Abstract
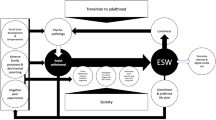
Childhood neglect is associated with risk behaviors in adolescence, including substance use. There is evidence that internalizing behaviors may serve as a mechanism linking childhood neglect and substance use; however, further research is needed to examine this developmental pathway. According to developmental and ecological approaches, the neighborhood context and the developmental timing of maltreatment should both be considered when examining the sequelae of childhood neglect. Hence, the present study uses a longitudinal sample of youth (N = 965, 49.1% female, 59.2% African-American) to examine the influence of timing in the relationship between childhood neglect and adolescent psychopathology, and to examine the indirect effects of child neglect on substance use via internalizing symptoms in adolescence. Furthermore, the role of neighborhood disorder in this indirect effect was tested. Five data collection time points were used: Time 1(M age = 4.557, SD age = .701), Time 2 (M age = 6.422, SD age = .518), Time 3 (M age = 12.370, SD age = .443), Time 4 (M age = 14.359, SD age = .452), and Time 5 (M age = 16.316, SD age = .615). The findings showed that internalizing problems mediated the link between the severity of neglect in early childhood and adolescent substance use, and this pathway was moderated by neighborhood disorder. These results have implications for preventative interventions aimed toward reducing substance use for at-risk adolescents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for child behavior checklist/ 4-18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Dept. of Psychiatry.
Barnett, D., Manly, J. T., & Cicchetti, D. (1993). Defining child maltreatment: The interface between policy and research. Child Abuse, Child Development, and Social Policy, 8, 7–73.
Bolger, K. E., & Patterson, C. J. (2001). Pathways from child maltreatment to internalizing problems perceptions of control as mediators and moderators. Development and Psychopathology, 13, 913–940.
Bolton, J. M., Robinson, J., & Sareen, J. (2009). Self-medication of mood disorders with alcohol and drugs in the National epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Journal of Affective Disorders, 115(3), 367–375. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2008.10.003.
Boyce, C. A., & Maholmes, V. (2013). Attention to the neglected: Prospects for research on child neglect for the next decade. Child Maltreatment, 18(1), 65–68. doi:10.1177/1077559513480426.
Brodsky, A. E. (1996). Resilient single mothers in risky neighborhoods: Negative psychological sense of community. Journal of Community Psychology, 24(4), 347–363.
Buu, A., Dipiazza, C., Wang, J., Puttler, L. I., Fitzgerald, H. E., & Zucker, R. A. (2009). Parent, family, and neighborhood effects on the development of child substance use and other psychopathology from preschool to the start of adulthood. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 70(4), 489–498.
Caughy, M. O. B., O’Campo, P. J., & Muntaner, C. (2003). When being alone might be better: Neighborhood poverty, social capital, and child mental health. Social Science & Medicine, 57(2), 227–237. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(02)00342-8.
Cicchetti, D. (2006). Development and psychopathology. In D. Cicchetti & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental psychopathology: Theory and method (2nd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 1–23). New York: Wiley.
Cicchetti, D. (2016). Socioemotional, personality, and biological development: Illustrations from a multilevel developmental psychopathology perspective on child maltreatment. Annual Review of Psychology, 67, 187–211. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033259.
Cicchetti, D., & Banny, A. (2014). A developmental psychopathology perspective on child maltreatment. In M. Lewis, & K. Rudolph (Eds.), Handbook of developmental psychopathology (pp. 723–741). New York: Springer.
Cicchetti, D., & Rogosch, F. A. (2002). A developmental psychopathology perspective on adolescence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 70(1), 6–20. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.70.1.6.
Cicchetti, D., & Valentino, K. (2006). An ecological transactional perspective on child maltreatment: Failure of the average expectable environment and its influence upon child development. In D. Cicchetti, & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental psychopathology (2nd ed., pp. 129–201). New York: Wiley. Vol. 3.
