Abstract
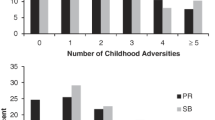
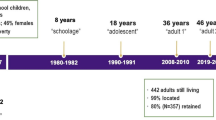
Child maltreatment represents a prevalent public health issue that has been shown to predict both adolescent and young adult depressive symptoms and heavy episodic drinking; however, little is known regarding how associations between specific types of maltreatment (e.g., physical abuse, sexual abuse, care neglect, supervisory neglect) and depressive symptoms and heavy episodic drinking change across adolescence and into young adulthood. Similarly, there is lack of research that has examined how an accumulation of child maltreatment types relates to depressive symptoms and heavy episodic drinking across ages. Time-varying effect models—a statistical approach that allows researchers to pinpoint specific ages where the association between two variables is strongest—were used in the current study to address these gaps. Nationally representative data came from the first four waves of the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health (Add Health; N = 16,053; 49.4% female; 51.0% European American/White, 21.0% African American, 10.2% Biracial, 9.1% Hispanic; MAGE W1 = 17.00). Results suggested that certain types of maltreatment are more predictive of negative outcomes than others and that different types of maltreatment confer greater risk in different developmental periods. In addition, while victims of between one and three types of maltreatment had comparable prevalence of depressive symptoms and heavy episodic drinking across adolescence and young adulthood, victims of four types of maltreatment had a much higher prevalence of these outcomes indicating the extreme risk that accompanies an accumulation of maltreatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afifi, T. O., Henriksen, C. A., Asmundson, G. J., & Sareen, J. (2012). Childhood maltreatment and substance use disorders among men and women in a nationally representative sample. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 57(11), 677–686.
Afifi, T. O., & MacMillan, H. L. (2011). Resilience following child maltreatment: A review of protective factors. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 56(5), 266–272.
Alink, L. R., Cicchetti, D., Kim, J., & Rogosch, F. A. (2012). Longitudinal associations among child maltreatment, social functioning, and cortisol regulation. Developmental Psychology, 48(1), 224.
Arnett, J. J. (2000). Emerging adulthood: A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. American Psychologist, 55(5), 469.
Baldwin, J. R., Reuben, A., Newbury, J. B., & Danese, A. (2019). Agreement between prospective and retrospective measures of childhood maltreatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 76(6), 584–593.
Blanco, C., Okuda, M., Wright, C., Hasin, D. S., Grant, B. F., Liu, S. M., & Olfson, M. (2008). Mental health of college students and their non–college-attending peers: results from the national epidemiologic study on alcohol and related conditions. Archives of General Psychiatry, 65(12), 1429–1437.
Brumley, L. D., Brumley, B. P., & Jaffee, S. R. (2019). Comparing cumulative index and factor analytic approaches to measuring maltreatment in the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health. Child Abuse & Neglect, 87, 65–76.
Chen, P., & Chantala, K. (2014). Guidelines for analyzing Add Health data. Carolina Population Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, 710.
Cicchetti, D., & Handley, E. D. (2019). Child maltreatment and the development of substance use and disorder. Neurobiology of Stress, 10, 100144.
Croft, J., Heron, J., Teufel, C., Cannon, M., Wolke, D., Thompson, A., & Zammit, S. (2019). Association of trauma type, age of exposure, and frequency in childhood and adolescence with psychotic experiences in early adulthood. JAMA Psychiatry, 76(1), 79–86.
Dalgleish, T., & Werner-Seidler, A. (2014). Disruptions in autobiographical memory processing in depression and the emergence of memory therapeutics. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 18(11), 596–604.
Debowska, A., Willmott, D., Boduszek, D., & Jones, A. D. (2017). What do we know about child abuse and neglect patterns of co-occurrence? A systematic review of profiling studies and recommendations for future research. Child Abuse & Neglect, 70, 100–111.
