lactide): formation, structure and the effect on shape memory behaviors and enzymatic hydrolysis of poly(D, L-lactide). RSC Adv 5:24352–24362
Yamane H, Sasai K (2003) Effect of the addition of poly(D-lactic acid) on the thermal property of poly (L-lactic acid). Polymer 44:2569–2575
Okihara T, Tsuji M, Kawaguchi A, Katayama KI, Tsuji H, Hyon SH, Ikada Y (1991) Crystal structure of stereocomplex of poly(L-lactide) and poly(D-lactide). J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 30:119–140
Schmidt SC, Hillmyer MA (2001) Polylactide stereocomplex crystallites as nucleating agents for isotactic polylactide. J Polym Sci Polym Phys 39:300–313
Acknowledgements
The authors thank by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 51303149) for support. The research was also sponsored by the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University (CX201625) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province in China (No.2015JQ2045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Jing, Z. & Zhang, G. Influence of PLA stereocomplex crystals and thermal treatment temperature on the rheology and crystallization behavior of asymmetric poly(L-Lactide)/poly(D-lactide) blends. J Polym Res 25, 71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1467-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1467-9