Colder, C. R., Scalco, M., Trucco, E. M., Read, J. P., Lengua, L. J., Wieczorek, W. F., & Hawk, Jr., L. W. (2013). Prospective associations of internalizing and externalizing problems and their co-occurrence with early adolescent substance use. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 41(4), 667–677. doi:10.1007/s10802-012-9701-0.
Cole, D. A., & Maxwell, S. E. (2003). Testing mediational models with longitudinal data: Questions and tips in the use of structural equation modeling. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 112(4), 558–577. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.112.4.558.
Coulton, C. J., Korbin, J. E., & Su, M. (1996). Measuring neighborhood context for young children in an urban area. American Journal of Community Psychology, 24(1), 5–32. doi:10.1007/BF02511881.
Cyr, C., Euser, E. M., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & Van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2010). Attachment security and disorganization in maltreating and high-risk families: A series of meta-analyses. Development and Psychopathology, 22(01), 87–87. doi:10.1017/S0954579409990289.
Dawson, J. F. (2014). Moderation in management research: What, why, when, and how. Journal of Business & Psychology, 29(1), 1–19. doi:10.1007/s10869-013-9308-7.
Diemer, M. A., Mistry, R. S., Wadsworth, M. E., López, I., & Reimers, F. (2013). Best practices in conceptualizing and measuring social class in psychological research. Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy, 13(1), 77–113. doi:10.1111/asap.12001.
Dube, S. R., Felitti, V. J., Dong, M., Chapman, D. P., Giles, W. H., & Anda, R. F. (2003). Child abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: The adverse childhood experiences study. Pediatrics, 111, 564–572. doi:10.1542/peds.111.3.564.
Dubowitz, H., & Bennett, S. (2007). Physical abuse and neglect of children. The Lancet, 369(9576), 1891–1899. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60856-3.
Dubowitz, H., Papas, M. A., Black, M. M., & Starr, R. H. (2002). Child neglect: Outcomes in high-risk urban preschoolers. Pediatrics, 109(6), 1100–1107. doi:10.1542/peds.109.6.1100.
Dubowitz, H., Pitts, S. C., & Black, M. M. (2004). Measurement of three major subtypes of child neglect. Child Maltreatment, 9(4), 344–356. doi:10.1177/1077559504269191.
Dunn, E. C., McLaughlin, K. A., Slopen, N., Rosand, J., & Smoller, J. W. (2013). Developmental timing of child maltreatment and symptoms of depression and suicidal ideation in young adulthood: Results from the national longitudinal study of adolescent health. Depression and Anxiety, 30(10), n/a-n/a. 10.1002/da.22102
Dunn, J. R., Schaefer-McDaniel, N. J., & Ramsay, J. T. (2010). Neighborhood chaos and children’s development: Questions and contradictions. In G. W. Evans, T. D. Wachs, G. W. Evans, & T. D. Wachs (Eds.), Chaos and its influence on children’s development: An ecological perspective (pp. 173–189). Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association.
Enders, C. K., & Bandalos, D. L. (2001). The relative performance of full information maximum likelihood estimation for missing data in structural equation models. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 8(3), 430–457. doi:10.1207/S15328007SEM0803_5.
English, D., & Investigators, L. (1997). Modified maltreatment classification system (MMCS). For more information visit the LONGSCAN website at http://www/.iprc. unc.edu/longscan.
Ennett, S. T., Flewelling, R. L., Lindrooth, R. C., & Norton, E. C. (1997). School and neighborhood characteristics associated with school rates of alcohol, cigarette, and marijuana use. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 38(1), 55–71.
Fujimoto, K., & Valente, T. W. (2012). Social network influences on adolescent substance use: Disentangling structural equivalence from cohesion. Social Science & Medicine, 74(12), 1952–1960. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.02.009.
Handley, E. D., Rogosch, F. A., Guild, D. J., & Cicchetti, D. (2015). Neighborhood disadvantage and adolescent substance use disorder: The moderating role of maltreatment. Child Maltreatment, 20(3), 193–202. doi:10.1177/1077559515584159.
Hankin, B. L. (2006). Childhood maltreatment and psychopathology: Prospective tests of attachment, cognitive vulnerability, and stress as mediating processes. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 29(6), 645–671. doi:10.1007/s10608-005-9631-z.