Dileo, J. F., Brewer, W., Northam, E., Yucel, M., & Anderson, V. (2017). Investigating the neurodevelopmental mediators of aggression in children with a history of child maltreatment: An exploratory field study. Child Neuropsychology, 23(6), 655–677.
Draucker, C. B., & Mazurczyk, J. (2013). Relationships between childhood sexual abuse and substance use and sexual risk behaviors during adolescence: An integrative review. Nursing Outlook, 61(5), 291–310.
Dube, S. R., Felitti, V. J., Dong, M., Chapman, D. P., Giles, W. H., & Anda, R. F. (2003). Childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: the adverse childhood experiences study. Pediatrics, 111(3), 564–572.
Dugal, C., Godbout, N., Bélanger, C., Hébert, M., & Goulet, M. (2018). Cumulative childhood maltreatment and subsequent psychological violence in intimate relationships: The role of emotion dysregulation. Partner Abuse, 9(1), 18–40.
Dunn, E. C., McLaughlin, K. A., Slopen, N., Rosand, J., & Smoller, J. W. (2013). Developmental timing of child maltreatment and symptoms of depression and suicidal ideation in young adulthood: results from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Depression and Anxiety, 30(10), 955–964.
Dziak, J. J., Li, R., & Wagner, A. T. (2017). Weighted TVEM SAS macro users’ guide (Version 2.6). The Methodology Center, Penn State, University Park, PA (Retrieved from) methodology.psu.edu.
Evans-Polce, R. J., Vasilenko, S. A., & Lanza, S. T. (2015). Changes in gender and racial/ethnic disparities in rates of cigarette use, regular heavy episodic drinking, and marijuana use: Ages 14 to 32. Addictive Behaviors, 41, 218–222.
Finkelhor, D., & Dziuba-Leatherman, J. (1994). Children as victims of violence: A national survey. Pediatrics-English Edition, 94(4), 413–420.
Gilbert, R., Widom, C. S., Browne, K., Fergusson, D., Webb, E., & Janson, S. (2009). Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. The Lancet, 373(9657), 68–81.
Hamburger, M. E., Leeb, R. T., & Swahn, M. H. (2008). Childhood maltreatment and early alcohol use among high-risk adolescents. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 69(2), 291–295.
Harris, K. M. (2018). The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health (Add Health), Waves I & II, 1994–1996; Wave III, 2001–2002; Wave IV, 2007-2009; Wave V, 2016-2018 [machine-readable data file and documentation]. Chapel Hill, NC: Carolina Population Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Henry, S. K., Grant, M. M., & Cropsey, K. L. (2018). Determining the optimal clinical cutoff on the CES-D for depression in a community corrections sample. Journal of Affective Disorders, 234, 270–275.
Huang, S., Trapido, E., Fleming, L., Arheart, K., Crandall, L., French, M., & Prado, G. (2011). The long-term effects of childhood maltreatment experiences on subsequent illicit drug use and drug-related problems in young adulthood. Addictive Behaviors, 36(1-2), 95–102.
Hudson, A., Wekerle, C., Goldstein, A. L., Ellenbogen, S., Waechter, R., Thompson, K., & Stewart, S. H. (2017). Gender differences in emotion-mediated pathways from childhood sexual abuse to problem drinking in adolescents in the child welfare system. Journal of Child & Adolescent Trauma, 10(1), 19–28.
Jonson-Reid, M., Kohl, P. L., & Drake, B. (2012). Child and adult outcomes of chronic child maltreatment. Pediatrics, 129(5), 839–845.
Keinan, G., Shrira, A., & Shmotkin, D. (2012). The association between cumulative adversity and mental health: considering dose and primary focus of adversity. Quality of Life Research, 21(7), 1149–1158.
Kim, K., Mennen, F. E., & Trickett, P. K. (2017). Patterns and correlates of co‐occurrence among multiple types of child maltreatment. Child & Family Social Work, 22(1), 492–502.
