Abstract
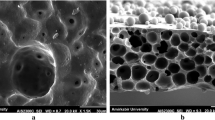
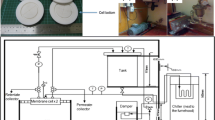
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) membranes are widely applied in many chemical engineering fields. In this research, novel asymmetric PAN membranes with high hydrophilicity and permeability were prepared from a PAN/polyoxyethylene (40) nonylphenyl ether (IGEPAL)/NMP system via immersion precipitation. Pure water was used as the gelation medium. The effects of adding IGEPAL, the coagulation bath temperature (CBT), and the PAN concentration on the morphology, wettability, and permeability of the prepared membranes were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), contact angle measurement, and permeation experiments. The results demonstrated that both the hydrophilicity and the permeability of the prepared membranes were significantly enhanced by the addition of IGEPAL surfactant to the casting solution. Also, it was found that decreasing the PAN concentration and increasing CBT resulted in the formation of membranes with high permeability and sublayer porosity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mousavi SM, Dehghan F, Saljoughi E, Hosseini SA (2012) Preparation of modified polyethersulfone membranes using variation in coagulation bath temperature and addition of hydrophilic surfactant. J Polym Res 19:9861–9872
Witte PVD, Dijkstra PJ, Berg JWAVD, Feijen J (1996) Phase separation processes in polymer solutions in relation to membrane formation. J Membr Sci 117:1–31
Azari S, Karimi M, Kish MH (2010) Structural properties of the poly(acrylonitrile) membrane prepared with different cast thicknesses. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:2442–2448
Smolders CA, Reuvers AJ, Boom RM, Wienk IM (1992) Microstructures in phase-inversion membranes. Part 1. Formation of macrovoids. J Membr Sci 73:259–275
Lim JW, Lee J-M, Yun S-M, Park B-J, Lee Y-S (2009) Hydrophilic modification of polyacrylonitrile membranes by oxyfluorination. J Ind Eng Chem 15:876–882
Jung B, Yoon JK, Kim B, Rhee H-W (2004) Effect of molecular weight of polymeric additives on formation, permeation properties and hypochlorite treatment of asymmetric polyacrylonitrile membranes. J Membr Sci 243:45–57
Wang J, Yue Z, Ince JS, Economy J (2006) Preparation of nanofiltration membranes from polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 286:333–341
Jung B (2004) Preparation of hydrophilic polyacrylonitrile blend membranes for ultrafiltration. J Membr Sci 229:129–136
Zhang H-F, Sun B-S, Zhao X-H, Sun J-M (2009) Membrane fouling caused by soluble microbial products in an activated sludge system under starvation. Desalination Water Treat 1:180–185
Houari A, Habarou H, Djafer M, Heim V, Martino PD (2009) Effect of storage of NF membranes on fouling deposits and cleaning efficiency. Desalination Water Treat 1:307–311
Saljoughi E, Amirilargani M, Mohammadi T (2010) Effect of PEG additive and coagulation bath temperature on the morphology, permeability and thermal/chemical stability of asymmetric CA membranes. Desalination 262:72–78
Saljoughi E, Mousavi SM (2012) Preparation and characterization of novel polysulfone nanofiltration membranes for removal of cadmium from contaminated water. Sep Purif Technol 90:22–30
Saljoughi E, Mousavi SM (2012) Development of high performance nanofiltration membranes with hydrophilic surface for the removal of cadmium from contaminated water. Sep Sci Technol 47:2305–2310
Saljoughi E, Amirilargani M, Mohammadi T (2010) Asymmetric cellulose acetate dialysis membranes: synthesis, characterization, and performance. J Appl Polym 116:2251–2259
Saljoughi E, Amirilargani M, Mohammadi T (2009) Effect of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) concentration and coagulation bath temperature on the morphology, permeability, and thermal stability of asymmetric cellulose acetate membranes. J Appl Polym 111:2537–2544
Amirilargani M, Saljoughi E, Mohammadi T (2010) Improvement of permeation performance of polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membranes via addition of Tween-20. J Appl Polym 115:504–513
Kim JH, Lee KH (1998) Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J Membr Sci 138:153–163
Amirilargani M, Saljoughi E, Moghbeli MR, Mohammadi T (2010) Effects of coagulation bath temperature and polyvinylpyrrolidone content on flat sheet asymmetric polyethersulfone membranes. J Polym Eng Sci 50:885–893
Mousavi SM, Saljoughi E, Sheikhi-Kouhsar MR (2013) Preparation and characterization of nanoporous polysulfone membranes with high hydrophilic property using variation in CBT and addition of Tetronic-1107 surfactant. J Appl Polym 127:4177–4185
Mousavi SM, Saljoughi E, Ghasemipour Z, Hosseini SA (2012) Preparation and characterization of modified polysulfone membranes with high hydrophilic property using variation in coagulation bath temperature and addition of surfactant. Polym Eng Sci 52:2196–2205
Pereira CC, Nobrega R, Borges CP (2002) Membrane formation with presence of Lewis acid–base complexes in polymer solution. J Appl Polym 83:2022–2034
Saljoughi E, Sadrzadeh M, Mohammadi T (2009) Effect of preparation variables on morphology and pure water permeation flux through asymmetric cellulose acetate membranes. J Membr Sci 326:627–634
Rahimpour A, Madaeni SS (2007) Polyethersulfone (PES)/cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP) blend ultrafiltration membranes: preparation, morphology, performance and antifouling properties. J Membr Sci 305:299–312
Mulder M (1997) Basic principles of membrane technology. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shekarian, E., Saljoughi, E. & Naderi, A. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)/IGEPAL blend asymmetric membranes: preparation, morphology, and performance. J Polym Res 20, 162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0162-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0162-0