Harris, K. M., & Udry, J. R. (2016). National longitudinal study of adolescent to adult health (add health), 1994-2008 [Public Use]. Retrieved from: doi:10.3886/ICPSR21600.v17.
Heim, C., & Nemeroff, C. B. (2001). The role of childhood trauma in the neurobiology of mood and anxiety disorders preclinical and clinical studies. Biological Psychiatry, 49, 1023–1039. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(01)01157-X.
Hildyard, K. L., & Wolfe, D. A. (2002). Child neglect: Developmental issues and outcomes. Child Abuse & Neglect, 26(6-7), 679–695. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(02)00341-1.
Hill, T. D., & Angel, R. J. (2005). Neighborhood disorder, psychological distress, and heavy drinking. Social Science & Medicine, 61(5), 965–975. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.12.027.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55. doi:10.1080/10705519909540118.
Humphreys, K. L., & Zeanah, C. H. (2015). Deviations from the expectable environment in early childhood and emerging psychopathology. Neuropsychopharmacology : Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 40(1), 154–170. doi:10.1038/npp.2014.165.
Hussey, J. M., Chang, J. J., & Kotch, J. B. (2006). Child maltreatment in the United States: Prevalence, risk factors, and adolescent health consequences. Pediatrics, 118(3), 933–942. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-2452.
Hussong, A. M., Jones, D. J., Stein, G. L., Baucom, D. H., & Boeding, S. (2011). An internalizing pathway to alcohol use and disorder. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 25(3), 390.
Jacobs, J. E., Bleeker, M. M., & Constantino, M. J. (2003). The self-system during childhood and adolescence: Development, influences, and implications. Journal of Psychotherapy Integration, 13(1), 33–65. doi:10.1037/1053-0479.13.1.33.
Kaplow, J. B., & Widom, C. S. (2007). Age of onset of child maltreatment predicts long-term mental health outcomes. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 116(1), 176–187. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.116.1.176.
Kenny, D. (2005). Cross-lagged panel design. In B. S. Everitt, & D. C. Howell (Eds.), Encyclopedia of statistics in behavioral science, (Vol. 1, pp. 450–451). West Sussex, UK: Wiley.
Kotch, J. B., Lewis, T., Hussey, J. M., English, D., Thompson, R., & Litrownik, A. J., et al. (2008). Importance of early neglect for childhood aggression. Pediatrics, 121(4), 725–731. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-3622.
Lalayants, M., & Prince, J. D. (2015). Child neglect and onset of substance use disorders among child welfare-involved adolescents. Child Abuse Review. doi:10.1002/car.2372. n/a-n/a.
Lee, A., & Hankin, B. L. (2009). Insecure attachment, dysfunctional attitudes, and low self-esteem predicting prospective symptoms of depression and anxiety during adolescence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 38(2), 219–231. doi:10.1080/15374410802698396.
Leventhal, T., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2000). The neighborhoods they live in: The effects of neighborhood residence on child and adolescent outcomes. Psychological Bulletin, 126(2), 309–337. doi:10.1037//0033-2909.126.2.309.
Lewis, T. L., Kotch, J., Wiley, T. R. A., Litrownik, A. J., English, D. J., & Thompson, R., et al. (2011). Internalizing problems: A potential pathway from childhood maltreatment to adolescent smoking. Journal of Adolescent Health, 48(3), 247–252. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.07.004.
Luthar, S. S., & Becker, B. E. (2002). Privileged but pressured? A study of affluent youth. Child Development, 73(5), 1593–1610.
Manly, J. T., Kim, J. E., Rogosch, F. A., & Cicchetti, D. (2001). Dimensions of child maltreatment and children’s adjustment: Contributions of developmental timing and subtype. Development and Psychopathology, 13(04), 759–782.