Lanza, S. T., Vasilenko, S. A., Liu, X., Li, R., & Piper, M. E. (2013). Advancing the understanding of craving during smoking cessation attempts: A demonstration of the time-varying effect model. Nicotine & Tobacco Research, 16(Suppl_2), S127–S134.
Lanza, S. T., Vasilenko, S. A., & Russell, M. A. (2016). Time-varying effect modeling to address new questions in behavioral research: Examples in marijuana use. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 30(8), 939.
Lee, M. R., Chassin, L., & Villalta, I. K. (2013). Maturing out of alcohol involvement: Transitions in latent drinking statuses from late adolescence to adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 25(4pt1), 1137–1153.
Leeb, R. T., Paulozzi, L., Melanson, C., Simon, T., Arias, I. (2008). Child maltreatment surveillance: Uniform definitions for public health and recommended data elements. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
Lewis, S. J., Arseneault, L., Caspi, A., Fisher, H. L., Matthews, T., Moffitt, T. E., & Danese, A. (2019). The epidemiology of trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder in a representative cohort of young people in England and Wales. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6(3), 247–256.
Liu, S. R., Schulz, M. S., & Waldinger, R. J. (2015). Cumulative contribution of child maltreatment to emotional experience and regulatory intent in intimate adult interactions. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma, 24(6), 636–655.
Lo, C. C., & Cheng, T. C. (2007). The impact of childhood maltreatment on young adults’ substance abuse. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 33(1), 139–146.
Matsumoto, M., Piersiak, H., Letterie, M., & Humphreys, K. L. (2020). Population-based estimates of associations between child maltreatment type: A meta-analysis. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/cv5qw.
McLaughlin, K. A., Peverill, M., Gold, A. L., Alves, S., & Sheridan, M. A. (2015). Child maltreatment and neural systems underlying emotion regulation. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 54(9), 753–762.
Miller, A. B., Esposito-Smythers, C., Weismoore, J. T., & Renshaw, K. D. (2013). The relation between child maltreatment and adolescent suicidal behavior: a systematic review and critical examination of the literature. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 16(2), 146–172.
Mirsu-Paun, A., & Oliver, J. A. (2017). How Much Does Love Really Hurt? A Meta-Analysis of the Association Between Romantic Relationship Quality, Breakups and Mental Health Outcomes in Adolescents and Young Adults. Journal of Relationships Research, 8(5), 1–12.
Morrongiello, B. A., & Cox, A. (2020). Issues in Defining and Measuring Supervisory Neglect and Conceptualizing Prevention. Child Indicators Research, 13(2), 369–385.
Nation, M., Crusto, C., Wandersman, A., Kumpfer, K. L., Seybolt, D., Morrissey-Kane, E., & Davino, K. (2003). What works in prevention: Principles of effective prevention programs. American Psychologist, 58(6-7), 449–456.
Norman, R. E., Byambaa, M., De, R., Butchart, A., Scott, J., & Vos, T. (2012). The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med, 9(11), e1001349.
Patrick, M. E., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2014). Prevalence and predictors of adolescent alcohol use and binge drinking in the United States. Alcohol. Research: Current Reviews, 35(2), 193.
Pedrelli, P., Shapero, B., Archibald, A., & Dale, C. (2016). Alcohol use and depression during adolescence and young adulthood: a summary and interpretation of mixed findings. Current Addiction Reports, 3(1), 91–97.
Primack, B. A., Swanier, B., Georgiopoulos, A. M., Land, S. R., & Fine, M. J. (2009). Association between media use in adolescence and depression in young adulthood: a longitudinal study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66(2), 181–188.
Raymond, C., Marin, M. F., Majeur, D., & Lupien, S. (2018). Early child adversity and psychopathology in adulthood: HPA axis and cognitive dysregulations as potential mechanisms. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 85, 152–160.
