Abstract
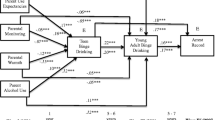
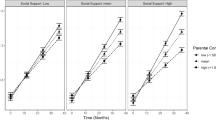
Discrepancies between parents and adolescents regarding parenting behaviors have been hypothesized to represent a deficit in the parent–child relationship and may represent unique risk factors for poor developmental outcomes. The current study examined the predictive utility of multiple methods for characterizing discrepancies in parents’ and adolescents’ reports of parental monitoring on youth alcohol use behaviors in order to inform future study design and predictive modeling. Data for the current study came from a prospective investigation of alcohol initiation and progression. The analyzed sample consisted of 606 adolescents (6th–8th grade; 54 % female) and their parents were surveyed at baseline, with youth followed up 12 months later. A series of hierarchical logistic regressions were performed for each monitoring-related construct examined (parental knowledge, parental control, parental solicitation, and child disclosure). The results showed that adolescents’ reports were more closely related to outcomes than parents’ reports, while greater discrepancies were frequently found to be uniquely associated with greater likelihood of alcohol use behaviors. Implications for future work incorporating parents’ and adolescents’ reports are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, G. M., Hoffman, J. H., Welte, J. W., Farrell, M. P., & Dintcheff, B. A. (2006). Effects of parental monitoring and peer deviance on substance use and delinquency. Journal of Marriage and Family, 68, 1084–1104.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Center for Injury Prevention and Control (NCIPC) (2004). Web-based injury statistics query and reporting system (WISQARS). http://www.cdc.gov/ncipc/wisqars/default.htm.
Cohen, J. (1983). The cost of dichotomization. Applied Psychological Measurement, 7, 249–253.
Cottrell, L., Li, X., Harris, C., D’Alessandri, D., & Stanton, B. (2003). Parent and adolescent perceptions of parental monitoring and adolescent risk involvement. Parenting: Science and Practice, 3, 179–195.
De Los Reyes, A. (2011). Introduction to special section: More than measurement error: Discovering meaning behind informant discrepancies in clinical assessments of children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 40, 1–9.
De Los Reyes, A., Goodman, K. L., Kliewer, W., & Reid-Quiñones, K. (2010). The longitudinal consistency of mother–child reporting discrepancies of parental monitoring and their ability to predict child delinquent behaviors two years later. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39, 1417–1430.
De Los Reyes, A., & Kazdin, A. E. (2005). Informant discrepancies in the assessment of childhood psychopathology: A critical review, theoretical framework, and recommendations for further study. Psychological Bulletin, 131, 483–509.
DiClemente, R. J., Wingood, G. M., Crosby, R., Sionean, C., & Oh, M. K. (2001). Parental monitoring: Association with adolescents’ risk behaviors. Pediatrics, 107, 1363–1368.
Dishion, T. J., & McMahon, R. J. (1998). Parental monitoring and the prevention of child and adolescent problem behavior: A conceptual and empirical formulation. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1, 61–75.
Dishion, T. J., Nelson, S. E., & Kavanagh, K. (2003). The Family check-up with high risk young adolescents: Preventing early-onset substance use by parent monitoring. Behavior Therapy, 34, 553–571.
Dodge, K. A., Malone, P. S., Lansford, J. E., Miller, S., Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (2009). A dynamic cascade model of the development of substance-use onset. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 74(3), vii–119. (Serial No. 294).
Feinberg, M., Howe, G., Reiss, D., & Hetherington, E. M. (2000). Relationship between perceptual differences of parenting and adolescent antisocial behavior and depressive symptoms. Family Psychology, 14, 531–555.
Furman, W., & Buhrmester, D. (1985). Children’s perceptions of the personal relationships in their social networks. Developmental Psychology, 21, 1016–1024.
Furman, W., & Buhrmester, D. (2009). The network of relationships inventory: Behavioral systems version. Journal of Behavioral Development, 33, 470–478.
Gaylord, N. K., Kitzmann, K. M., & Coleman, J. K. (2003). Parents’ and children’s perceptions of parental behavior: Associations with children’s psychosocial adjustment in the classroom. Parenting, 3, 23–47.
Gonzales, N., Cauce, A. M., & Mason, C. (1997). Interobserver agreement in the assessment of parental behavior and parent-child conflict: African American mothers, daughters, and independent observes. Child Development, 67, 1483–1498.
Guion, K., Mrug, S., & Windle, M. (2009). Predictive value of informant discrepancies in reports of parenting: Relations to early adolescents’ adjustment. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 17–30.
Hingson, R. W., Heeren, T., & Winter, M. R. (2006). Age at drinking onset and alcohol dependence: Age of onset, duration, and severity. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 160, 739–746.
Jaccard, J., Dittus, P. J., & Gordon, V. V. (1998). Parent-adolescent congruency in reports of adolescent sexual behavior and in communications about sexual behavior. Child Development, 69, 247–261.