McLaughlin, K. A., Sheridan, M. A., & Nelson, C. A. (2017). Neglect as a violation of species-expectant experience: Neurodevelopmental consequences. Biological Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.02.1096.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (1998–2010). Mplus user’s guide: Sixth edition. Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Nikulina, V., Widom, C. S., & Brzustowicz, L. M. (2012). Child abuse and neglect, MAOA, and mental health outcomes: A prospective examination. Biological Psychiatry, 71(4), 350–357.
Nixon, K., & McClain, J. A. (2010). Adolescence as a critical window for developing an alcohol use disorder: Current findings in neuroscience. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 23(3), 227–232. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e32833864fe.
Oshri, A., Carlson, M. W., Kwon, J. A., Zeichner, A., & Wickrama, K. A. S. (2016). Developmental growth trajectories of self-esteem in adolescence: Associations with child neglect and drug use and abuse in young adulthood. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 1–14. doi:10.1007/s10964-016-0483-5.
Oshri, A., Rogosch, F. A., Burnette, M. L., & Cicchetti, D. (2011). Developmental pathways to adolescent cannabis abuse and dependence: Child maltreatment, emerging personality, and internalizing versus externalizing psychopathology. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors : Journal of the Society of Psychologists in Addictive Behaviors, 25(4), 634–644. doi:10.1037/a0023151.
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42(1), 185–227. doi:10.1080/00273170701341316.
Proctor, L. J., & Dubowitz, H. (2014). Child neglect: Challenges and controversies. Handbook of Child Maltreatment, 2, 27.
Ray, J. V., Thornton, L. C., Frick, P. J., Steinberg, L., & Cauffman, E. (2016). Impulse control and callous-unemotional traits distinguish patterns of delinquency and substance use in justice involved adolescents: Examining the moderating role of neighborhood context. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 44(3), 599–611. doi:10.1007/s10802-015-0057-0.
Rogosch, F. A., Oshri, A., & Cicchetti, D. (2010). From child maltreatment to adolescent cannabis abuse and dependence: A developmental cascade model. Development and Psychopathology, 22(04), 883–897. doi:10.1017/S0954579410000520.
Runyan, D., Dubowitz, H., English, D. J., Kotch, J. B., Litrownik, A., Thompson, R., & The LONGSCAN Investigator Group (2014). Longitudinal studies of child abuse and neglect (LONGSCAN) assessments 0-18 [Dataset].
Runyan, D. K., Curtis, P. A., Hunter, W. M., Black, M. M., Kotch, J. B., & Bangdiwala, S., et al. (1998). LONGSCAN: A consortium for longitudinal studies of maltreatment and the life course of children. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 3(3), 275–285. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(96)00027-4.
Schafer, J. L., & Graham, J. W. (2002). Missing data: Our view of the state of the art. Psychological Methods, 7(2), 147–177. doi:10.1037//1082-989X.7.2.147.
Sedlak, A. J., Mettenburg, J., Basena, M., Peta, I., McPherson, K., & Greene, A. (2010). Fourth national incidence study of child abuse and neglect (NIS-4). Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services.
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., Lucas, C. P., Dulcan, M. K., & Schwab-Stone, M. E. (2000). NIMH diagnostic interview schedule for children version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): Description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. 39, 28–38.
Shin, S. H., Miller, D. P., & Teicher, M. H. (2013). Exposure to childhood neglect and physical abuse and developmental trajectories of heavy episodic drinking from early adolescence into young adulthood. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 127(1), 31–38.
Skeer, M., McCormick, M. C., Normand, S. L., Buka, S. L., & Gilman, S. E. (2009). A prospective study of familial conflict, psychological stress, and the development of substance use disorders in adolescence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 104(1-2), 65–72. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.03.017.
Stride, C. B., Gardner, S., Catley, N., & Thomas, F. (2015). Mplus code for the mediation, moderation, and moderated mediation model templates from Andrew Hayes’ PROCESS analysis examples. Retrieved from http://www.figureitout.org.uk/.
Stronach, E. P., Toth, S. L., Rogosch, F., Oshri, A., Manly, J. T., & Cicchetti, D. (2011). Child maltreatment, attachment security, and internal representations of mother and mother-child relationships. Child Maltreatment, 16(2), 137–145. doi:10.1177/1077559511398294.
