Abstract
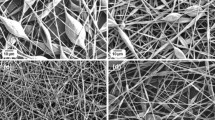
Composite nanofibers of Poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT)/multiwalled-carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) were prepared by electrospinning technique in the form of a random fibers web. The effect of MWCNTs on the morphology, crystallinity, and mechanical properties of the electrospun composite nanofibers was investigated by SEM, DSC, and tensile testing, respectively. SEM observations indicated that the presence of MWCNTs resulted in finer nanofibers for lower loading; however, a broader diameter was found for nanofibers with higher amounts of carbon nanotubes.It was also observed that the melt-crystallization temperature (Tc) of PBT nanofibers shifted to a higher temperature (about 8 °C) by the incorporation of MWCNTs which might be due to the nucleating effect of the nanotubes. The mechanical properties (specific strength and modulus) of the PBT nanofibers were significantly enhanced by the incorporation of MWCNTs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayutsede J, Gandhi M, Sukigara S, Ye H, Hsu CM, Gogotsi Y, Ko F (2006) Carbon nanotube reinforced Bombyxmori silk nanofibers by the electrospinning process. Biomacromolecules 7:208–214
Ijima S (1991) Helicalmicrotubles of grafitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58
Tucknott R, Yaliraki SN (2002) Aggregation properties of carbon nanotubes at interfaces. Chem Phys 281:455–463
Sundaray B, Subramanian V, Natarajan TS, Krishnamurthy K (2006) Electrical conductivity of a single electrospun fiber of poly(methyl methacrylate) and multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite. Appl Phys Lett 88:143114–143117
Shin YM, Hohman MM, Brenner MP, RutledgeG C (2001) Electrospinning: a whipping fluid jet generates submicron polymer fibers. Appl Phys Lett 78(8):1149–1151
Ko F, Gogotsi Y, AliA NN, Ye H, Yang GL, Li C, Willis P (2003) Electrospinning of continuous carbon nanotube-filled nanofiber yarns. Adv Mater 15(14):1161–1165
Dror Y, SalalhaW KRL, Cohen Y, Yarin AL, Zussman E (2003) Carbon nanotubes embeddedin oriented polymer nanofibers by electrospinning. Langmuir 19(17):7012–7020
GaoJ YA, Itkis ME, Bekyarova E, Zhao B, Niyogi S, Haddon RC (2004) Large-scalefabrication of aligned single-walled carbon nanotube array and hierarchical single-walled carbonnanotube assembly. J Am Chem Soc 126(51):16698–16699
Salalha W, Dror Y, KhalfinR L, Cohen Y, Yarin AL, Zussman E (2004) Single-walled carbonnanotubes embedded in oriented polymeric nanofibers by electrospinning. Langmuir 20(22):9852–9855
Buchko CJ, Chen LC, Shen Y, MartinD C (1999) Processing and microstructureal characterization of porous biocompatible protein polymer thin films. Polymer 40:7397–7407
MacDiarmid AG, Jones J, We NID, Llaguno H, Okuzaki M (2001) Electrostatically generated nanofibers of electronic polymers. Synth Met 119:27–30
Ma Z, Kotakia M, YongaT HW, Ramakrishna S (2005) Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 26:2527–2536
Kosmider K, Scott J (2002) Polymeric nanofibers exhibit an enhanced air filtration performance. Filtr Sep 39:20–22
Luis J, Valle D, Camps R, Díaz A, Franco L, Rodríguez-Galán A, Puiggalí J (2011) Electrospinning of polylactide and polycaprolactone mixtures for preparation of materials with tunable drug release properties. J Polym Res 18:1903–1917
Fang J, Niu HT, Lin T, Wang X (2008) Apllications ofelectrospunnanofibers. Chin Sci Bull 53:2265–2286
Gibson P, Schreuder-Gibson H, Rivin D (2001) Transport properties of porous membranes based on electrospunnanofibers. Colloid Surf A Phys-Chem Eng A Sp 187–188:469–481
Saeed K, Park SY, Lee HJ, Baek JB, Huh WS (2006) Preparation of electrospunnanofibers of carbon nanotube/polycaprolactonenanocomposite. Polymer 47:8019–8025