Jackson, C., Ennett, S. T., Dickinson, D. M., & Bowling, J. M. (2012). Letting children sip: Understanding why parents allow alcohol use by elementary school-aged children. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, 17, 1–5.
Jackson, K. M., Roberts, M., Colby, S. M., Barnett, N. P., Abar, C. C., & Merrill, J. (2014). Willingness to drink as a function of peer offers and peer norms in early adolescence. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 75, 404–414.
Kalina, O., Geckova, A. M., Klein, D., Jarcuska, P., & Reijneveld, S. A. (2013). Mother’s and father’s monitoring is more important that parental social support regarding sexual risk behavior among 15-year-old adolescents. The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care, 18, 95–103.
Kerr, M., & Stattin, H. (2000). What parents know, how they know it, and several forms of adolescent adjustment: Further support for a reinterpretation of monitoring. Developmental Psychology, 36, 366–380.
Kopak, A. M., Ayers, S., Lopez, V., & Stevenson, P. (2011). Parental monitoring, alcohol, and marijuana use among Hispanic and non-Hispanic White adolescents: Findings from the Arizona Youth Survey. Journal of Drug Issues, 41, 461–486.
Latendresse, S. J., Rose, R. J., Viken, R. J., Pulkkinen, L., Kaprio, J., & Dick, D. M. (2009). Parental socialization and adolescents’ alcohol use behaviors: Predictive disparities in parents’ versus adolescents’ perceptions of the parenting environment. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 38, 232–244.
Lippold, M. A., Greenberg, M. T., & Feinberg, M. E. (2011). A dyadic approach to understanding the relationship of maternal knowledge of youths’ activities to youths’ problem behavior among rural adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40, 1178–1191.
Maurizi, L., Gershoff, E. T., & Aber, J. L. (2012). Item-level discordance in parent and adolescent reports of parenting behavior and its implications for adolescents’ mental health and relationships with parents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41, 1035–1052.
Pelton, J., Steele, R. G., Chance, M. W., & Forehand, R. (2001). Discrepancy between mother and child perceptions of their relationship: II. Consequences for children considered within the context of maternal physical illness. Journal of Family Violence, 16, 17–35.
Pettit, G. S., Bates, J. E., Dodge, K. A., & Meece, D. W. (1999). The impact of after-school peer contact on early adolescent externalizing problems is moderated by parental monitoring, perceived neighborhood safety, and prior adjustment. Child Development, 70, 768–778.
Pettit, G. S., Laird, R. D., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Criss, M. M. (2001). Antecedents and behavior-problem outcomes of parental monitoring and psychological control in early adolescence. Child Development, 72, 583–598.
Reidler, E. B., & Swenson, L. P. (2012). Discrepancies between youth and mother’s perceptions of their mother-child relationship quality and self-disclosure: Implications for youth- and mother-reported youth adjustment. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41, 1151–1167.
Reynolds, E. K., MacPherson, L., Matusiewicz, A. K., Schreiber, W. M., & Lejuez, C. W. (2011). Discrepancy between mother and child reports of parental knowledge and the relation to risk behavior engagement. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 40, 67–79.
Soenens, B., Vansteenkiste, M., Luyckx, K., & Goossens, L. (2006). Parenting and adolescent problem behavior: An integrated model with adolescent self-disclosure and perceived parental knowledge as intervening variables. Developmental Psychology, 42, 305–318.
Stattin, H., & Kerr, M. (2000). Parental monitoring: A reinterpretation. Child Development, 71, 1072–1085.
Tein, J. Y., Roosa, M. W., & Michaels, M. (1994). Agreement between parent and child reports on parental behaviors. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 56(2), 341–355.
Tobler, A. L., & Komro, K. A. (2010). Trajectories of parental monitoring and communication and effects on drug use among urban young adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46, 560–568.
Warner, L. A., & White, H. R. (2003). Longitudinal effects of age at onset and first drinking situations on problem drinking. Substance Use and Misuse, 38(14), 1983–2016.
Windle, M. (2000). Parental, sibling, and peer influences on adolescent alcohol use and alcohol problems. Applied Developmental Science, 4, 98–110.
Acknowledgments
This paper was written with funding support through the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism to K. Jackson (R01 AA016838).
Author contributions
CA conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, performed the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript; KJ participated in the design and interpretation of the data, helped with the statistical analysis, and helped to draft the manuscript; SC participated in the design and coordination of the study and helped to draft the manuscript; NB participated in the design and coordination of the study and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abar, C.C., Jackson, K.M., Colby, S.M. et al. Parent–Child Discrepancies in Reports of Parental Monitoring and Their Relationship to Adolescent Alcohol-Related Behaviors. J Youth Adolescence 44, 1688–1701 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-014-0143-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-014-0143-6