Ruiz-Casares, M., Trocmé, N., & Fallon, B. (2012). Supervisory neglect and risk of harm. Evidence from the Canadian Child Welfare System. Child Abuse & Neglect, 36(6), 471–480.
Russell, M. A., Vasilenko, S. A., & Lanza, S. T. (2016). Age-varying links between violence exposure and behavioral, mental, and physical health. Journal of Adolescent Health, 59(2), 189–196.
Salazar, A. M., Keller, T. E., & Courtney, M. E. (2011). Understanding social support’s role in the relationship between maltreatment and depression in youth with foster care experience. Child Maltreatment, 16(2), 102–113.
Schuler, M. S., Vasilenko, S. A., & Lanza, S. T. (2015). Age-varying associations between substance use behaviors and depressive symptoms during adolescence and young adulthood. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 157, 75–82.
Snyder, S. M., & Merritt, D. H. (2016). The effect of childhood supervisory neglect on emerging adults’ drinking. Substance Use & Misuse, 51(1), 1–14.
Strine, T. W., Dube, S. R., Edwards, V. J., Prehn, A. W., Rasmussen, S., Wagenfeld, M., & Croft, J. B. (2012). Associations between adverse childhood experiences, psychological distress, and adult alcohol problems. American Journal of Health Behavior, 36(3), 408–423.
Szumilas, M. (2010). Explaining odds ratios. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 19(3), 227.
Tan, X., Shiyko, M. P., Li, R., Li, Y., Dierker, L. (2010). Intensive longitudinal data and model with varying effects (Technical Report No 10–106) University Park, PA: The Methodology Center, The Pennsylvania State University.
Teicher, M. H., Samson, J. A., Anderson, C. M., & Ohashi, K. (2016). The effects of childhood maltreatment on brain structure, function and connectivity. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 17(10), 652.
Thompson, K., Roemer, A., & Leadbeater, B. (2015). Impulsive personality, parental monitoring, and alcohol outcomes from adolescence through young adulthood. Journal of Adolescent Health, 57(3), 320–326.
Tonmyr, L., Thornton, T., Draca, J., & Wekerle, C. (2010). A review of childhood maltreatment and adolescent substance use relationship. Current Psychiatry Reviews, 6(3), 223–234.
Trickett, P. K., Negriff, S., Ji, J., & Peckins, M. (2011). Child maltreatment and adolescent development. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(1), 3–20.
Vachon, D. D., Krueger, R. F., Rogosch, F. A., & Cicchetti, D. (2015). Assessment of the harmful psychiatric and behavioral effects of different forms of child maltreatment. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(11), 1135–1142.
Walker, E. C., Holman, T. B., & Busby, D. M. (2009). Childhood sexual abuse, other childhood factors, and pathways to survivors’ adult relationship quality. Journal of Family Violence, 24(6), 397–406.
Wanklyn, S. G., Day, D. M., Hart, T. A., & Girard, T. A. (2012). Cumulative childhood maltreatment and depression among incarcerated youth: impulsivity and hopelessness as potential intervening variables. Child Maltreatment, 17(4), 306–317.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.B. conducted analyses, provided input on the study design, and drafted the majority of the manuscript; Y.H. conceived the study and drafted the method section of the manuscript; D.C. provided input into the study design and implications of the results. All authors read, edited, and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse awards P50DA010075 and T32DA017629.
Data Sharing Declaration
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Carolina Population Center, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. However, data are available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the Carolina Population Center.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All participants provided written informed consent for participation in all aspects of Add Health in accordance with the University of North Carolina School of Public Health Institutional Review Board.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This study was approved by the first author’s Institutional Review Board and the study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayly, B.L., Hung, Y.W. & Cooper, D.K. Age-Varying Associations between Child Maltreatment, Depressive Symptoms, and Frequent Heavy Episodic Drinking. J Youth Adolescence 51, 927–939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-021-01522-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-021-01522-z