Saeed K, Park SY, HaiderS BJB (2009) In situ polymerization of multi-walled carbon nanotube/nylon-6 nanocomposites and their electrospunnanofibers. Nanoscale Res Lertt 4:39–46
Zhou WP, Wu YL, Wei F, Luo G, Qian W (2005) Elastic deformation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in electrospun MWCNTs-PEO and MWCNTs-PVA nanofibers. Polymer 46:12689–12695
Kim GM, Michler GH, Poetschke P (2005) Deformation processes of ultrahigh porous multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polycarbonate composite fibers prepared by electrospinning. Polymer 46:7346–7351
Saeed KH, Young PS (2010) Preparation and characterization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyacrylonitrilenanofibers. J Polym Res 17:535–540
Hou HQ, Ge JJ, Zeng J, Reneker Li Q, Griener A, Cheng SZD (2005) Electrospunpolyacrylonitrilenanofibers containing a high concentration of well-aligned multiwall carbon nanotubes. Chem Mater 17:967–973
Chen H, Liu Z, Cebe P (2009) Chain confinement in electrospunnanofibers of PET with carbon nanotubes. Polymer 28:872–880
Liu LQ, Tasis D, Prato M, Wagner HD (2007) Tensile mechanics of electrospunmultiwalled nanotube/poly(methylmethacrylate) nanofibers. Adv Mater 19:1228–1233
SalighehO AR, ForouharshadM FRE (2011) Poly(Butylene Terephthalate)/single wall carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers by electrospinning. J Macromol Sci Part B: Phys 50(6):1031–1041
ForouharshadM SO, ArastehR FRE (2010) Manufacture and characterization of poly (butylenes terephthalate) nanofibers by electrospinning. J Macromol Sci Part B: Phys 49(4):833–842
Ra EJ, An KH, KimK K, Jeong SY, Lee YH (2005) Anisotropic electrical conductivity of MWCNT/PAN nanofiber paper. Chem Phys Lett 413(1–3):188–193
Naebe M, Lin T, TianW DL, Wang X (2007) Effects of MWNT nanofillers on structures and properties of PVA electrospunnanofibres. Nanotechnology 18:225605
Chen H, Liu Z, Cebe P (2009) Chain confinement in electrospunnanofibers of PET with carbon nanotubes. Polymer 50:872–880
Reneker DH, Chun I (1996) Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 7(3):216–223
Kim JS, Reneker DH (1999) Polybenzimidazolenanofiber produced by electrospinning. Polym Eng Sci 39(5):849–854
Doshi J, Reneker DH (1995) Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J Electro Stat 35(2–3):151–160
Kaganj AB, Rashidi AL, Arasteh R (2009) Crystallisationbehaviour and morphological characteristics of poly(propylene)/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites. J Exp Nanosci 4(1):21–34
Illers KH (1980) Heat of fusion and specific volume of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and poly(butylene terephthalate). Coll Polym Sci 258(2):117–124
Goa J, Itkis ME, Yu A, Bekyarova E, Zhao B, Haddon R (2005) Continuous spinning of singlewalled carbon nanotube-nylon composite fiber. J Am Chem Soc 127:3847–3854
McCullen SD, Stevens DR, Roberts WA, Ojha SS, Clarke LI, Gorga RE (207) Morphological, electrical, and mechanical characterization of electrospunnanofiber mats containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes Macromolecules 40:997–1003.
Jeon HJ, Kim JS, Kim TG, Hyun J, Ryeol YW, Ho JY (2008) Preparation of poly(ε-caprolactone)-based-polyurethane nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 254:5886–5890
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saligheh, O., Forouharshad, M., Arasteh, R. et al. The effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on morphology, crystallinity and mechanical properties of PBT/MWCNT composite nanofibers. J Polym Res 20, 65 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-0065-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-0065-5