Taussig, H. N. (2002). Risk behaviors in maltreated youth placed in foster care a longitudinal study of protective and vulnerability factors. Child Abuse & Neglect, 26, 1179–1199.
Thompson, R., Jiyoung Kim, T., Litrownik, A. J., Briggs, E. C., Hussey, J. M., English, D. J., & Dubowitz, H. (2011). Early adolescent risk behavior outcomes of childhood externalizing behavioral trajectories. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 31(2), 234–257. doi:10.1177/0272431609361203.
Tofighi, D., & MacKinnon, D. P. (2011). RMediation: An R package for mediation analysis confidence intervals. Behavior Research Methods, 43(3), 692–700. doi:10.3758/s13428-011-0076-x.
Tyler, S., Allison, K., & Winsler, A. (2006). Child neglect: Developmental consequences, intervention, and policy implications. Child and Youth Care Forum, 35(1), 1–20. doi:10.1007/s10566-005-9000-9.
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. (2016). Child maltreatment 2014. Available from http://www.acf.hhs.gov/programs/cb/research-data-technology/statistics-research/child-maltreatment.
Wilson, N., Syme, S. L., Boyce, W. T., Battistich, V. A., & Selvin, S. (2005). Adolescent alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use: The influence of neighborhood disorder and hope. American Journal of Health Promotion, 20(1), 11–19.
Winstanley, E. L., Steinwachs, D. M., Ensminger, M. E., Latkin, C. A., Stitzer, M. L., & Olsen, Y. (2008). The association of self-reported neighborhood disorganization and social capital with adolescent alcohol and drug use, dependence, and access to treatment. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 92(1-3), 173–182. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.07.012.
Wismer Fries, A. B., Shirtcliff, E. A., & Pollak, S. D. (2008). Neuroendocrine dysregulation following early social deprivation in children. Developmental Psychobiology, 50(6), 588–599. doi:10.1002/dev.20319.
Zenk, S. N., Schulz, A. J., Mentz, G., House, J. S., Gravlee, C. C., & Miranda, P. Y., et al. (2007). Inter-rater and test-retest reliability: Methods and results for the neighborhood observational checklist. Health & Place, 13(2), 452–465. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2006.05.003.
Zimmerman, G. M., & Farrell, C. (2017). Parents, peers, perceived risk of harm, and the neighborhood: Contextualizing key influences on adolescent substance use. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 46(1), 228–247.
Acknowledgements
The data used in this publication were made available by the National Data Archive on Child Abuse and Neglect, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, and have been used with permission. Data from Longitudinal Studies of Child Abuse and Neglect (LONGSCAN) Assessments 0–12 were originally collected by Desmond K. Runyan, Howard Dubowitz, Diana J. English, Jonathan Kotch, Alan Litrownik, Richard Thompson and Terri Lewis & The LONGSCAN Investigator Group. Funding for the project was provided by the Office on Child Abuse and Neglect (OCAN), Children’s Bureau, Administration for Children and Families, Dept. of Health and Human Services (The National Center on Child Abuse and Neglect (NCCAN), under the Office of Human Services funded this consortium of studies during the early years of data collection from 04/01/1991 until NCCAN became part of OCAN in 1998. The collector of the original data, the funder, NDACAN, Cornell University and their agents or employees bear no responsibility for the analyses or interpretations presented here.
Funding
There are no funding sources to disclose for the present study.
Author Contributions
E.D. conceived of the study, analyzed data, and drafted the manuscript; A.O. participated in conception of the study, interpretation of results, and critically revised the manuscript; M.C. contributed to interpretation of data and critically revised the manuscript. All authors gave final approval of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent and assent was obtained from all individual participants included in the LONGSCAN study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duprey, E.B., Oshri, A. & Caughy, M.O. Childhood Neglect, Internalizing Symptoms and Adolescent Substance Use: Does the Neighborhood Context Matter?. J Youth Adolescence 46, 1582–1597 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-017-0672-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-017-0672-x