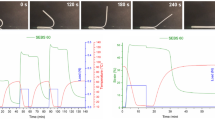
Abstract
Shape recovery in a commercial ether–vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) was systematically characterized by studying its creep and the thermoresponsive shape-memory effect (SME). The influences of the programming temperature and maximum uniaxial tension strain on the shape-fixity ratio and the shape-recovery ratio were investigated quantitatively. In addition to excellent SME, high elasticity and high creep were observed at around room temperature (with the EVA in the glassy state). The underlying mechanisms for the different shape-recovery phenomena (i.e., creep and the SME) are discussed. Two potential applications utilizing the shape-recovery property and high elasticity of this EVA are presented.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka K, Wayman CM (eds) (1998) Shape memory materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Huang WM, Ding Z, Wang CC, Wei J, Zhao Y, Purnawali H (2010) Shape memory materials. Mater Today 13:54–61
Sun L, Huang WM, Ding Z, Zhao Y, Wang CC, Purnawali H, Tang C (2012) Stimulus-responsive shape memory materials: a review. Mater Des 33:577–640
Huang WM, Zhao Y, Wang CC, Ding Z, Purnawali H, Tang C, Zhang JL (2012) Thermo/chemo-responsive shape memory effect in polymers: a sketch of working mechanisms, fundamentals and optimization. J Polym Res 19:9952
Huang W (2002) On the selection of shape memory alloys for actuators. Mater Des 23:11–19
Lendlein A (2010) Shape-memory polymers. Springer, Berlin
Ge YL, Heczko O, Soderberg O, Hannula SP (2006) Magnetic domain evolution with applied field in a Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape memory alloy. Scripta Mater 54:2155–2160
Funakubo H (ed) (1987) Shape memory alloys. Gordon and Breach, New York
Miyazaki S, Fu YQ, Huang WM (2009) Thin film shape memory alloys: fundamentals and device applications. Cambridge University Press, New York
Wang CC, Huang WM, Ding Z, Zhao Y, Purnawali H (2012) Cooling-/water-responsive shape memory hybrids. Compos Sci Technol 72:1178–1182
Huang WM, Yang B, An L, Li C, Chan YS (2005) Water-driven programmable polyurethane shape memory polymer: demonstration and mechanism. Appl Phys Lett 86:114105
Jung YC, So HH, Cho JW (2006) Water-responsive shape memory polyurethane block copolymer modified with polyhedral oligometric silsesquioxane. J Macromol Sci B 45:1189–1189
Zhao Y, Wang CC, Huang WM, Purnawali H (2011) Buckling of poly(methyl methacrylate) in stimulus-responsive shape recovery. Appl Phys Lett 99:131911
Zhao CS, Nie SQ, Tang M, Sun SD (2011) Polymeric pH-sensitive membranes—a review. Prog Polym Sci 36:1499–1520
Wang CC, Zhao Y, Purnawali H, Huang WM, Sun L (2012) Chemically induced morphing in polyurethane shape memory polymer micro fibers/springs. React Funct Polym 72:757–764
Willett JL (2008) Humidity-responsive starch-poly(methyl acrylate) films. Macromol Chem Physic 209:764–772
Lendlein A, Jiang HY, Junger O, Langer R (2005) Light-induced shape-memory polymers. Nature 434:879–882
Kumpfer JR, Rowan SJ (2011) Thermo-, photo-, and chemo-responsive shape-memory properties from photo-cross-linked metallo-supramolecular polymers. J Am Chem Soc 133:12866–12874
Hussein H, Harrison D (2008) New technologies for active disassembly: using the shape memory effect in engineering polymers. Int J Prod Dev 6:431–439
Purnawali H, Xu WW, Zhao Y, Ding Z, Wang CC, Huang WM, Fan H (2012) Poly(methyl methacrylate) for active disassembly. Smart Mater Struct 21:075006
Yang FQ, Zhang SL, Li JCM (1997) Impression recovery of amorphous polymers. J Electron Mater 26:859–862
Bianchi O, Oliveira RVB, Fiorio R, Martins JDN, Zattera AJ, Canto LB (2008) Assessment of Avrami, Ozawa and Avrami–Ozawa equations for determination of EVA crosslinking kinetics from DSC measurements. Polym Test 27:722–729
Stelescu MD, Manaila E, Craciun G, Zuga N (2012) Crosslinking and grafting ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer with accelerated electrons in the presence of polyfunctional monomers. Polym Bull 68:263–285
Matsumura K, Hyon SH, Nakajima N, Peng C, Tsutsumi S (2000) Surface modification of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) (EVA). Part I. Introduction of carboxyl groups and immobilization of collagen. J Biomed Mater Res 50:512–517
Arun M, Silja PK, Mohanan PV (2011) Evaluation of hydroxyapatite-bioglass and hydroxyapatite-ethyl vinyl acetate composite extracts on antioxidant defense mechanism and genotoxicity: an in vitro study. Toxicol Mech Methods 21:561–566
Tanrattanakul V, Kaewprakob T (2011) Effect of different curing systems on heat shrinkability and mechanical properties of ethylene vinyl acetate/epoxidized natural rubber blends. J Appl Polym Sci 119:38–46
Li FK, Zhu W, Zhang X, Zhao CT, Xu M (1999) Shape memory effect of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers. J Appl Polym Sci 71:1063–1070
Tanrattanakul V, Kaewprakob T (2009) Effect of rubber content on mechanical properties and heat shrinkage of ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer blended with epoxidized natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 112:1817–1825
Mishra JK, Das CK (2001) Effect of interchain crosslinking on the shrinkability of the blends consisting of grafted poly (ethylene vinyl acetate) and polyurethane elastomer. J Mater Sci Lett 20:1877–1879
Huang WM, Yang B, Zhao Y, Ding Z (2010) Thermo-moisture responsive polyurethane shape-memory polymer and composites: a review. J Mater Chem 20:3367–3381
Huang W, Toh W (2000) Training two-way shape memory alloy by reheat treatment. J Mater Sci Lett 19:1549–1550
Liu N, Huang WM, Phee SJ (2007) A secret garden of micro butterflies: phenomenon and mechanism. Surf Rev Lett 14:1187–1190
Sun L, Huang WM, Wang CC, Zhao Y, Ding Z, Purnawali H (2011) Optimization of the shape memory effect in shape memory polymers. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 49:3574–3581
Wang CC, Huang WM, Ding Z, Zhao Y, Purnawali H, Zheng LX, Fan H, He CB (2012) Rubber-like shape memory polymeric materials with repeatable thermal-assisted healing function. Smart Mater Struct 21:115010
Xie T, Xiao XC, Li JJ, Wang RM (2010) Encoding localized strain history through wrinkle based structural colors. Adv Mater 22:4390–4394
Li J, Shim JM, Deng J, Overvelde JTB, Zhu XL, Bertoldi K, Yang S (2012) Switching periodic membranes via pattern transformation and shape memory effect. Soft Matter 8:10322–10328
Li JJ, An YH, Huang R, Jiang HQ, Xie T (2012) Unique aspects of a shape memory polymer as the substrate for surface wrinkling. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:598–603
Zhao Y, Huang WM, Wang CC (2012) Thermo/chemo-responsive shape memory effect for micro/nano surface patterning atop polymers. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 4:862–878
Liu N, Xie Q, Huang WM, Phee SJ, Guo NQ (2008) Formation of micro protrusion arrays atop shape memory polymer. J Micromech Microeng 18:027001
Sun L, Huang WM (2010) Mechanisms of the multi-shape memory effect and temperature memory effect in shape memory polymers. Soft Matter 6:4403–4406
Xie T (2010) Tunable polymer multi-shape memory effect. Nature 464:267–270
PR China patent application No. 201210480325.5
PR China patent application No. 201210206952.X
Sun L, Huang WM (2010) Thermo/moisture responsive shape-memory polymer for possible surgery/operation inside living cells in future. Mater Des 31:2684–2689
Acknowledgments
This project is partially supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (1721110233) and the Research Foundation for Scholars of Jiangsu University (1281110025), PR China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X.L., Huang, W.M. & Tan, H.X. Characterization of shape recovery via creeping and shape memory effect in ether-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA). J Polym Res 20, 150 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0150-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0150-4